Tensorflow tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d如何实现深度卷积的
实验环境:tensorflow版本1.2.0,python2.7
介绍
depthwise_conv2d来源于深度可分离卷积:
Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions
tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input,filter,strides,padding,rate=None,name=None,data_format=None)
除去name参数用以指定该操作的name,data_format指定数据格式,与方法有关的一共五个参数:
input:
指需要做卷积的输入图像,要求是一个4维Tensor,具有[batch, height, width, in_channels]这样的shape,具体含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数]
filter:
相当于CNN中的卷积核,要求是一个4维Tensor,具有[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]这样的shape,具体含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,输入通道数,输出卷积乘子],同理这里第三维in_channels,就是参数value的第四维
strides:
卷积的滑动步长。
padding:
string类型的量,只能是”SAME”,”VALID”其中之一,这个值决定了不同边缘填充方式。
rate:
这个参数的详细解释见【Tensorflow】tf.nn.atrous_conv2d如何实现空洞卷积?
结果返回一个Tensor,shape为[batch, out_height, out_width, in_channels * channel_multiplier],注意这里输出通道变成了in_channels * channel_multiplier
实验
为了形象的展示depthwise_conv2d,我们必须要建立自定义的输入图像和卷积核
img1 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img2 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img = tf.concat(values=[img1,img2],axis=3)
filter1 = tf.constant(value=0, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter2 = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter3 = tf.constant(value=2, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter4 = tf.constant(value=3, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter_out1 = tf.concat(values=[filter1,filter2],axis=2) filter_out2 = tf.concat(values=[filter3,filter4],axis=2) filter = tf.concat(values=[filter_out1,filter_out2],axis=3)
建立好了img和filter,就可以做卷积了
out_img = tf.nn.conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='VALID')
好了,用一张图来详细展示这个过程


这是普通的卷积过程,我们再来看深度卷积。
out_img = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], rate=[1,1], padding='VALID')
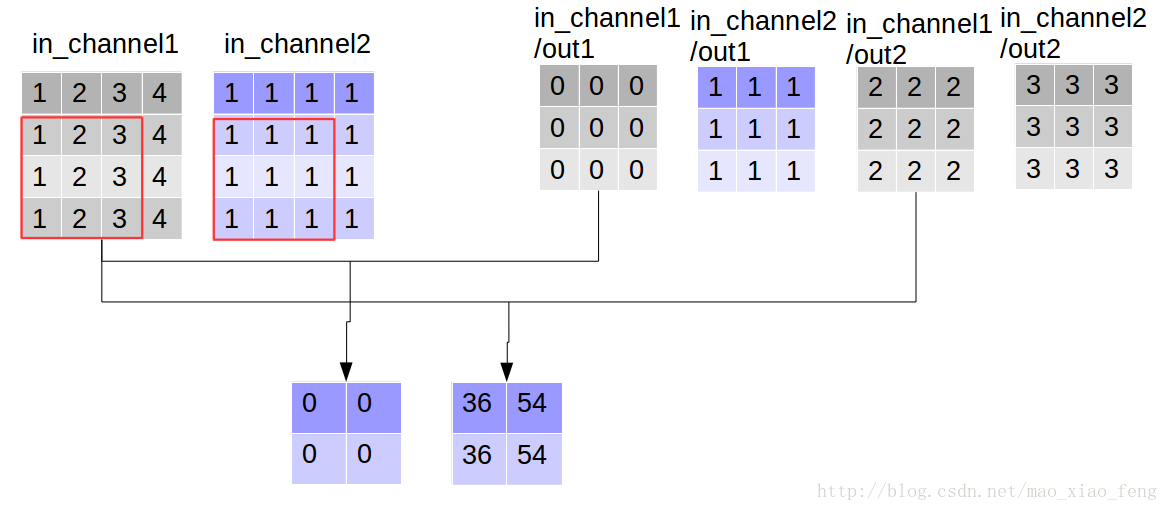
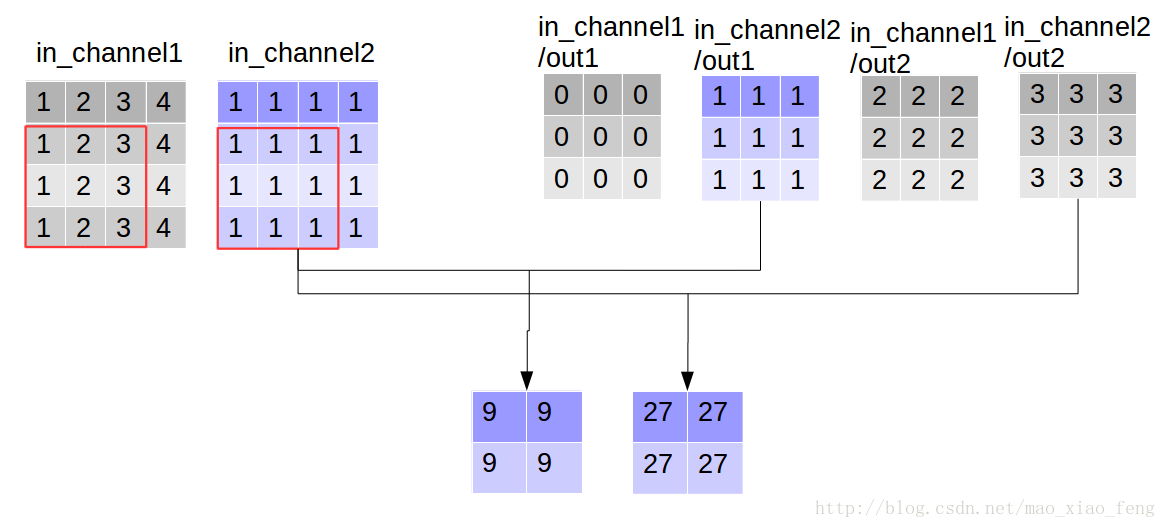
现在我们可以形象的解释一下depthwise_conv2d卷积了。看普通的卷积,我们对卷积核每一个out_channel的两个通道分别和输入的两个通道做卷积相加,得到feature map的一个channel,而depthwise_conv2d卷积,我们对每一个对应的in_channel,分别卷积生成两个out_channel,所以获得的feature map的通道数量可以用in_channel* channel_multiplier来表达,这个channel_multiplier,就可以理解为卷积核的第四维。
代码清单
import tensorflow as tf img1 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img2 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]]]],dtype=tf.float32) img = tf.concat(values=[img1,img2],axis=3) filter1 = tf.constant(value=0, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter2 = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter3 = tf.constant(value=2, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter4 = tf.constant(value=3, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32) filter_out1 = tf.concat(values=[filter1,filter2],axis=2) filter_out2 = tf.concat(values=[filter3,filter4],axis=2) filter = tf.concat(values=[filter_out1,filter_out2],axis=3) out_img = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], rate=[1,1], padding='VALID')
输出:
rate=1, VALID mode result:
[[[[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]][[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]]]]
到此这篇关于Tensorflow tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d如何实现深度卷积的的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Tensorflow tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d深度卷积内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

