解决SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong()引发的线程阻塞问题
目录
- 1. 背景介绍
- 2. 现象展示
- 2.1 windows7下运行结果
- 2.2 centos7下运行结果
- 3. 现象分析
- 3.1 linux阻塞分析
- 3.2 windows下运行结果分析
- 4. 结论
- 4.1 推荐使用方式
- 4.2 关于/dev/random的扩展
1. 背景介绍
sonar扫描到使用Random随机函数不安全, 推荐使用SecureRandom替换之, 当使用SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong()获取SecureRandom并调用next方式时, 在生产环境(linux)产生较长时间的阻塞, 但开发环境(windows7)并未重现
2. 现象展示
使用测试代码:
package com.youai.test;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
public class TestRandom {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
System.out.println("start.....");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
SecureRandom random = SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong();
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "个随机数.");
random.nextInt(10000);
}
System.out.println("finish...time/ms:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
2.1 windows7下运行结果
第94个随机数.
第95个随机数.
第96个随机数.
第97个随机数.
第98个随机数.
第99个随机数.
finish...time/ms:100
windows下未出现明显阻塞现象, 耗时100ms
2.2 centos7下运行结果
第52个随机数.
第53个随机数.
第54个随机数.
第55个随机数.
第56个随机数.
第57个随机数.
第58个随机数.
第59个随机数.
第60个随机数.
第61个随机数.
第62个随机数.
第63个随机数.
第64个随机数.
...
linux下运行阻塞在第65次获取随机数.(如果实验结果未阻塞, 可以尝试增加获取随机数的次数)
3. 现象分析
3.1 linux阻塞分析
通过
jstack -l <你的java进程>
得到如下堆栈信息
"main" #1 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00007f894c009000 nid=0x1129 runnable [0x00007f8952aa9000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at java.io.FileInputStream.readBytes(Native Method)
at java.io.FileInputStream.read(FileInputStream.java:255)
at sun.security.provider.NativePRNG$RandomIO.readFully(NativePRNG.java:424)
at sun.security.provider.NativePRNG$RandomIO.ensureBufferValid(NativePRNG.java:525)
at sun.security.provider.NativePRNG$RandomIO.implNextBytes(NativePRNG.java:544)
- locked <0x000000076c77cb28> (a java.lang.Object)
at sun.security.provider.NativePRNG$RandomIO.access$400(NativePRNG.java:331)
at sun.security.provider.NativePRNG$Blocking.engineNextBytes(NativePRNG.java:268)
at java.security.SecureRandom.nextBytes(SecureRandom.java:468)
at java.security.SecureRandom.next(SecureRandom.java:491)
at java.util.Random.nextInt(Random.java:390)
at TestRandom.main(TestRandom.java:12)
可以看到main线程阻塞在了java.io.FileInputStream.readBytes(Native Method)这个读取文件的IO处.
对NativePRNG的部分关键源码进行分析:
// name of the pure random file (also used for setSeed())
private static final String NAME_RANDOM = "/dev/random";
// name of the pseudo random file
private static final String NAME_URANDOM = "/dev/urandom";
private static RandomIO initIO(final Variant v) {
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<RandomIO>() {
@Override
public RandomIO run() {
File seedFile;
File nextFile;
switch(v) {
//...忽略中间代码
case BLOCKING: // blocking状态下从/dev/random文件中读取
seedFile = new File(NAME_RANDOM);
nextFile = new File(NAME_RANDOM);
break;
case NONBLOCKING: // unblocking状态下从/dev/urandom文件中读取数据
seedFile = new File(NAME_URANDOM);
nextFile = new File(NAME_URANDOM);
break;
//...忽略中间代码
try {
return new RandomIO(seedFile, nextFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
});
}
// constructor, called only once from initIO()
private RandomIO(File seedFile, File nextFile) throws IOException {
this.seedFile = seedFile;
seedIn = new FileInputStream(seedFile);
nextIn = new FileInputStream(nextFile);
nextBuffer = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE];
}
private void ensureBufferValid() throws IOException {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ((buffered > 0) && (time - lastRead < MAX_BUFFER_TIME)) {
return;
}
lastRead = time;
readFully(nextIn, nextBuffer);
buffered = nextBuffer.length;
}
从源代码分析, 发现导致阻塞的原因是因为从/dev/random中读取随机数导致, 可以通过如下代码验证:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestReadUrandom {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("start.....");
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("第" + i + "次读取随机数");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("/dev/random");
byte[] buf = new byte[32];
inputStream.read(buf, 0, buf.length);
}
}
}
上述代码在linux环境下同样会产生阻塞.
通过hotspot源码分析, java通过c调用操作系统的读取文件api, 通过一个c代码的案例论证:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main() {
int randnum = 0;
int fd = open("/dev/random", O_RDONLY);
if(fd == -1) {
printf("open error.\n");
return 1;
}
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
read(fd, (char *)&randnum, sizeof(int));
printf("random number = %d\n", randnum);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
这个例子再次论证了读取/dev/random会导致阻塞
3.2 windows下运行结果分析
- NativePRNG.java这个文件在linux和windows下的环境中实现不同
- windows的调用堆栈过程
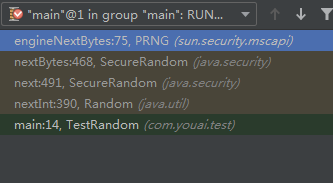
- windows在通过SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong()获取随机数的过程, 并没有使用到NativePRNG, 而是最终调用sun.security.mscapi.PRNG#generateSeed的native方法, 所以windows并没有明显的阻塞现象(但明显比 new SecureRandom()生成的对象产生随机数要慢许多).
- sun.security.mscapi.PRNG#generateSeed的native方法实现, 阅读hotspot中security.cpp代码
#include <windows.h>
JNIEXPORT jbyteArray JNICALL Java_sun_security_mscapi_PRNG_generateSeed
(JNIEnv *env, jclass clazz, jint length, jbyteArray seed)
{
//省略不关键代码...
else if (length > 0) {
pbData = new BYTE[length];
if (::CryptGenRandom( // 此处通过调用windows提供的apiCryptGenRandom获取随机数
hCryptProv,
length,
pbData) == FALSE) {
ThrowException(env, PROVIDER_EXCEPTION, GetLastError());
__leave;
}
result = env->NewByteArray(length);
env->SetByteArrayRegion(result, 0, length, (jbyte*) pbData);
}
//省略不关键代码...
}
没有详细研究CryptGenRandom的具体实现
4. 结论
4.1 推荐使用方式
- 不推荐使用SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong()方式获取SecureRandom(除非对随机要求很高)
- 推荐使用new SecureRandom()获取SecureRandom, linux下从/dev/urandom读取. 虽然是伪随机, 但大部分场景下都满足.
4.2 关于/dev/random的扩展
- 由于/dev/random中的数据来自系统的扰动, 比如键盘输入, 鼠标点击, 等等, 当系统扰动很小时, 产生的随机数不够, 导致读取/dev/random的进程会阻塞等待. 可以做个小实验, 当阻塞时, 多点击鼠标, 键盘输入数据等操作, 会加速结束阻塞
- 可以从通过这个命令cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/entropy_avail获取当前系统的熵, 值越大, /dev/random中随机数产生效率越高
- 熵补偿:可通过安装linux下的工具haveged, 进行系统熵补偿, 安装后, 启动haveged, 发现系统熵值从几十增加到一千多, 此时在运行前面阻塞的程序(运行结果如下), 发现不再阻塞, 获取100个随机数只要29毫秒, 效率大大提升.
第91个随机数.
第92个随机数.
第93个随机数.
第94个随机数.
第95个随机数.
第96个随机数.
第97个随机数.
第98个随机数.
第99个随机数.
finish...time/ms:29
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

