解决SpringBoot加载application.properties配置文件的坑
SpringBoot加载application.properties配置文件的坑
事情的起因是这样的
一次,本人在现场升级程序,升级完成后进行测试,结果接口调用都报了这么个错误:

大概意思是https接口需要证书校验,这就奇怪了,项目启动加载的是包外的application.properties配置文件,配置文件里没有配置使用https啊。本人马上检查了下包内的application.properties配置文件,发现包内确实配置了https相关的配置项:
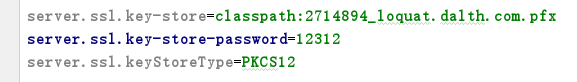
明明包外的配置文件优先级高于包内的,为啥包内的一部分配置项起作用了呢,我们了解的配置文件优先级是这样的:

这是为啥呢?后来才了解到除了高优先级覆盖低优先级外,还有一条重要的规则:如有不同内容,高优先级和低优先级形成互补配置。这下才恍然大悟,我包外的配置文件里把https相关的配置项注释掉了,相当于没有这个配置项,但是包内的配置文件有,根据互补原则,包内的这几个配置项起作用了。
问题原因找到了,如何解决呢?
要不我把包内的那几个配置项也注释掉,重新打个包?其实不必这么麻烦,通过-Dspring.config.location命令直接指定包外的配置文件就可以了,试了下,果然没有问题了。问题虽然解决了,但是还有些疑问,为啥指定包外的配置文件后就不存在互补情况了呢?
通过阅读springboot相关源码,找到了答案:
大概意思是:
如果-Dspring.config.location指定了配置文件,则只加载指定的那一个配置文件,如果没有专门指定配置文件则遍历包外、包内相关的配置文件,按照高优先级覆盖低优先级和互补原则进行加载。
弄明白这些问题后,实地部署项目的时候,保险起见还是通过-Dspring.config.location命令直接指定加载的配置文件比较好,避免出现一些不必要的麻烦。
Spring Boot加载application.properties探究
基于Spring Boot的多Module项目中,有许多公共的配置项,为避免在每个接入层都配置一遍,一个设想是在公共依赖的Module的application.properties(application.yml)中进行配置。原来的配置文件位于接入层的classpath,可由Spring Boot打包插件打入,一旦置于公共Module,配置文件就不再直接被打入jar包,而是位于内嵌的jar包中,并不确认Spring Boot会去扫内嵌于jar包中的application文件,因此可行性有待验证。
探索
实验准备,项目结构如下所示:
Demo
- web(接入层)
- src
- main
- java
- resources
- application.properties // 1
- test
- pom.xml
- common(公共层)
- src
- main
- java
- resources
- application-dev.properties // 2
- pom.xml(父Module pom)
接入层为web,在resources下存在application.properties,内容为spring.profiles.active=dev,目的是为了激活dev的profile
公共同为common,在在resources下存在application-dev.properties,内容为name=demo_test
因此,如果配置项name=demo_test能够被应用成功读取到,那么就验证了在背景中提及的设想
实验结果:成功读取
原理分析
一般地,Spring Boot 默认的配置文件名称为:application.properties或application.yml,为方便描述,统一为application.properties。从Spring Boot 官方文档得知,Spring Boot可以从下述位置按顺序加载配置文件
A /config subdirectory of the current directory(file:./config/) The current directory(file:./) A classpath /config package(classpath:/config/) The classpath root(classpath:/)
优先级表述如下:
The list is ordered by precedence (properties defined in locations higher in the list override those defined in lower locations).
也即是说,排在前边的优先级高于排在后边的。这里有几层隐含的含义,在官方文档中并没有表述清楚,为方便记忆与理解
总结如下:
1、上边的4个位置均可放置配置文件(application.properties)
它们之间是一个并集关系而不是互斥关系,Spring Boot 默认都会加载到它们,而不是加载到高优先级的配置文件之后就停止加载低优先级的
2、如果在两个以上的application.properties里配置
同一个配置项(如: name=demo),那么优先级高的配置项会生效
举个例子,项目结构如下
src
- main
- resources
- config
- application.properties // 3 (k1=v1, k2=v2)
- application.properties // 4 (k1=v3, k4=v4)
在优先级排名第3的配置文件中,存在两个配置项(k1=v1, k2=v2);在优先级排名第4的配置文件中,存在两个配置项(k1=v3, k4=v4)。内存中,四个配置项都存在,但生效的配置项只有三个:k1=v1,k2=v2,k4=v4,而k1=v3由于优先级比较低,并不生效
在Spring Boot应用启动过程中,需要创建ConfigurableEnvironment,当Environment创建完,Spring 会发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,告知Environment创建完毕。ConfigFileApplicationListener会监听这个事件,在事件处理中,使用Spring SPI机制加载EnvironmentPostProcessor集合,并回调EnvironmentPostProcessor#postProcessEnvironment方法。很巧的是,ConfigFileApplicationListener同时也实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor,因此,会回调到自身的postProcessEnvironment方法中。
注:下边的源码基于Spring Boot 2.1.10.RELEASE
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ...(省略)
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 创建ConfigurableEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// ...(省略)
}
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...)
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// ...(省略)
}
// org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListeners#environmentPrepared
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
// org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener#environmentPrepared
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
// 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
// org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 利用Spring SPI机制加载EnvironmentPostProcessor
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 回调
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
在postProcessEnvironment回调中,添加了RandomValuePropertySource,并调用内部类Loader的load方法,对application.properties进行加载
// org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// 添加`RandomValuePropertySource`到Environment
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
// load()方法是重点;
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
// org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener.Loader#load()
public void load() {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 以上四个变量默认状态为空集合或false,用于在下边迭代的过程中收集数据
// 初始化profiles集合,如果存在active的profile,会将activatedProfiles变量设置为true
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (profile != null && !profile.isDefaultProfile()) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
resetEnvironmentProfiles(this.processedProfiles);
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
}
初始化profiles集合,如果存在active的profile,会将activatedProfiles变量设置为true。这里需要注意的是,在案例demo中,是将spring.profiles.active=dev写在classpath的application.properties,而此时application.properties都还没有读取,所以该配置项并未生效。故此,active的profile指的是那些通过system property、system enviroment、手动调用AbstractEnvironment#setActiveProfiles等方式设置active profile,他们的共同特点是优先级都较高,配置项初始化早,在执行load方法前就已生效
先往profiles集合添加null,表示将要加载那些跟profile无关的application.properties,并且如果没有active profile,那还会加载名为default的profile
private void initializeProfiles() {
// The default profile for these purposes is represented as null. We add it
// first so that it is processed first and has lowest priority.
this.profiles.add(null);
Set<Profile> activatedViaProperty = getProfilesActivatedViaProperty();
this.profiles.addAll(getOtherActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty));
// Any pre-existing active profiles set via property sources (e.g.
// System properties) take precedence over those added in config files.
addActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty);
if (this.profiles.size() == 1) { // only has null profile
for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) {
// 加载名为`default`的profile
Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true);
this.profiles.add(defaultProfile);
}
}
}
initializeProfiles方法执行完毕之后,只要profiles非空,就从队首取出并进行加载。profiles是个双端队列,加载的过程有可能往队列里添加或者移除元素,因此使用的是while (!this.profiles.isEmpty())的判断方式。
接着看load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
该方法结构很清晰,迭代每一个location(搜索路径),如果搜索路径是个目录(以/结尾),则获取配置文件名,然后结合搜索路径+配件文件名对配置文件进行加载。这儿隐含一层意思:location可以直接指定为配置文件,但是此种方式不被推荐使用,因为这会导致Profile机制失效,建议还是按正常的姿势去使用
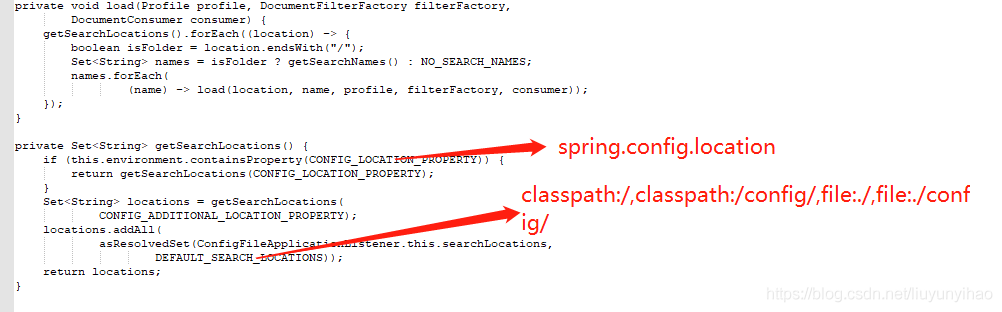
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {
boolean isFolder = location.endsWith("/");
Set<String> names = isFolder ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
获取搜索路径,
可由spring.config.location指定或者spring.config.additional-location + classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/。注意此处,spring.config.location指定的搜索顺序跟定义的顺序相反,例如指定的位置为a, b, c,则按c, b, a的顺序进行搜索,而搜索顺序反应的是配置项的优先级,在上边已提过,不再赘述
private Set<String> getSearchLocations() {
// 若通过 spring.config.location 指定配置文件目录,则到指定路径查找,不再走默认的搜索路径和额外添加的路径,可以指定多个,以逗号进行分隔
// CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY = spring.config.location
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY)) {
return getSearchLocations(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY);
}
// 除了默认路径,还可以通过 spring.config.additional-location 指定额外的搜索路径
// CONFIG_ADDITIONAL_LOCATION_PROPERTY = spring.config.additional-location
Set<String> locations = getSearchLocations(CONFIG_ADDITIONAL_LOCATION_PROPERTY);
// 默认搜索路径
// DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/
locations.addAll(
asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.searchLocations, DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS));
return locations;
}
该方法将搜索路径或者指定的配置文件名以逗号分割后倒置
private Set<String> asResolvedSet(String value, String fallback) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(StringUtils.trimArrayElements(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
(value != null) ? this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(value) : fallback)));
Collections.reverse(list);
return new LinkedHashSet<>(list);
}
获取待搜索的配置文件名,可由spring.config.name指定或者使用默认值application,同上面的搜索路径一样,spring.config.name指定的搜索顺序跟定义的顺序相反
private Set<String> getSearchNames() {
// 若通过 spring.config.name 指定配置文件名称,则只会搜索该名称的配置文件,可以指定多个,以逗号进行分隔
// CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY = spring.config.name
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
String property = this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY);
return asResolvedSet(property, null);
}
// 默认搜索的配置文件名称为application
// DEFAULT_NAMES = application
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}
在我们的案例中,没有通过spring.config.location指定配置文件目录,也没有通过spring.config.name指定配置文件名,因此都采用默认值,且顺序倒置:
localtion:file:./config/, file:./, classpath:/config/, classpath:/
config.name: application
且只在classpath:/放有配置文件application.properties与application-dev.properties
接着,遍历propertySourceLoaders对配置文件进行加载。propertySourceLoaders是在构造Loader类时进行初始化的,它利用Spring SPI机制对实现类进行加载,默认实现类有两个
PropertiesPropertySourceLoader: 加载.properties与.xml的配置文件
YamlPropertySourceLoader: 加载.yml和.yaml的配置文件
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
// ...(省略)
Set<String> processed = new HashSet<>();
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {
// .properties\.xml\.yml\.yaml
if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {
loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory,
consumer);
}
}
}
}
private void loadForFileExtension(PropertySourceLoader loader, String prefix, String fileExtension, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
DocumentFilter defaultFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(null);
DocumentFilter profileFilter = filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile);
if (profile != null) {
// Try profile-specific file & profile section in profile file (gh-340)
// profileSpecificFile = file:./application-dev.properties
String profileSpecificFile = prefix + "-" + profile + fileExtension;
// 加载profile对应的配置文件
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, defaultFilter, consumer);
load(loader, profileSpecificFile, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
// Try profile specific sections in files we've already processed
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
String previouslyLoaded = prefix + "-" + processedProfile + fileExtension;
load(loader, previouslyLoaded, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
}
}
// Also try the profile-specific section (if any) of the normal file
// 加载非profile的配置文件
load(loader, prefix + fileExtension, profile, profileFilter, consumer);
}
使用resourceLoader到location获取配置文件资源,resourceLoader也是在Loader类构造的时候初始化的,默认是DefaultResourceLoader,它是Spring提供的ResourceLoader的默认实现类,能够获取classpath资源以及URL资源或类URL资源,资源用Resource进行抽象表示。
此处,已经可以解释文章探索实验的结果:资源的获取是靠Spring提供的DefaultResourceLoader实现的,它能够实现classpath的扫描,进而加载资源,因此,只要是classpath下的配置文件,无论是否在内嵌jar包内,最终都能加载到
有了Loader,以及Resource,就可以进行资源的加载,加载的结果是List,代表对配置文件属性源的抽象以及封装。用DocumentFilter对满足条件的Document进行过滤,满足条件的则被添加进MutablePropertySources中
private void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
try {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
// ...(省略)
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
List<Document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource);
// ...(省略)
List<Document> loaded = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
if (filter.match(document)) {
addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles());
addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles());
loaded.add(document);
}
}
Collections.reverse(loaded);
if (!loaded.isEmpty()) {
loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document));
// ...(省略)
}
最终,被加载的配置文件存在loaded变量中,调用addLoadedPropertySources方法,将loaded倒置之后添加进environment的PropertySources中,倒置的目的,是为了使profile的配置文件优先级更高。而一旦将配置项添加进environment的属性源集合中,应用程序就能正确取读到配置项。
// org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener.Loader#addLoadedPropertySources
private void addLoadedPropertySources() {
MutablePropertySources destination = this.environment.getPropertySources();
List<MutablePropertySources> loaded = new ArrayList<>(this.loaded.values());
Collections.reverse(loaded);
String lastAdded = null;
Set<String> added = new HashSet<>();
for (MutablePropertySources sources : loaded) {
for (PropertySource<?> source : sources) {
if (added.add(source.getName())) {
addLoadedPropertySource(destination, lastAdded, source);
lastAdded = source.getName();
}
}
}
}
其实,application-{profile}.properties配置文件加载位置同标准的application.properties,但是它有一点显著不同的是,无论application-{profile}.properties放哪,profile类的配置文件优先级最高,当配置项冲突时,总是"覆盖"一切非profile的配置文件
总结
本文开篇提出一个问题:在依赖的公共Module的classpath放置application.properties,Spring Boot应用能否正确读取?之后通过案例进行实验,证明了此行为的可行性。为了了解Spring Boot对application.properties加载的过程,先是阅读了Spring Boot 官方文档对application.properties的介绍,并对其中关于配置项优先级的模糊描述做了进一步的解释。接着从源码的角度,对application.properties的加载过程从头到尾简单介绍了一遍,了解到ResourceLoader及其默认实现类DefaultResourceLoader正是用于从classpath加载资源,因此能成功加载内嵌jar包中位于classpath的application.properties
最后,介绍了Spring Boot对于PropertySource优先级处理的原则:后赢策略(last-wins),加载的过程按代码定义的顺序先加载,放入数据源之前进行倒置(reverse)放入,在后边的反而优先级高
题外话
1、配置文件前2优先级位置分别是:file:./config/、file:./,在IDEA中是指当前项目的/config目录以及当前项目根目录。如果是多module项目,那么当前项目指的是父module目录。其实在IDEA环境中使用这俩位置的配置文件意义不大,更多的,是与发布系统结合,发布系统将服务打成Executable Jar之后,将应用相关的基础配置信息(如server.port、Apollo apollo.meta\env )配置在./config/或者./,用以覆盖项目内有可能误配或漏配的选项
2、本文的一些规律,不单适用于application.properties,还适用于别的配置文件。例如:配置项优先级原则,基本思想是:由Spring加载所有的属性源到Environment中,通过属性源的方式将配置项进行隔离,不同的属性源互不干扰,在此基础上,靠前的属性源的配置项优先级高。这种行为是Spring默认的行为,该行为定义在PropertySourcesPropertyResolver,也意味着,我们可以自定义PropertyResolver,来改变这种默认的行为,实现自定义的优先级顺序,达到我们的目的
3、关于application.properties的加载过程,还有很多细节未曾提及,这并非意味着不重要,而是一篇文章难以面面俱到,而陷入源码细节容易一叶障目。从问题出发,梳理主干脉络,把握核心思想,是为首要条件,之后每次根据需要,像剥洋葱般一层层深入,能更容易掌握知识
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

