Yml转properties文件工具类YmlUtils的详细过程(不用引任何插件和依赖)
目录
- 【诞生背景】
- 【Convert YAML and Properties File 插件的不足】
- 【自写小工具 YmlUtils 实现】
- 【源码展示】
【诞生背景】
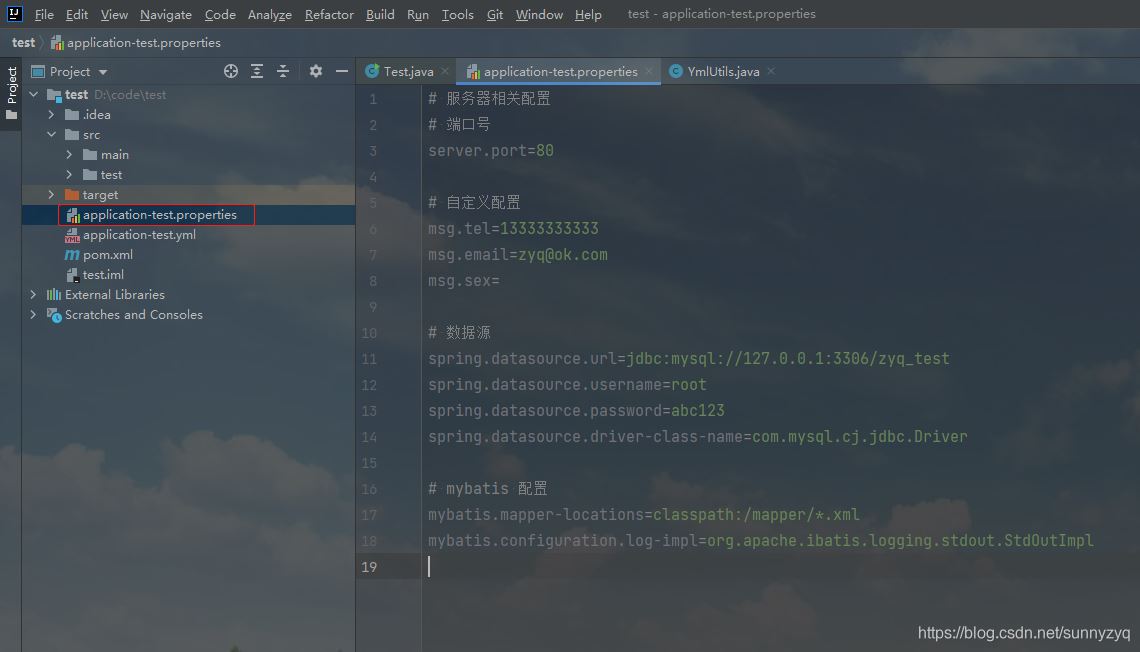
最近在做某配置中心的时候,配置中心采用properties格式进行配置的(如下图)。

而我们工程的项目配置文件是yml格式的(如下图)。

如果人为手动的一条一条,将yml文件中的配置数据,添加到配置中心,难免会消耗大量的人力和精力,况且还容易输入错误。因此,需要一个工具或插件,将 yml 文件的格式,转换为properties文件。
【Convert YAML and Properties File 插件的不足】
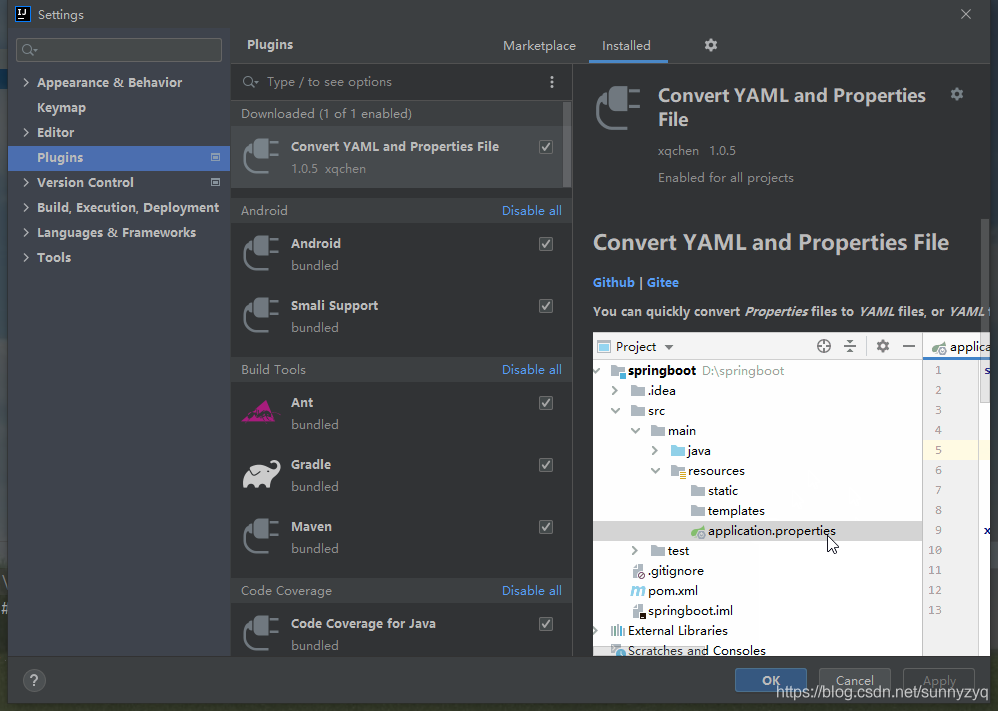
IDEA 有一个插件叫 Convert YAML and Properties File, 于是,首先用了一下 这个插件后,发现了,发现这个插件不太友好,具体有以下几点。
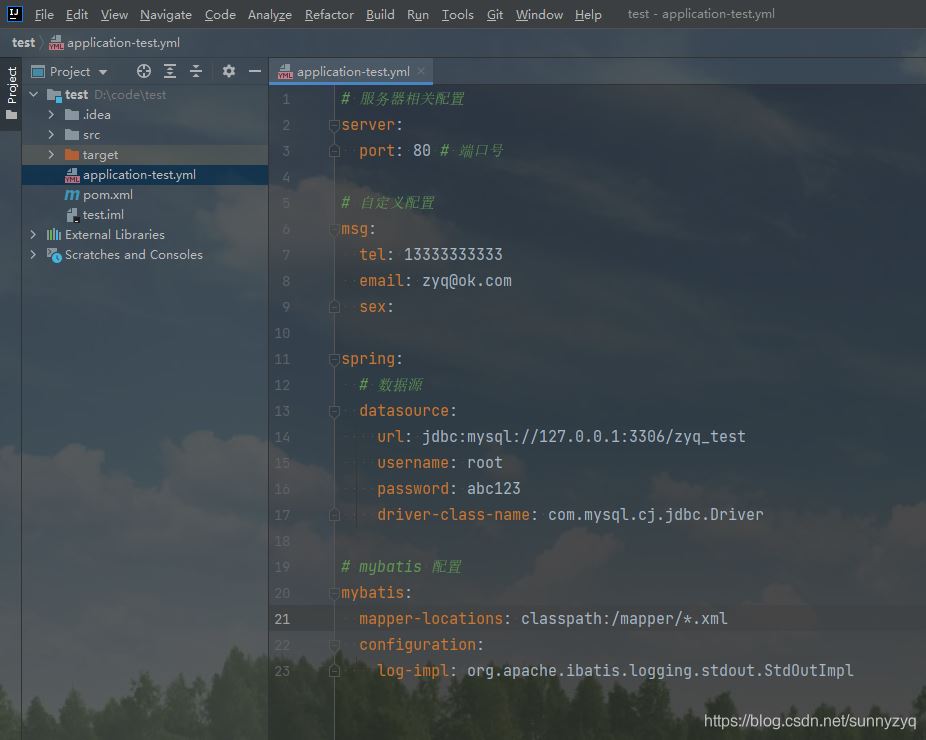
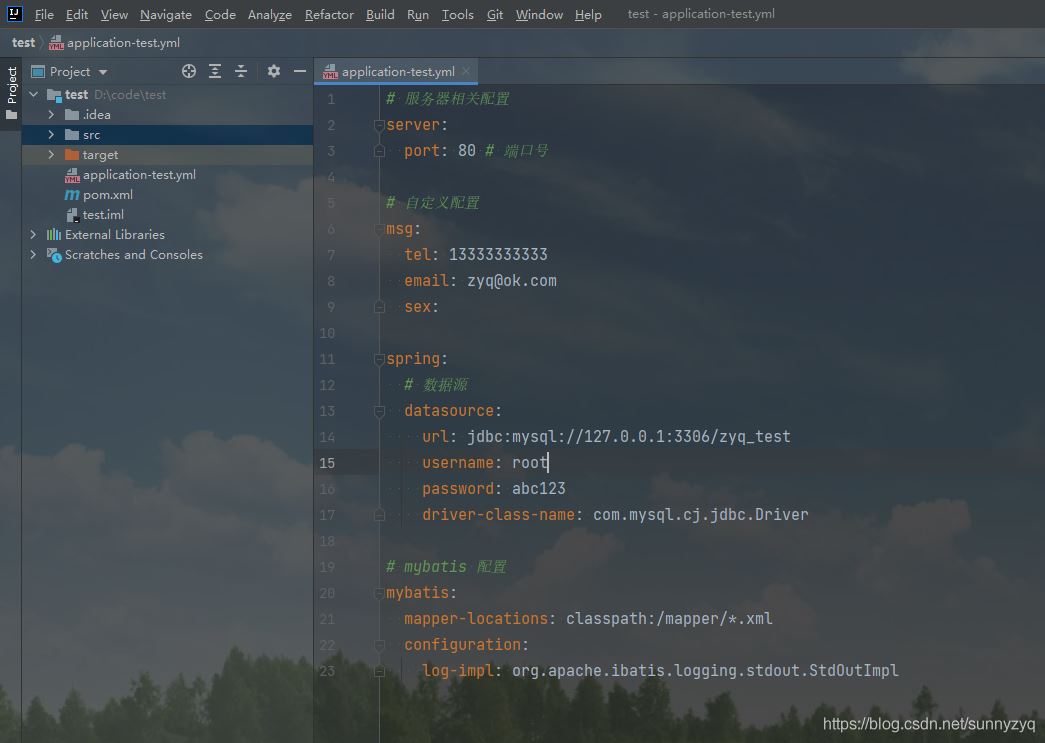
比如,现在我们有如下的 yml 配置文件:
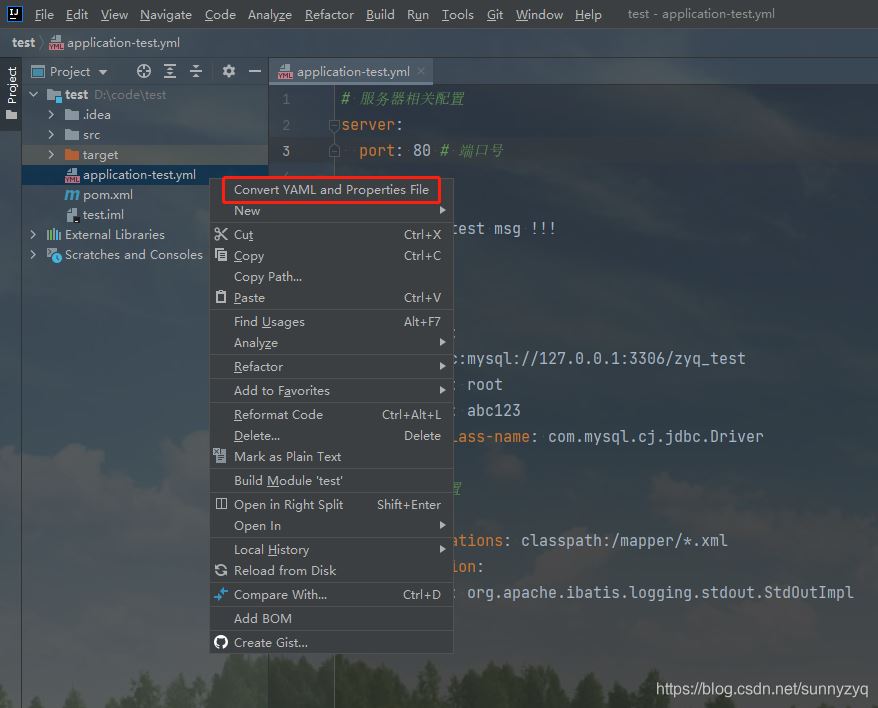
我们用插件将它转化为 properties 文件。
下面是转化后的效果:
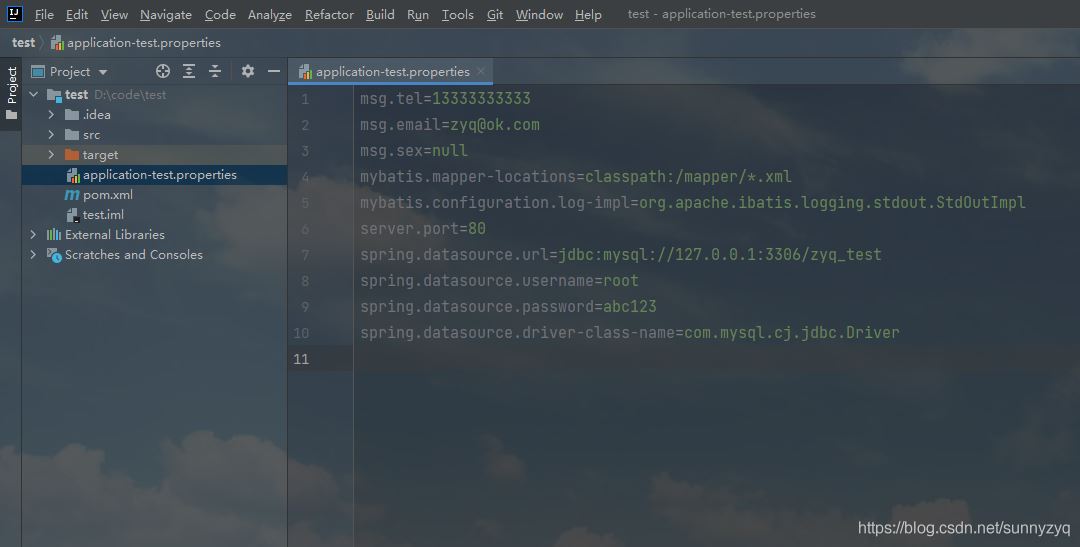
从这转换后的效果,我们不难发现该插件有以下几点问题:
(1)转化后,原 yml 配置文件消失(如果转出了问题,想看原配置文件,还看不了了);
(2)排序出现混乱,没有按照原 yml 文件数据进行输出(msg相关的配置本来在原yml文件中是第二个配置,转换后却成为了第一个;同理,mybatis的配置本是最后一个,转化后却放在了第二个);
(3)所有注释均不见了(所有相关的注释全都不见了,包括行级注释和末尾注释);
(4)某些值没有进行配置,但转化后,却显示为了 null 字符串(如 msg.sex 的配置);
(5)该插件仅IDEA有,Eclipse中还没有,不能垮开发工具使用;
【自写小工具 YmlUtils 实现】
针对上面 IDEA 插件的不足,于是自己写了一款小工具 YmlUtils(源码在文章结尾处 ),你可以将它放在工程中的任何位置。
现在,我们同样以刚刚的 yml 配置文件为测试模板,来测试下这款小工具。
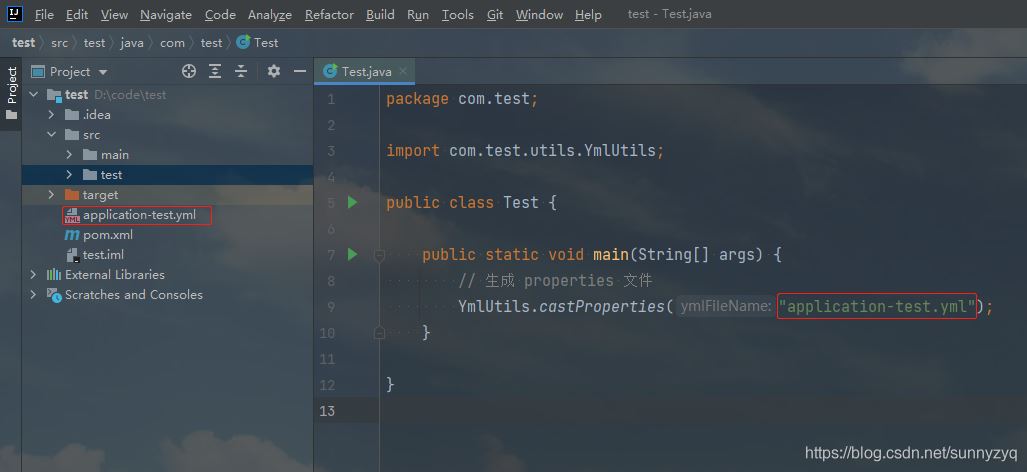
测试的方法很简单,只需要将 yml 配置文件放在根目录下,然后写个 Test 类,调用里面的 castProperties 方法即可。
YmlUtils.castProperties("application-test.yml");
执行方法后,首先我们可以看到控制台会将 porperties 文件的内容打印到控制台上面:
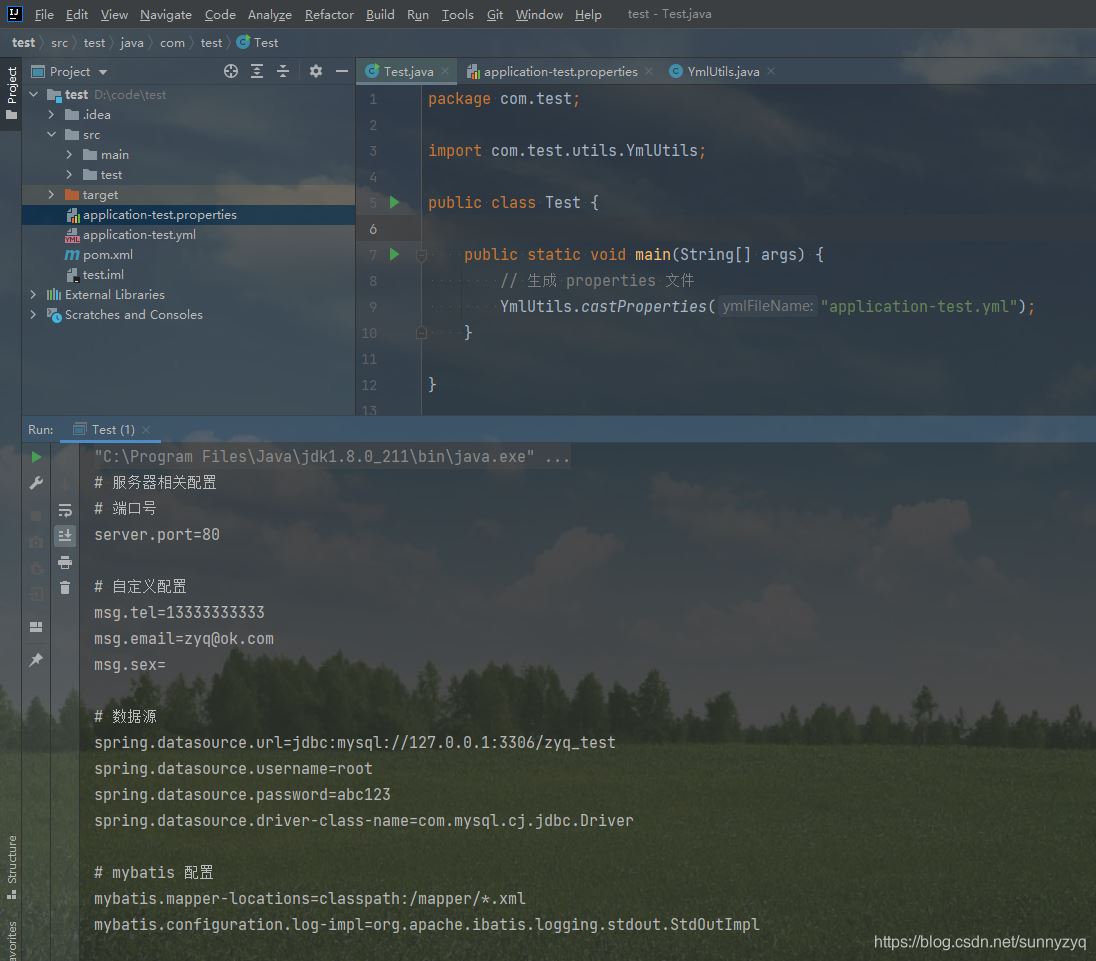
程序运行完成后,根目录下会多出一个与yml同名的properties文件,该文件就直接拷贝到相应的地方进行使用,而且原文件也并未收到任何损坏和影响。
【源码展示】
最后附上工具类源码,如果对你有用,记得一键三连(支持原创)。
package com.test.utils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Yaml 配置文件转 Properties 配置文件工具类
* @author https://zyqok.blog.csdn.net/
* @since 2021/08/24
*/
public class YmlUtils {
/**
* 将 yml 文件转化为 properties 文件
*
* @param ymlFileName 工程根目录下(非resources目录)的 yml 文件名称(如:abc.yml)
* @return List<Node> 每个Nyml 文件中每行对应解析的数据
*/
public static List<YmlNode> castProperties(String ymlFileName) {
if (ymlFileName == null || ymlFileName.isEmpty() || !ymlFileName.endsWith(".yml")) {
throw new RuntimeException("请输入yml文件名称!!");
}
File ymlFile = new File(ymlFileName);
if (!ymlFile.exists()) {
throw new RuntimeException("工程根目录下不存在 " + ymlFileName + "文件!!");
}
String fileName = ymlFileName.split(".yml", 2)[0];
// 获取文件数据
String yml = read(ymlFile);
List<YmlNode> nodeList = getNodeList(yml);
// 去掉多余数据,并打印
String str = printNodeList(nodeList);
// 将数据写入到 properties 文件中
String propertiesName = fileName + ".properties";
File file = new File(propertiesName);
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file)) {
writer.write(str);
writer.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return nodeList;
}
/**
* 将yml转化为porperties文件,并获取转化后的键值对
*
* @param ymlFileName 工程根目录下的 yml 文件名称
* @return 转化后的 porperties 文件键值对Map
*/
public static Map<String, String> getPropertiesMap(String ymlFileName) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
List<YmlNode> list = castProperties(ymlFileName);
for (YmlNode node : list) {
if (node.getKey().length() > 0) {
map.put(node.getKey(), node.getValue());
}
}
return map;
}
private static String read(File file) {
if (Objects.isNull(file) || !file.exists()) {
return "";
}
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)) {
byte[] b = new byte[(int) file.length()];
fis.read(b);
return new String(b, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "";
}
private static String printNodeList(List<YmlNode> nodeList) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (YmlNode node : nodeList) {
if (node.getLast().equals(Boolean.FALSE)) {
continue;
}
if (node.getEmptyLine().equals(Boolean.TRUE)) {
System.out.println();
sb.append("\r\n");
continue;
}
// 判断是否有行级注释
if (node.getHeadRemark().length() > 0) {
String s = "# " + node.getHeadRemark();
System.out.println(s);
sb.append(s).append("\r\n");
continue;
}
// 判断是否有行末注释 (properties中注释不允许末尾注释,故而放在上面)
if (node.getTailRemark().length() > 0) {
String s = "# " + node.getTailRemark();
System.out.println(s);
sb.append(s).append("\r\n");
}
//
String kv = node.getKey() + "=" + node.getValue();
System.out.println(kv);
sb.append(kv).append("\r\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
private static List<YmlNode> getNodeList(String yml) {
String[] lines = yml.split("\r\n");
List<YmlNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, String> keyMap = new HashMap<>();
Set<String> keySet = new HashSet<>();
for (String line : lines) {
YmlNode node = getNode(line);
if (node.getKey() != null && node.getKey().length() > 0) {
int level = node.getLevel();
if (level == 0) {
keyMap.clear();
keyMap.put(0, node.getKey());
} else {
int parentLevel = level - 1;
String parentKey = keyMap.get(parentLevel);
String currentKey = parentKey + "." + node.getKey();
keyMap.put(level, currentKey);
node.setKey(currentKey);
}
}
keySet.add(node.getKey() + ".");
nodeList.add(node);
}
// 标识是否最后一级
for (YmlNode each : nodeList) {
each.setLast(getNodeLast(each.getKey(), keySet));
}
return nodeList;
}
private static boolean getNodeLast(String key, Set<String> keySet) {
if (key.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
key = key + ".";
int count = 0;
for (String each : keySet) {
if (each.startsWith(key)) {
count++;
}
}
return count == 1;
}
private static YmlNode getNode(String line) {
YmlNode node = new YmlNode();
// 初始化默认数据(防止NPE)
node.setEffective(Boolean.FALSE);
node.setEmptyLine(Boolean.FALSE);
node.setHeadRemark("");
node.setKey("");
node.setValue("");
node.setTailRemark("");
node.setLast(Boolean.FALSE);
node.setLevel(0);
// 空行,不处理
String trimStr = line.trim();
if (trimStr.isEmpty()) {
node.setEmptyLine(Boolean.TRUE);
return node;
}
// 行注释,不处理
if (trimStr.startsWith("#")) {
node.setHeadRemark(trimStr.replaceFirst("#", "").trim());
return node;
}
// 处理值
String[] strs = line.split(":", 2);
// 拆分后长度为0的,属于异常数据,不做处理
if (strs.length == 0) {
return node;
}
// 获取键
node.setKey(strs[0].trim());
// 获取值
String value;
if (strs.length == 2) {
value = strs[1];
} else {
value = "";
}
// 获取行末备注
String tailRemark = "";
if (value.contains(" #")) {
String[] vs = value.split("#", 2);
if (vs.length == 2) {
value = vs[0];
tailRemark = vs[1];
}
}
node.setTailRemark(tailRemark.trim());
node.setValue(value.trim());
// 获取当前层级
int level = getNodeLevel(line);
node.setLevel(level);
node.setEffective(Boolean.TRUE);
return node;
}
private static int getNodeLevel(String line) {
if (line.trim().isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
char[] chars = line.toCharArray();
int count = 0;
for (char c : chars) {
if (c != ' ') {
break;
}
count++;
}
return count / 2;
}
}
class YmlNode {
/** 层级关系 */
private Integer level;
/** 键 */
private String key;
/** 值 */
private String value;
/** 是否为空行 */
private Boolean emptyLine;
/** 当前行是否为有效配置 */
private Boolean effective;
/** 头部注释(单行注释) */
private String headRemark;
/** 末尾注释 */
private String tailRemark;
/** 是否为最后一层配置 */
private Boolean last;
public Boolean getLast() {
return last;
}
public void setLast(Boolean last) {
this.last = last;
}
public Integer getLevel() {
return level;
}
public void setLevel(Integer level) {
this.level = level;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Boolean getEmptyLine() {
return emptyLine;
}
public void setEmptyLine(Boolean emptyLine) {
this.emptyLine = emptyLine;
}
public Boolean getEffective() {
return effective;
}
public void setEffective(Boolean effective) {
this.effective = effective;
}
public String getHeadRemark() {
return headRemark;
}
public void setHeadRemark(String headRemark) {
this.headRemark = headRemark;
}
public String getTailRemark() {
return tailRemark;
}
public void setTailRemark(String tailRemark) {
this.tailRemark = tailRemark;
}
}
到此这篇关于Yml转properties文件工具类YmlUtils(不用引任何插件和依赖)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Yml转properties文件工具类YmlUtils内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

