Android通过RemoteViews实现跨进程更新UI示例
一、概述
前面一篇文章Android通过AIDL实现跨进程更新UI我们学习了aidl跨进程更新ui,这种传统方式实现跨进程更新UI是可行的,但有以下弊端:
- View中的方法数比较多,在IPC中需要增加对应的方法比较繁琐。
- View的每一个方法都会涉及到IPC操作,多次IPC带来的开销问题不容小觑。
- View中方法的某些参数可能不支持IPC传输。例如:OnClickListener,它仅仅是个接口没有序列化。
接下来我们通过RemoteViews实现跨进程更新UI
二、实现效果图
在同一个应用中有两个Activity,MainActivity和Temp2Activity,这两个Activity不在同一个进程中。

现在需要通过Temp2Activity来改变MainActivity中的视图,即在MainActivity中添加两个Button,也就是实现跨进程更新UI这么一个功能。
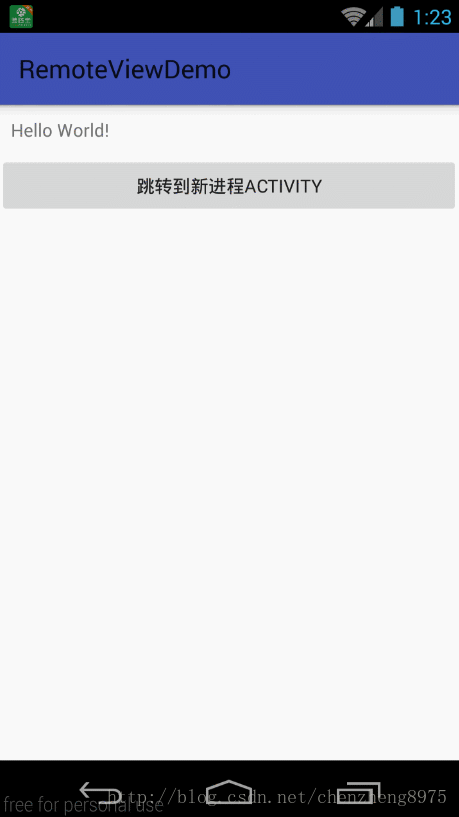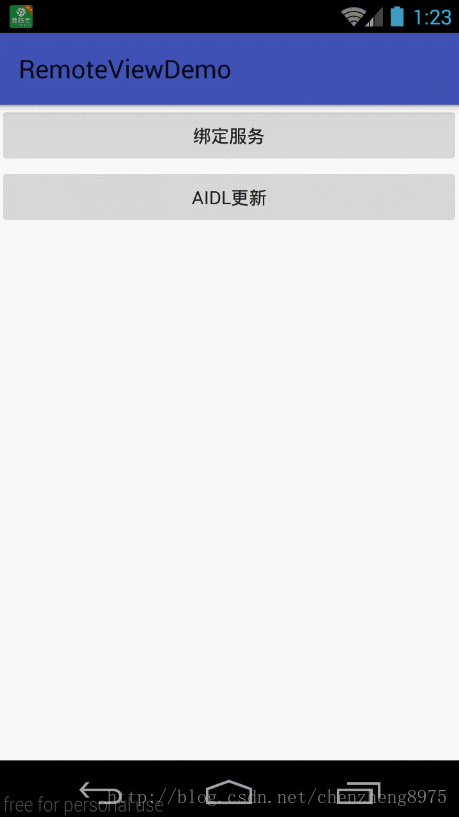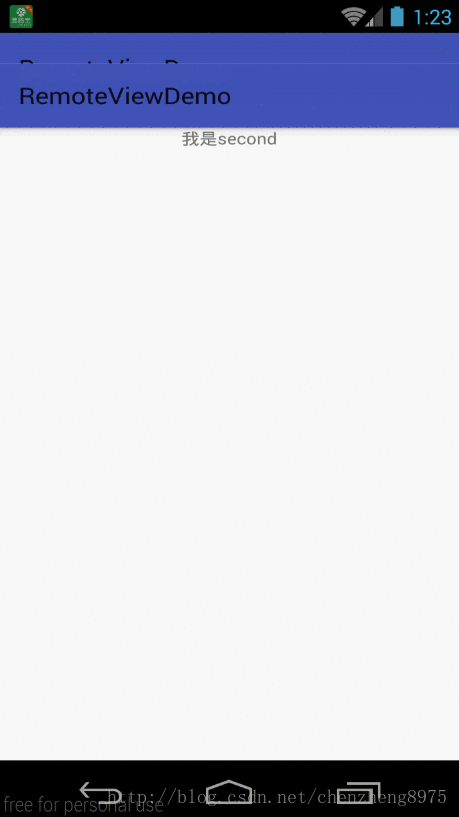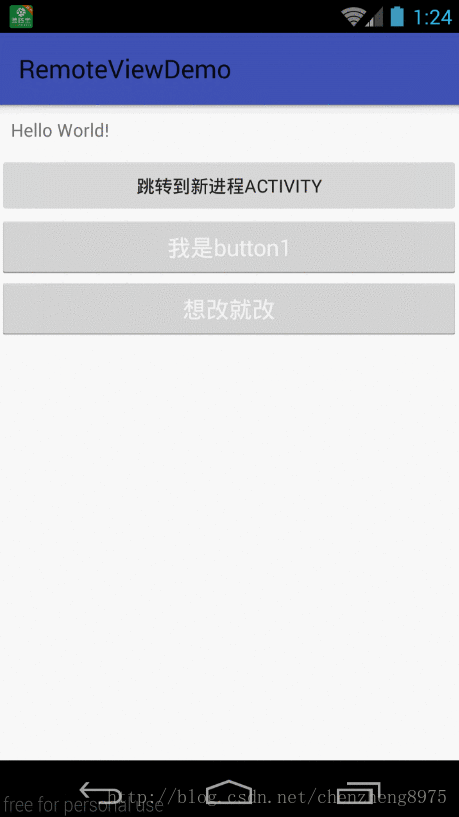
在MainActivity里点击“跳转到新进程ACTIVITY”按钮,会启动一个新进程的Temp2Activity,我们先点击“绑定服务”,这样我们就启动了服务,再点击“AIDL更新”按钮,通过调用handler来实现跨进程更新UI,点击返回,我们发现MainActivity页面中新添加了两个按钮,并且按钮还具有点击事件。
三、核心代码
IremoteViewsManager.aidl
里面提供了两个方法,一个是根据id更新TextView里面的内容,一个是根据id添加view视图
// IremoteViewsManager.aidl.aidl
package com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo;
interface IremoteViewsManager {
void addRemoteView(in RemoteViews remoteViews);
}
RemoteViewsAIDLService.Java
package com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.IremoteViewsManager;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.activity.MainActivity;
/**
* Description:
* User: chenzheng
* Date: 2017/2/10 0010
* Time: 10:56
*/
public class RemoteViewsAIDLService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "RemoteViewsAIDLService";
private Binder remoteViewsBinder = new IremoteViewsManager.Stub(){
@Override
public void addRemoteView(RemoteViews remoteViews) throws RemoteException {
Message message = new Message();
message.what = 1;
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putParcelable("remoteViews",remoteViews);
message.setData(bundle);
new MainActivity.MyHandler(RemoteViewsAIDLService.this,getMainLooper()).sendMessage(message);
}
};
public RemoteViewsAIDLService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return remoteViewsBinder;
}
}
MainActivity.java
package com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.R;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static String TAG = "MainActivity";
private static LinearLayout mLinearLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mLinearLayout = (LinearLayout) this.findViewById(R.id.mylayout);
}
public static class MyHandler extends Handler {
WeakReference<Context> weakReference;
public MyHandler(Context context, Looper looper) {
super(looper);
weakReference = new WeakReference<>(context);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
Log.i(TAG, "handleMessage");
switch (msg.what) {
case 1: //RemoteViews的AIDL实现
RemoteViews remoteViews = msg.getData().getParcelable("remoteViews");
if (remoteViews != null) {
Log.i(TAG, "updateUI");
View view = remoteViews.apply(weakReference.get(), mLinearLayout);
mLinearLayout.addView(view);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
public void readyGo(View view){
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, Temp2Activity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
Temp2Activity.java
package com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.activity;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.IremoteViewsManager;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.R;
import com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.service.RemoteViewsAIDLService;
/**
* Description:
* User: chenzheng
* Date: 2017/2/9 0009
* Time: 16:05
*/
public class Temp2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String TAG = "Temp2Activity";
private IremoteViewsManager remoteViewsManager;
private boolean isBind = false;
private ServiceConnection remoteViewServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
Log.i(TAG,"onServiceConnected");
remoteViewsManager = IremoteViewsManager.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
//回收
remoteViewsManager = null;
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setContentView(R.layout.activity_temp);
}
/**
* 绑定服务
*/
public void bindService(View view) {
Intent viewServiceIntent = new Intent(this,RemoteViewsAIDLService.class);
isBind = bindService(viewServiceIntent,remoteViewServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
/**
* 更新UI
*/
public void UpdateUI(View view){
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(Temp2Activity.this.getPackageName(),R.layout.button_layout);
Intent intentClick = new Intent(Temp2Activity.this,FirstActivity.class);
PendingIntent openFirstActivity = PendingIntent.getActivity(Temp2Activity.this,0,intentClick,0);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.firstButton,openFirstActivity);
Intent secondClick = new Intent(Temp2Activity.this,SecondActivity.class);
PendingIntent openSecondActivity = PendingIntent.getActivity(Temp2Activity.this,0,secondClick,0);
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.secondButton,openSecondActivity);
remoteViews.setCharSequence(R.id.secondButton,"setText","想改就改");
try {
remoteViewsManager.addRemoteView(remoteViews);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if(isBind){
unbindService(remoteViewServiceConnection);
isBind = false;
}
}
}
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".activity.MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".activity.FirstActivity" />
<activity android:name=".activity.SecondActivity" />
<activity
android:name=".activity.Temp2Activity"
android:process=":remote2" />
<service android:name="com.czhappy.remoteviewdemo.service.RemoteViewsAIDLService" />
</application>
</manifest>
四、总结
RemoteViews就是为跨进程更新UI而生的,内部封装了很多方法用来实现跨进程更新UI。但这并不代表RemoteViews是就是万能的了,它也有不足之处,目前支持的布局和View有限
layout:
FrameLayout LinearLayout RelativeLayout GridLayout
View:
AnalogClock button Chronometer ImageButton ImageView ProgressBar TextView ViewFlipper ListView GridView StackView AdapterViewFlipper ViewStub
不支持自定义View 所以具体使用RemoteViews还是aidl或者BroadCastReceiver还得看实际的需求。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。
