Python+matplotlib实现折线图的美化
目录
- 1. 导入包
- 2. 获得数据
- 3. 对数据做一些预处理
- 4. 画图
- 4.1 优化:添加点
- 4.2 优化:设置刻度
- 4.3 优化:设置填充
- 4.4 优化:设置填充颜色
- 5. 把功能打包成函数
- 6.测试函数
- 最后
大家好,今天分享一个非常有趣的 Python 教程,如何美化一个 matplotlib 折线图,喜欢记得收藏、关注、点赞。
1. 导入包
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.ticker as ticker import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
2. 获得数据
file_id = '1yM_F93NY4QkxjlKL3GzdcCQEnBiA2ltB'
url = f'https://drive.google.com/uc?id={file_id}'
df = pd.read_csv(url, index_col=0)
df
数据长得是这样的:

3. 对数据做一些预处理
按照需要,对数据再做一些预处理,代码及效果如下:
home_df = df.copy()
home_df = home_df.melt(id_vars = ["date", "home_team_name", "away_team_name"])
home_df["venue"] = "H"
home_df.rename(columns = {"home_team_name":"team", "away_team_name":"opponent"}, inplace = True)
home_df.replace({"variable":{"home_team_xG":"xG_for", "away_team_xG":"xG_ag"}}, inplace = True)
away_df = df.copy()
away_df = away_df.melt(id_vars = ["date", "away_team_name", "home_team_name"])
away_df["venue"] = "A"
away_df.rename(columns = {"away_team_name":"team", "home_team_name":"opponent"}, inplace = True)
away_df.replace({"variable":{"away_team_xG":"xG_for", "home_team_xG":"xG_ag"}}, inplace = True)
df = pd.concat([home_df, away_df]).reset_index(drop = True) df

4. 画图
# ---- Filter the data Y_for = df[(df["team"] == "Lazio") & (df["variable"] == "xG_for")]["value"].reset_index(drop = True) Y_ag = df[(df["team"] == "Lazio") & (df["variable"] == "xG_ag")]["value"].reset_index(drop = True) X_ = pd.Series(range(len(Y_for))) # ---- Compute rolling average Y_for = Y_for.rolling(window = 5, min_periods = 0).mean() # min_periods is for partial avg. Y_ag = Y_ag.rolling(window = 5, min_periods = 0).mean()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200) ax.plot(X_, Y_for) ax.plot(X_, Y_ag)

使用matplotlib倒是可以快速把图画好了,但是太丑了。接下来进行优化。
4.1 优化:添加点
这里为每一个数据添加点
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200) # --- Remove spines and add gridlines ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False) ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False) ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False) ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.5, color = "#4E616C") # --- The data ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o") ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o")

4.2 优化:设置刻度
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200)
# --- Remove spines and add gridlines
ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.25, color = "#4E616C")
# --- The data
ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
# --- Adjust tickers and spine to match the style of our grid
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2)) # ticker every 2 matchdays
xticks_ = ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([x - 1 for x in range(0, len(X_) + 3, 2)])
# This last line outputs
# [-1, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33, 35]
# and we mark the tickers every two positions.
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_edgecolor("#4E616C")

4.3 优化:设置填充
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200)
# --- Remove spines and add gridlines
ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.25, color = "#4E616C")
# --- The data
ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
# --- Fill between
ax.fill_between(x = X_, y1 = Y_for, y2 = Y_ag, alpha = 0.5)
# --- Adjust tickers and spine to match the style of our grid
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2)) # ticker every 2 matchdays
xticks_ = ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([x - 1 for x in range(0, len(X_) + 3, 2)])
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_edgecolor("#4E616C")

4.4 优化:设置填充颜色
1.当橙色线更高时,希望填充为橙色。但是上面的还无法满足,这里再优化一下.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200)
# --- Remove spines and add gridlines
ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.25, color = "#4E616C")
# --- The data
ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
# --- Fill between
# Identify points where Y_for > Y_ag
pos_for = (Y_for > Y_ag)
ax.fill_between(x = X_[pos_for], y1 = Y_for[pos_for], y2 = Y_ag[pos_for], alpha = 0.5)
pos_ag = (Y_for <= Y_ag)
ax.fill_between(x = X_[pos_ag], y1 = Y_for[pos_ag], y2 = Y_ag[pos_ag], alpha = 0.5)
# --- Adjust tickers and spine to match the style of our grid
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2)) # ticker every 2 matchdays
xticks_ = ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([x - 1 for x in range(0, len(X_) + 3, 2)])
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_edgecolor("#4E616C")

上面的图出现异常,再修改一下:
X_aux = X_.copy()
X_aux.index = X_aux.index * 10 # 9 aux points in between each match
last_idx = X_aux.index[-1] + 1
X_aux = X_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
X_aux = X_aux.interpolate()
# --- Aux series for the xG created (Y_for)
Y_for_aux = Y_for.copy()
Y_for_aux.index = Y_for_aux.index * 10
last_idx = Y_for_aux.index[-1] + 1
Y_for_aux = Y_for_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
Y_for_aux = Y_for_aux.interpolate()
# --- Aux series for the xG conceded (Y_ag)
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag.copy()
Y_ag_aux.index = Y_ag_aux.index * 10
last_idx = Y_ag_aux.index[-1] + 1
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag_aux.interpolate()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (7,3), dpi = 200)
# --- Remove spines and add gridlines
ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.25, color = "#4E616C")
# --- The data
for_ = ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
ag_ = ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 5)
# --- Fill between
for index in range(len(X_aux) - 1):
# Choose color based on which line's on top
if Y_for_aux.iloc[index + 1] > Y_ag_aux.iloc[index + 1]:
color = for_[0].get_color()
else:
color = ag_[0].get_color()
# Fill between the current point and the next point in pur extended series.
ax.fill_between([X_aux[index], X_aux[index+1]],
[Y_for_aux.iloc[index], Y_for_aux.iloc[index+1]],
[Y_ag_aux.iloc[index], Y_ag_aux.iloc[index+1]],
color=color, zorder = 2, alpha = 0.2, ec = None)
# --- Adjust tickers and spine to match the style of our grid
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2)) # ticker every 2 matchdays
xticks_ = ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([x - 1 for x in range(0, len(X_) + 3, 2)])
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_edgecolor("#4E616C")

5. 把功能打包成函数
上面的样子都还不错啦,接下来把这些东西都打包成一个函数。方便后面直接出图。
def plot_xG_rolling(team, ax, window = 5, color_for = "blue", color_ag = "orange", data = df):
'''
This function creates a rolling average xG plot for a given team and rolling
window.
team (str): The team's name
ax (obj): a Matplotlib axes.
window (int): The number of periods for our rolling average.
color_for (str): A hex color code for xG created.
color_af (str): A hex color code for xG conceded.
data (DataFrame): our df with the xG data.
'''
# -- Prepping the data
home_df = data.copy()
home_df = home_df.melt(id_vars = ["date", "home_team_name", "away_team_name"])
home_df["venue"] = "H"
home_df.rename(columns = {"home_team_name":"team", "away_team_name":"opponent"}, inplace = True)
home_df.replace({"variable":{"home_team_xG":"xG_for", "away_team_xG":"xG_ag"}}, inplace = True)
away_df = data.copy()
away_df = away_df.melt(id_vars = ["date", "away_team_name", "home_team_name"])
away_df["venue"] = "A"
away_df.rename(columns = {"away_team_name":"team", "home_team_name":"opponent"}, inplace = True)
away_df.replace({"variable":{"away_team_xG":"xG_for", "home_team_xG":"xG_ag"}}, inplace = True)
df = pd.concat([home_df, away_df]).reset_index(drop = True)
# ---- Filter the data
Y_for = df[(df["team"] == team) & (df["variable"] == "xG_for")]["value"].reset_index(drop = True)
Y_ag = df[(df["team"] == team) & (df["variable"] == "xG_ag")]["value"].reset_index(drop = True)
X_ = pd.Series(range(len(Y_for)))
if Y_for.shape[0] == 0:
raise ValueError(f"Team {team} is not present in the DataFrame")
# ---- Compute rolling average
Y_for = Y_for.rolling(window = 5, min_periods = 0).mean() # min_periods is for partial avg.
Y_ag = Y_ag.rolling(window = 5, min_periods = 0).mean()
# ---- Create auxiliary series for filling between curves
X_aux = X_.copy()
X_aux.index = X_aux.index * 10 # 9 aux points in between each match
last_idx = X_aux.index[-1] + 1
X_aux = X_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
X_aux = X_aux.interpolate()
# --- Aux series for the xG created (Y_for)
Y_for_aux = Y_for.copy()
Y_for_aux.index = Y_for_aux.index * 10
last_idx = Y_for_aux.index[-1] + 1
Y_for_aux = Y_for_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
Y_for_aux = Y_for_aux.interpolate()
# --- Aux series for the xG conceded (Y_ag)
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag.copy()
Y_ag_aux.index = Y_ag_aux.index * 10
last_idx = Y_ag_aux.index[-1] + 1
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag_aux.reindex(range(last_idx))
Y_ag_aux = Y_ag_aux.interpolate()
# --- Plotting our data
# --- Remove spines and add gridlines
ax.spines["left"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.grid(ls = "--", lw = 0.25, color = "#4E616C")
# --- The data
for_ = ax.plot(X_, Y_for, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 4, color = color_for)
ag_ = ax.plot(X_, Y_ag, marker = "o", mfc = "white", ms = 4, color = color_ag)
# --- Fill between
for index in range(len(X_aux) - 1):
# Choose color based on which line's on top
if Y_for_aux.iloc[index + 1] > Y_ag_aux.iloc[index + 1]:
color = for_[0].get_color()
else:
color = ag_[0].get_color()
# Fill between the current point and the next point in pur extended series.
ax.fill_between([X_aux[index], X_aux[index+1]],
[Y_for_aux.iloc[index], Y_for_aux.iloc[index+1]],
[Y_ag_aux.iloc[index], Y_ag_aux.iloc[index+1]],
color=color, zorder = 2, alpha = 0.2, ec = None)
# --- Ensure minimum value of Y-axis is zero
ax.set_ylim(0)
# --- Adjust tickers and spine to match the style of our grid
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(2)) # ticker every 2 matchdays
xticks_ = ax.xaxis.set_ticklabels([x - 1 for x in range(0, len(X_) + 3, 2)])
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.yaxis.set_tick_params(length = 2, color = "#4E616C", labelcolor = "#4E616C", labelsize = 6)
ax.spines["bottom"].set_edgecolor("#4E616C")
# --- Legend and team name
Y_for_last = Y_for.iloc[-1]
Y_ag_last = Y_ag.iloc[-1]
# -- Add the team's name
team_ = ax.text(
x = 0, y = ax.get_ylim()[1] + ax.get_ylim()[1]/20,
s = f'{team}',
color = "#4E616C",
va = 'center',
ha = 'left',
size = 7
)
# -- Add the xG created label
for_label_ = ax.text(
x = X_.iloc[-1] + 0.75, y = Y_for_last,
s = f'{Y_for_last:,.1f} xGF',
color = color_for,
va = 'center',
ha = 'left',
size = 6.5
)
# -- Add the xG conceded label
ag_label_ = ax.text(
x = X_.iloc[-1] + 0.75, y = Y_ag_last,
s = f'{Y_ag_last:,.1f} xGA',
color = color_ag,
va = 'center',
ha = 'left',
size = 6.5
)
6.测试函数
file_id = '1yM_F93NY4QkxjlKL3GzdcCQEnBiA2ltB'
url = f'https://drive.google.com/uc?id={file_id}'
df = pd.read_csv(url, index_col=0)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 2), dpi = 200)
ax = plt.subplot(111)
plot_xG_rolling("Sassuolo", ax, color_for = "#00A752", color_ag = "black", data = df)
plt.tight_layout()

再设置更加丰富的颜色:
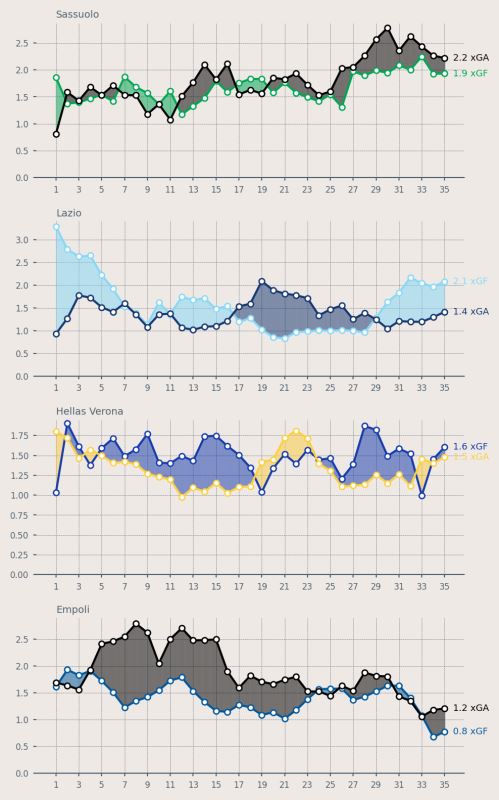
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 8), dpi = 200, facecolor = "#EFE9E6")
ax1 = plt.subplot(411, facecolor = "#EFE9E6")
ax2 = plt.subplot(412, facecolor = "#EFE9E6")
ax3 = plt.subplot(413, facecolor = "#EFE9E6")
ax4 = plt.subplot(414, facecolor = "#EFE9E6")
plot_xG_rolling("Sassuolo", ax1, color_for = "#00A752", color_ag = "black", data = df)
plot_xG_rolling("Lazio", ax2, color_for = "#87D8F7", color_ag = "#15366F", data = df)
plot_xG_rolling("Hellas Verona", ax3, color_for = "#153aab", color_ag = "#fdcf41", data = df)
plot_xG_rolling("Empoli", ax4, color_for = "#00579C", color_ag = "black", data = df)
plt.tight_layout()
最后
其实本文主要是对两个折线图做了一系列的优化和改进而已,主要是强调细节部分。
涉及到的matplotlib的知识,也主要是在ticks、背景颜色、fill_between部分。
以上就是Python+matplotlib实现折线图的美化的详细内容,更多关于Python matplotlib折线图的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!
赞 (0)

