Pytorch - TORCH.NN.INIT 参数初始化的操作
路径:
https://pytorch.org/docs/master/nn.init.html#nn-init-doc
初始化函数:torch.nn.init
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on 2019
@author: fancp
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
w = torch.empty(3,5)
#1.均匀分布 - u(a,b)
#torch.nn.init.uniform_(tensor, a=0.0, b=1.0)
print(nn.init.uniform_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[0.9160, 0.1832, 0.5278, 0.5480, 0.6754],
# [0.9509, 0.8325, 0.9149, 0.8192, 0.9950],
# [0.4847, 0.4148, 0.8161, 0.0948, 0.3787]])
# =============================================================================
#2.正态分布 - N(mean, std)
#torch.nn.init.normal_(tensor, mean=0.0, std=1.0)
print(nn.init.normal_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[ 0.4388, 0.3083, -0.6803, -1.1476, -0.6084],
# [ 0.5148, -0.2876, -1.2222, 0.6990, -0.1595],
# [-2.0834, -1.6288, 0.5057, -0.5754, 0.3052]])
# =============================================================================
#3.常数 - 固定值 val
#torch.nn.init.constant_(tensor, val)
print(nn.init.constant_(w, 0.3))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000],
# [0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000],
# [0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000, 0.3000]])
# =============================================================================
#4.全1分布
#torch.nn.init.ones_(tensor)
print(nn.init.ones_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
# [1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
# =============================================================================
#5.全0分布
#torch.nn.init.zeros_(tensor)
print(nn.init.zeros_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
# =============================================================================
#6.对角线为 1,其它为 0
#torch.nn.init.eye_(tensor)
print(nn.init.eye_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
# [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.]])
# =============================================================================
#7.xavier_uniform 初始化
#torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain=1.0)
#From - Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks - Bengio 2010
print(nn.init.xavier_uniform_(w, gain=nn.init.calculate_gain('relu')))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[-0.1270, 0.3963, 0.9531, -0.2949, 0.8294],
# [-0.9759, -0.6335, 0.9299, -1.0988, -0.1496],
# [-0.7224, 0.2181, -1.1219, 0.8629, -0.8825]])
# =============================================================================
#8.xavier_normal 初始化
#torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_(tensor, gain=1.0)
print(nn.init.xavier_normal_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[ 1.0463, 0.1275, -0.3752, 0.1858, 1.1008],
# [-0.5560, 0.2837, 0.1000, -0.5835, 0.7886],
# [-0.2417, 0.1763, -0.7495, 0.4677, -0.1185]])
# =============================================================================
#9.kaiming_uniform 初始化
#torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(tensor, a=0, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='leaky_relu')
#From - Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification - HeKaiming 2015
print(nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(w, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='relu'))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[-0.7712, 0.9344, 0.8304, 0.2367, 0.0478],
# [-0.6139, -0.3916, -0.0835, 0.5975, 0.1717],
# [ 0.3197, -0.9825, -0.5380, -1.0033, -0.3701]])
# =============================================================================
#10.kaiming_normal 初始化
#torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(tensor, a=0, mode='fan_in', nonlinearity='leaky_relu')
print(nn.init.kaiming_normal_(w, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu'))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[-0.0210, 0.5532, -0.8647, 0.9813, 0.0466],
# [ 0.7713, -1.0418, 0.7264, 0.5547, 0.7403],
# [-0.8471, -1.7371, 1.3333, 0.0395, 1.0787]])
# =============================================================================
#11.正交矩阵 - (semi)orthogonal matrix
#torch.nn.init.orthogonal_(tensor, gain=1)
#From - Exact solutions to the nonlinear dynamics of learning in deep linear neural networks - Saxe 2013
print(nn.init.orthogonal_(w))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[-0.0346, -0.7607, -0.0428, 0.4771, 0.4366],
# [-0.0412, -0.0836, 0.9847, 0.0703, -0.1293],
# [-0.6639, 0.4551, 0.0731, 0.1674, 0.5646]])
# =============================================================================
#12.稀疏矩阵 - sparse matrix
#torch.nn.init.sparse_(tensor, sparsity, std=0.01)
#From - Deep learning via Hessian-free optimization - Martens 2010
print(nn.init.sparse_(w, sparsity=0.1))
# =============================================================================
# tensor([[ 0.0000, 0.0000, -0.0077, 0.0000, -0.0046],
# [ 0.0152, 0.0030, 0.0000, -0.0029, 0.0005],
# [ 0.0199, 0.0132, -0.0088, 0.0060, 0.0000]])
# =============================================================================
补充:【pytorch参数初始化】 pytorch默认参数初始化以及自定义参数初始化
本文用两个问题来引入
1.pytorch自定义网络结构不进行参数初始化会怎样,参数值是随机的吗?
2.如何自定义参数初始化?
先回答第一个问题
在pytorch中,有自己默认初始化参数方式,所以在你定义好网络结构以后,不进行参数初始化也是可以的。
1.Conv2d继承自_ConvNd,在_ConvNd中,可以看到默认参数就是进行初始化的,如下图所示
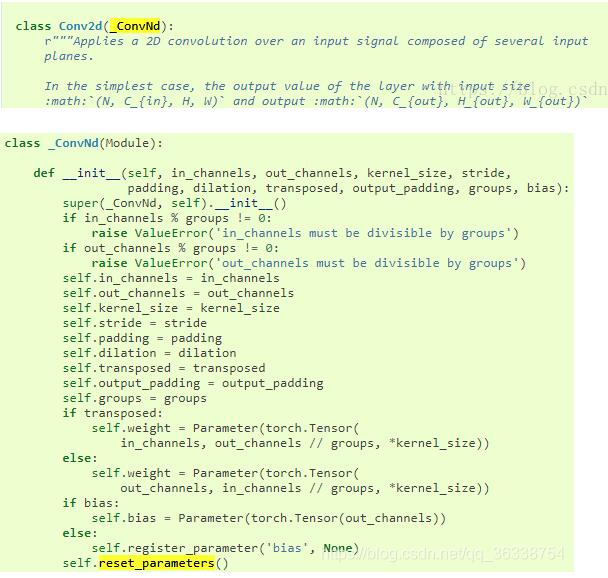
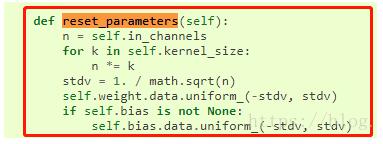
2.torch.nn.BatchNorm2d也一样有默认初始化的方式
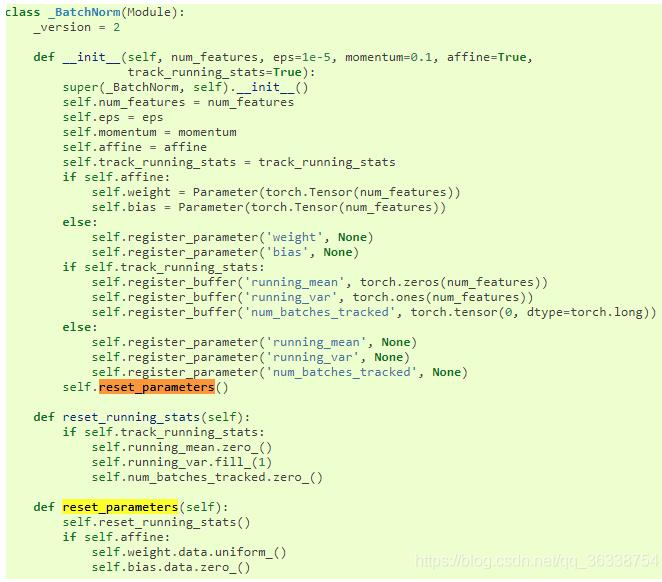
3.torch.nn.Linear也如此

现在来回答第二个问题。
pytorch中对神经网络模型中的参数进行初始化方法如下:
from torch.nn import init
#define the initial function to init the layer's parameters for the network
def weigth_init(m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight.data)
init.constant_(m.bias.data,0.1)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
m.weight.data.normal_(0,0.01)
m.bias.data.zero_()
首先定义了一个初始化函数,接着进行调用就ok了,不过要先把网络模型实例化:
#Define Network model = Net(args.input_channel,args.output_channel) model.apply(weigth_init)
此上就完成了对模型中训练参数的初始化。
在知乎上也有看到一个类似的版本,也相应的贴上来作为参考了:
def initNetParams(net):
'''Init net parameters.'''
for m in net.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.xavier_uniform(m.weight)
if m.bias:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant(m.weight, 1)
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal(m.weight, std=1e-3)
if m.bias:
init.constant(m.bias, 0)
initNetParams(net)
再说一下关于模型的保存及加载
1.保存有两种方式,第一种是保存模型的整个结构信息和参数,第二种是只保存模型的参数
#保存整个网络模型及参数 torch.save(net, 'net.pkl') #仅保存模型参数 torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'net_params.pkl')
2.加载对应保存的两种网络
# 保存和加载整个模型
torch.save(model_object, 'model.pth')
model = torch.load('model.pth')
# 仅保存和加载模型参数
torch.save(model_object.state_dict(), 'params.pth')
model_object.load_state_dict(torch.load('params.pth'))
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
赞 (0)

