Android函数抽取壳的实现代码
目录
- 0x0 前言
- 0x1 项目的结构
- 0x2 proccessor
- 0x3 shell模块
- 0x4 总结
0x0 前言
函数抽取壳这个词不知道从哪起源的,但我理解的函数抽取壳是那种将dex文件中的函数代码给nop,然后在运行时再把字节码给填回dex的这么一种壳。
函数抽取前:

函数抽取后:
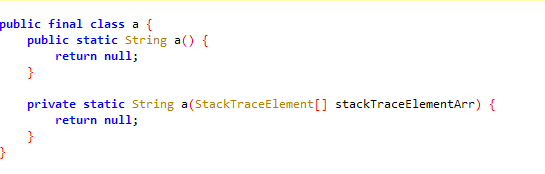
很早之前就想写这类的壳,最近终于把它做出来了,取名为dpt。现在将代码分享出来,欢迎把玩。项目地址:https://github.com/luoyesiqiu/dpt-shell
0x1 项目的结构
dpt代码分为两个部分,一个是proccessor,另一个是shell。
proccessor是可以将普通apk处理成加壳apk的模块。它的主要功能有:
- 解压apk
- 提取apk中的dex的codeitem保存起来
- 修改Androidmanifest.xml中的Application类名
- 生成新的apk
流程如下:

shell模块最终生成的dex文件和so文件将被集成到需要加壳的apk中。它的要功能有:
- 处理App的启动
- 替换dexElements
- hook相关函数
- 调用目标Application
- codeitem文件读取
- codeitem填回
流程如下:

0x2 proccessor
proccessor比较重要的逻辑两点,AndroidManiest.xml的处理和Codeitem的提取
(1)处理Androidmanifest.xml
我们处理AndroidManifest.xml的操作主要是备份原Application的类名和写入壳的代理Application的类名。备份原Application类名目的是在壳的流程执行完成后,调用我们原APK的Application。写入壳的代理Application类名的目的是在app启动时尽早的启动我们的代理Application,这样我们就可以做一些准备工作,比如自定义加载dex,Hook一些函数等。我们知道,AndroidManifest.xml在生成apk后它不是以普通xml文件的格式来存放的,而是以axml格式来存放的。不过幸运的是,已经有许多大佬写了对axml解析和编辑的库,我们直接拿来用就行。这里用到的axml处理的库是ManifestEditor。
提取原Androidmanifest.xml Application完整类名代码如下,直接调用getApplicationName函数即可
public static String getValue(String file,String tag,String ns,String attrName){
byte[] axmlData = IoUtils.readFile(file);
AxmlParser axmlParser = new AxmlParser(axmlData);
try {
while (axmlParser.next() != AxmlParser.END_FILE) {
if (axmlParser.getAttrCount() != 0 && !axmlParser.getName().equals(tag)) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < axmlParser.getAttrCount(); i++) {
if (axmlParser.getNamespacePrefix().equals(ns) && axmlParser.getAttrName(i).equals(attrName)) {
return (String) axmlParser.getAttrValue(i);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String getApplicationName(String file) {
return getValue(file,"application","android","name");
}
写入Application类名的代码如下:
public static void writeApplicationName(String inManifestFile, String outManifestFile, String newApplicationName){
ModificationProperty property = new ModificationProperty();
property.addApplicationAttribute(new AttributeItem(NodeValue.Application.NAME,newApplicationName));
FileProcesser.processManifestFile(inManifestFile, outManifestFile, property);
}
(2) 提取CodeItem
CodeItem是dex文件中存放函数字节码相关数据的结构。下图显示的就是CodeItem大概的样子。

说是提取CodeItem,其实我们提取的是CodeItem中的insns,它里面存放的是函数真正的字节码。提取insns,我们使用的是Android源码中的dx工具,使用dx工具可以很方便的读取dex文件的各个部分。
下面的代码遍历所有ClassDef,并遍历其中的所有函数,再调用extractMethod对单个函数进行处理。
public static List<Instruction> extractAllMethods(File dexFile, File outDexFile) {
List<Instruction> instructionList = new ArrayList<>();
Dex dex = null;
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
byte[] dexData = IoUtils.readFile(dexFile.getAbsolutePath());
IoUtils.writeFile(outDexFile.getAbsolutePath(),dexData);
try {
dex = new Dex(dexFile);
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(outDexFile, "rw");
Iterable<ClassDef> classDefs = dex.classDefs();
for (ClassDef classDef : classDefs) {
......
if(classDef.getClassDataOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("class '%s' data offset is zero",classDef.toString());
logger.warn(log);
continue;
}
ClassData classData = dex.readClassData(classDef);
ClassData.Method[] directMethods = classData.getDirectMethods();
ClassData.Method[] virtualMethods = classData.getVirtualMethods();
for (ClassData.Method method : directMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex,randomAccessFile,classDef,method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
for (ClassData.Method method : virtualMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex, randomAccessFile,classDef, method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
IoUtils.close(randomAccessFile);
}
return instructionList;
}
处理函数的过程中发现没有代码(通常为native函数)或者insns的容量不足以填充return语句则跳过处理。这里就是对应函数抽取壳的抽取操作
private static Instruction extractMethod(Dex dex ,RandomAccessFile outRandomAccessFile,ClassDef classDef,ClassData.Method method)
throws Exception{
String returnTypeName = dex.typeNames().get(dex.protoIds().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getProtoIndex()).getReturnTypeIndex());
String methodName = dex.strings().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getNameIndex());
String className = dex.typeNames().get(classDef.getTypeIndex());
//native函数
if(method.getCodeOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("method code offset is zero,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
Instruction instruction = new Instruction();
//16 = registers_size + ins_size + outs_size + tries_size + debug_info_off + insns_size
int insnsOffset = method.getCodeOffset() + 16;
Code code = dex.readCode(method);
//容错处理
if(code.getInstructions().length == 0){
String log = String.format("method has no code,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
int insnsCapacity = code.getInstructions().length;
//insns容量不足以存放return语句,跳过
byte[] returnByteCodes = getReturnByteCodes(returnTypeName);
if(insnsCapacity * 2 < returnByteCodes.length){
logger.warn("The capacity of insns is not enough to store the return statement. {}.{}() -> {} insnsCapacity = {}byte(s),returnByteCodes = {}byte(s)",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName),
insnsCapacity * 2,
returnByteCodes.length);
return null;
}
instruction.setOffsetOfDex(insnsOffset);
//这里的MethodIndex对应method_ids区的索引
instruction.setMethodIndex(method.getMethodIndex());
//注意:这里是数组的大小
instruction.setInstructionDataSize(insnsCapacity * 2);
byte[] byteCode = new byte[insnsCapacity * 2];
//写入nop指令
for (int i = 0; i < insnsCapacity; i++) {
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
byteCode[i * 2] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
byteCode[i * 2 + 1] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
outRandomAccessFile.writeShort(0);
}
instruction.setInstructionsData(byteCode);
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset);
//写出return语句
outRandomAccessFile.write(returnByteCodes);
return instruction;
}
0x3 shell模块
shell模块是函数抽取壳的主要逻辑,它的功能我们上面已经讲过。
(1) Hook函数
Hook函数时机最好要早点,dpt在_init函数中开始进行一系列HOOK
extern "C" void _init(void) {
dpt_hook();
}
Hook框架使用的Dobby,主要Hook两个函数:MapFileAtAddress和LoadMethod。
Hook MapFileAtAddress函数的目的是在我们加载dex能够修改dex的属性,让加载的dex可写,这样我们才能把字节码填回dex,有大佬详细的分析过,具体参考这篇文章。
void* MapFileAtAddressAddr = DobbySymbolResolver(GetArtLibPath(),MapFileAtAddress_Sym()); DobbyHook(MapFileAtAddressAddr, (void *) MapFileAtAddress28,(void **) &g_originMapFileAtAddress28);
Hook到了之后,给prot参数追加PROT_WRITE属性
void* MapFileAtAddress28(uint8_t* expected_ptr,
size_t byte_count,
int prot,
int flags,
int fd,
off_t start,
bool low_4gb,
bool reuse,
const char* filename,
std::string* error_msg){
int new_prot = (prot | PROT_WRITE);
if(nullptr != g_originMapFileAtAddress28) {
return g_originMapFileAtAddress28(expected_ptr,byte_count,new_prot,flags,fd,start,low_4gb,reuse,filename,error_msg);
}
}
在Hook LoadMethod函数之前,我们需要了解LoadMethod函数流程。为什么是这个LoadMethod函数,其他函数是否可行?
当一个类被加载的时候,它的调用链是这样的(部分流程已省略):
ClassLoader.java::loadClass -> DexPathList.java::findClass -> DexFile.java::defineClass -> class_linker.cc::LoadClass -> class_linker.cc::LoadClassMembers -> class_linker.cc::LoadMethod
也就是说,当一个类被加载,它是会去调用LoadMethod函数的,我们看一下它的函数原型:
void ClassLinker::LoadMethod(const DexFile& dex_file,
const ClassDataItemIterator& it,
Handle<mirror::Class> klass,
ArtMethod* dst);
这个函数太爆炸了,它有两个爆炸性的参数,DexFile和ClassDataItemIterator,我们可以从这个函数得到当前加载函数所在的DexFile结构和当前函数的一些信息,可以看一下ClassDataItemIterator结构:
class ClassDataItemIterator{
......
// A decoded version of the method of a class_data_item
struct ClassDataMethod {
uint32_t method_idx_delta_; // delta of index into the method_ids array for MethodId
uint32_t access_flags_;
uint32_t code_off_;
ClassDataMethod() : method_idx_delta_(0), access_flags_(0), code_off_(0) {}
private:
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(ClassDataMethod);
};
ClassDataMethod method_;
// Read and decode a method from a class_data_item stream into method
void ReadClassDataMethod();
const DexFile& dex_file_;
size_t pos_; // integral number of items passed
const uint8_t* ptr_pos_; // pointer into stream of class_data_item
uint32_t last_idx_; // last read field or method index to apply delta to
DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(ClassDataItemIterator);
};
其中最重要的字段就是code_off_它的值是当前加载的函数的CodeItem相对于DexFile的偏移,当相应的函数被加载,我们就可以直接访问到它的CodeItem。其他函数是否也可以?在上面的流程中没有比LoadMethod更适合我们Hook的函数,所以它是最佳的Hook点。
Hook LoadMethod稍微复杂一些,倒不是Hook代码复杂,而是Hook触发后处理的代码比较复杂,我们要适配多个Android版本,每个版本LoadMethod函数的参数都可能有改变,幸运的是,LoadMethod改动也不是很大。那么,我们如何读取ClassDataItemIterator类中的code_off_呢?比较直接的做法是计算偏移,然后在代码中维护一份偏移。不过这样的做法不易阅读很容易出错。dpt的做法是把ClassDataItemIterator类拷过来,然后将ClassDataItemIterator引用直接转换为我们自定义的ClassDataItemIterator引用,这样就可以方便的读取字段的值。
下面是LoadMethod被调用后做的操作,逻辑是读取存在map中的insns,然后将它们填回指定位置。
void LoadMethod(void *thiz, void *self, const void *dex_file, const void *it, const void *method,
void *klass, void *dst) {
if (g_originLoadMethod25 != nullptr
|| g_originLoadMethod28 != nullptr
|| g_originLoadMethod29 != nullptr) {
uint32_t location_offset = getDexFileLocationOffset();
uint32_t begin_offset = getDataItemCodeItemOffset();
callOriginLoadMethod(thiz, self, dex_file, it, method, klass, dst);
ClassDataItemReader *classDataItemReader = getClassDataItemReader(it,method);
uint8_t **begin_ptr = (uint8_t **) ((uint8_t *) dex_file + begin_offset);
uint8_t *begin = *begin_ptr;
// vtable(4|8) + prev_fields_size
std::string *location = (reinterpret_cast<std::string *>((uint8_t *) dex_file +
location_offset));
if (location->find("base.apk") != std::string::npos) {
//code_item_offset == 0说明是native方法或者没有代码
if (classDataItemReader->GetMethodCodeItemOffset() == 0) {
DLOGW("native method? = %s code_item_offset = 0x%x",
classDataItemReader->MemberIsNative() ? "true" : "false",
classDataItemReader->GetMethodCodeItemOffset());
return;
}
uint16_t firstDvmCode = *((uint16_t*)(begin + classDataItemReader->GetMethodCodeItemOffset() + 16));
if(firstDvmCode != 0x0012 && firstDvmCode != 0x0016 && firstDvmCode != 0x000e){
NLOG("this method has code no need to patch");
return;
}
uint32_t dexSize = *((uint32_t*)(begin + 0x20));
int dexIndex = dexNumber(location);
auto dexIt = dexMap.find(dexIndex - 1);
if (dexIt != dexMap.end()) {
auto dexMemIt = dexMemMap.find(dexIndex);
if(dexMemIt == dexMemMap.end()){
changeDexProtect(begin,location->c_str(),dexSize,dexIndex);
}
auto codeItemMap = dexIt->second;
int methodIdx = classDataItemReader->GetMemberIndex();
auto codeItemIt = codeItemMap->find(methodIdx);
if (codeItemIt != codeItemMap->end()) {
CodeItem* codeItem = codeItemIt->second;
uint8_t *realCodeItemPtr = (uint8_t*)(begin +
classDataItemReader->GetMethodCodeItemOffset() +
16);
memcpy(realCodeItemPtr,codeItem->getInsns(),codeItem->getInsnsSize());
}
}
}
}
}
(2) 加载dex
其实dex在App启动的时候已经被加载过一次了,但是,我们为什么还要再加载一次?因为系统加载的dex是以只读方式加载的,我们没办法去修改那一部分的内存。而且App的dex加载早于我们Application的启动,这样,我们在代码根本没法感知到,所以我们要重新加载dex。
private ClassLoader loadDex(Context context){
String sourcePath = context.getApplicationInfo().sourceDir;
String nativePath = context.getApplicationInfo().nativeLibraryDir;
ShellClassLoader shellClassLoader = new ShellClassLoader(sourcePath,nativePath,ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
return shellClassLoader;
}
自定义的ClassLoader
public class ShellClassLoader extends PathClassLoader {
private final String TAG = ShellClassLoader.class.getSimpleName();
public ShellClassLoader(String dexPath,ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(dexPath,classLoader);
}
public ShellClassLoader(String dexPath, String librarySearchPath,ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(dexPath, librarySearchPath, classLoader);
}
}
(3) 替换dexElements
这一步也非常重要,这一步的目的是使ClassLoader从我们新加载的dex文件中加载类。代码如下:
void mergeDexElements(JNIEnv* env,jclass klass,jobject oldClassLoader,jobject newClassLoader){
jclass BaseDexClassLoaderClass = env->FindClass("dalvik/system/BaseDexClassLoader");
jfieldID pathList = env->GetFieldID(BaseDexClassLoaderClass,"pathList","Ldalvik/system/DexPathList;");
jobject oldDexPathListObj = env->GetObjectField(oldClassLoader,pathList);
if(env->ExceptionCheck() || nullptr == oldDexPathListObj ){
env->ExceptionClear();
DLOGW("mergeDexElements oldDexPathListObj get fail");
return;
}
jobject newDexPathListObj = env->GetObjectField(newClassLoader,pathList);
if(env->ExceptionCheck() || nullptr == newDexPathListObj){
env->ExceptionClear();
DLOGW("mergeDexElements newDexPathListObj get fail");
return;
}
jclass DexPathListClass = env->FindClass("dalvik/system/DexPathList");
jfieldID dexElementField = env->GetFieldID(DexPathListClass,"dexElements","[Ldalvik/system/DexPathList$Element;");
jobjectArray newClassLoaderDexElements = static_cast<jobjectArray>(env->GetObjectField(
newDexPathListObj, dexElementField));
if(env->ExceptionCheck() || nullptr == newClassLoaderDexElements){
env->ExceptionClear();
DLOGW("mergeDexElements new dexElements get fail");
return;
}
jobjectArray oldClassLoaderDexElements = static_cast<jobjectArray>(env->GetObjectField(
oldDexPathListObj, dexElementField));
if(env->ExceptionCheck() || nullptr == oldClassLoaderDexElements){
env->ExceptionClear();
DLOGW("mergeDexElements old dexElements get fail");
return;
}
jint oldLen = env->GetArrayLength(oldClassLoaderDexElements);
jint newLen = env->GetArrayLength(newClassLoaderDexElements);
DLOGD("mergeDexElements oldlen = %d , newlen = %d",oldLen,newLen);
jclass ElementClass = env->FindClass("dalvik/system/DexPathList$Element");
jobjectArray newElementArray = env->NewObjectArray(oldLen + newLen,ElementClass, nullptr);
for(int i = 0;i < newLen;i++) {
jobject elementObj = env->GetObjectArrayElement(newClassLoaderDexElements, i);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(newElementArray,i,elementObj);
}
for(int i = newLen;i < oldLen + newLen;i++) {
jobject elementObj = env->GetObjectArrayElement(oldClassLoaderDexElements, i - newLen);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(newElementArray,i,elementObj);
}
env->SetObjectField(oldDexPathListObj, dexElementField,newElementArray);
DLOGD("mergeDexElements success");
}
0x4 总结
做这个壳确实花了不少的时间,其中走过的弯路只有自己知道,不过还好做出来了。dpt未经过大量测试,后续发现问题再慢慢解决。
到此这篇关于Android函数抽取壳的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android函数抽取壳内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

