Springboot项目实现将类从@ComponentScan中排除
目录
- 将类从@ComponentScan中排除
- 问题描述
- 方案一
- 方案二
- 方案三
- 方案四
- @ComponentScan 详解
将类从@ComponentScan中排除
问题描述
最近在学习SpringCloud的Ribbon,在使用
@RibbonClient(name = "SPRINGCLOUD-P-DEPT", configuration = RibbonConfig.class)
为服务指定负载均衡策略的时候,根据Ribbon官方文档介绍,自定义的Ribbon配置类不允许被Springboot的**@ComponentScan**注解扫描到,所以需要将自定义的配置类RibbonConfig从在Springboot自动注入的范围内排除
方案一
我们都知道,Springboot的**@SpringBootApplication**会自动扫描本类所在包下的所有类和子类,所以只需要将RibbonConfig定义在Springboot启动类所在包外面即可
方案二
通过在启动类中添加
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter( type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE, classes = RibbonConfig.class))
通过FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE来指定要排除的类
如果需要排除的类太多了这个就很麻烦
方案三
通过自定义注解实现
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter( type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = ScanIgnore.class))
与方案二不同的是,这里用的是FilterType.ANNOTATION
方案四
通过实现TypeFilter类来自定义过滤器
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
此处给出的就是**@SpringbootApplication中的实现方式,通过FilterType.CUSTOM**来根据自动一过滤器来排除bean
最后贴出枚举类FilterType:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
/**
* Enumeration of the type filters that may be used in conjunction with
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Mark Fisher
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 2.5
* @see ComponentScan
* @see ComponentScan#includeFilters()
* @see ComponentScan#excludeFilters()
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter
*/
public enum FilterType {
/**
* Filter candidates marked with a given annotation.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AnnotationTypeFilter
*/
ANNOTATION,
/**
* Filter candidates assignable to a given type.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AssignableTypeFilter
*/
ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
/**
* Filter candidates matching a given AspectJ type pattern expression.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.AspectJTypeFilter
*/
ASPECTJ,
/**
* Filter candidates matching a given regex pattern.
* @see org.springframework.core.type.filter.RegexPatternTypeFilter
*/
REGEX,
/** Filter candidates using a given custom
* {@link org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter} implementation.
*/
CUSTOM
}
@ComponentScan 详解
@ComponentScan 的作用就是根据定义的扫描路径,把符合扫描规则的类装配到spring容器中,注解定义如下。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> scopeResolver() default AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver.class;
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxy() default ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT;
String resourcePattern() default "**/*.class";
boolean useDefaultFilters() default true;
ComponentScan.Filter[] includeFilters() default {};
ComponentScan.Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};
boolean lazyInit() default false;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
public @interface Filter {
FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION;
@AliasFor("classes")
Class<?>[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
Class<?>[] classes() default {};
String[] pattern() default {};
}
}
basePackages与value: 用于指定包的路径,进行扫描basePackageClasses: 用于指定某个类的包的路径进行扫描nameGenerator: bean的名称的生成器useDefaultFilters: 是否开启对@Component,@Repository,@Service,@Controller的类进行检测includeFilters: 包含的过滤条件
FilterType.ANNOTATION:按照注解过滤
FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按照给定的类型
FilterType.ASPECTJ:使用ASPECTJ表达式
FilterType.REGEX:正则
FilterType.CUSTOM:自定义规则
excludeFilters: 排除的过滤条件,用法和includeFilters一样
我的工程结构如下,测试对controller和service的扫描,其中HelloController没有加@Controller等任何注解,就是一个普通类。

修改配置类如下:应用默认的过滤器,扫描service包:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring.service",
useDefaultFilters = true
)
public class MyConfig {
}
系统注入了两个service进去

改成如下所示:HelloController所在的包的类也被扫描了进去
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring.service",
useDefaultFilters = true,
basePackageClasses = HelloController.class
)
public class MyConfig {
}
系统中会注入下面就给类
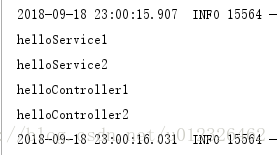
把默认的过滤器关掉,扫描带Controller注解的。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",
useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
}
)
public class MyConfig {
}

按照类的类型扫描,虽然HelloController没有加注解,但是被注入到了spring容器中
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",
useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {HelloController.class})
}
)
public class MyConfig {
}

自定义扫描过滤器
package com.xhx.spring.componentscan.config;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* xuhaixing
* 2018/9/18 23:07
**/
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
String className = metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();
if(className.contains("Controller")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
修改配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value = "com.xhx.spring",
useDefaultFilters = false,
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class})
}
)
public class MyConfig {
}
输出结果:

输出spring容器中的bean的测试类:只过滤输出了名字中含有hello的类。
package com.xhx.spring.componentscan;
import com.xhx.spring.componentscan.config.MyConfig;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class ComponentScanApplicationTests {
@Test
public void testLoads() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
List<String> hello = Arrays.stream(context.getBeanDefinitionNames()).collect(Collectors.toList());
hello.stream().filter(name->name.contains("hello")).peek(System.out::println).count();
}
}
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

