Babel自动生成Attribute文档实现详解
目录
- 1. 前言
- 2. 开发自动生成属性文档插件
- 2.1 生成Babel插件模板:
- 2.2 转换思路详解:
- 2.3 单元测试用例:
- 2.4 AST分析详解:
- 2.5 插件开发过程:
- 2.5.1 定义Comment、ApiTable类型对象:
- 2.5.2 插件主逻辑分析:
- 2.5.3 主逻辑实现:
- 2.5.4 注释解析函数:
- 2.5.5 Markdown表格拼装:
- 2.5.6生成结果展示~
- 3. 总结
1. 前言
利用Babel自动解析源码属性上的注释生成对应Markdown文档,这个场景的应用主要包括在组件库文档对组件属性的介绍中,这一篇就通过编写一个Babel插件来实现这个功能~
2. 开发自动生成属性文档插件
2.1 生成Babel插件模板:
- 2.1.1 创建
babel-plugin-auto-attr-doc文件夹; - 2.1.2 安装
npm i -g yo generator-babel-plugin-x; - 2.1.3 在新建目录下执行
yo babel-plugin-x:v7-ts;
生成的插件模板如下:
babel-plugin-auto-attr-doc ├─ lib │ └─ index.js ├─ src │ └─ index.ts ├─ __tests__ │ ├─ fixtures │ │ └─ example │ │ ├─ actual.ts │ │ └─ expected.ts │ └─ index.js ├─ package-lock.json ├─ package.json ├─ README.md └─ tsconfig.json
2.2 转换思路详解:
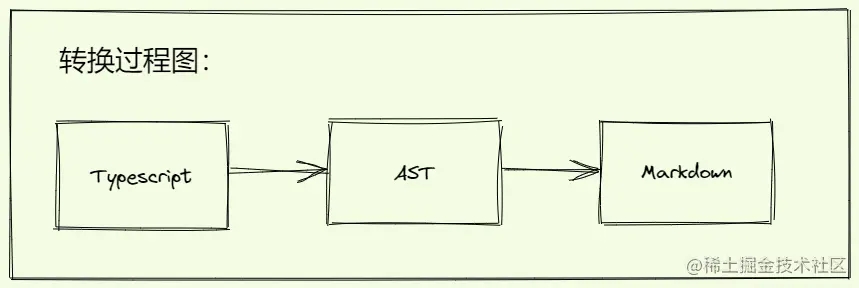
转换过程:利用Babel将Typescript脚本解析为AST,通过对AST结构分析抽离对应的注释部分,再拼接Markdown表格风格的语法;
源码要求:**我们应该将组件涉及到对外提供的属性统一到对应的types.ts文件管理,分别导出对应的type字段;
注释要求:**分别定义字段描述、类型、可选项、默认值4项,由于解析器关键词冲突原因,我们应该尽量避免;
/** * @cDescribe 类型 * @cType string * @cOptions * @cDefault */ export type IType = "primary" | "success" | "warning" | "danger" | "info"; /** * @cDescribe 图标组件 * @cType string * @cOptions * @cDefault */ export type IIcon = string; /** * @cDescribe 是否为朴素按钮 * @cType boolean * @cOptions * @cDefault false */ export type IPlain = boolean;
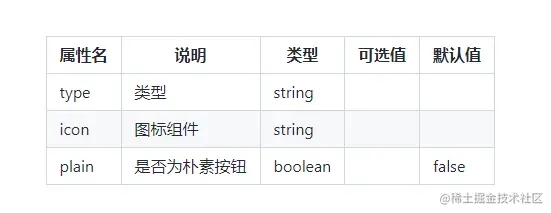
Markdown表格:**展示组件的属性、描述、类型、可选值和默认值这几项;
2.3 单元测试用例:
- 准备插件待解析源码文件
source-code.ts; - 准备实际生成MD后应该显示的内容文件
actual.md;
| 属性名 | 说明 | 类型 | 可选值 | 默认值 | | ------ | ---- | ---- | ----- | ----- | | type | 类型 | string | | | | icon | 图标组件 | string | | | | plain | 是否为朴素按钮 | boolean | | false |
- 调整单元测试文件读取:
it(`should ${caseName.split("-").join(" ")}`, () => {
const actualPath = path.join(fixtureDir, "source-code.ts");
// 对源码进行加载解析
transformFileSync(actualPath);
// 读取我们准备好的md文件
const actual = fs
.readFileSync(path.join(fixtureDir, "actual.md"))
.toString();
// 读取插件解析生成的md文件
const expected = fs
.readFileSync(path.join(fixtureDir, "api-doc.md"))
.toString();
// diff
const diff = diffChars(actual, expected);
diff.length > 1 && _print(diff);
expect(diff.length).toBe(1);
});
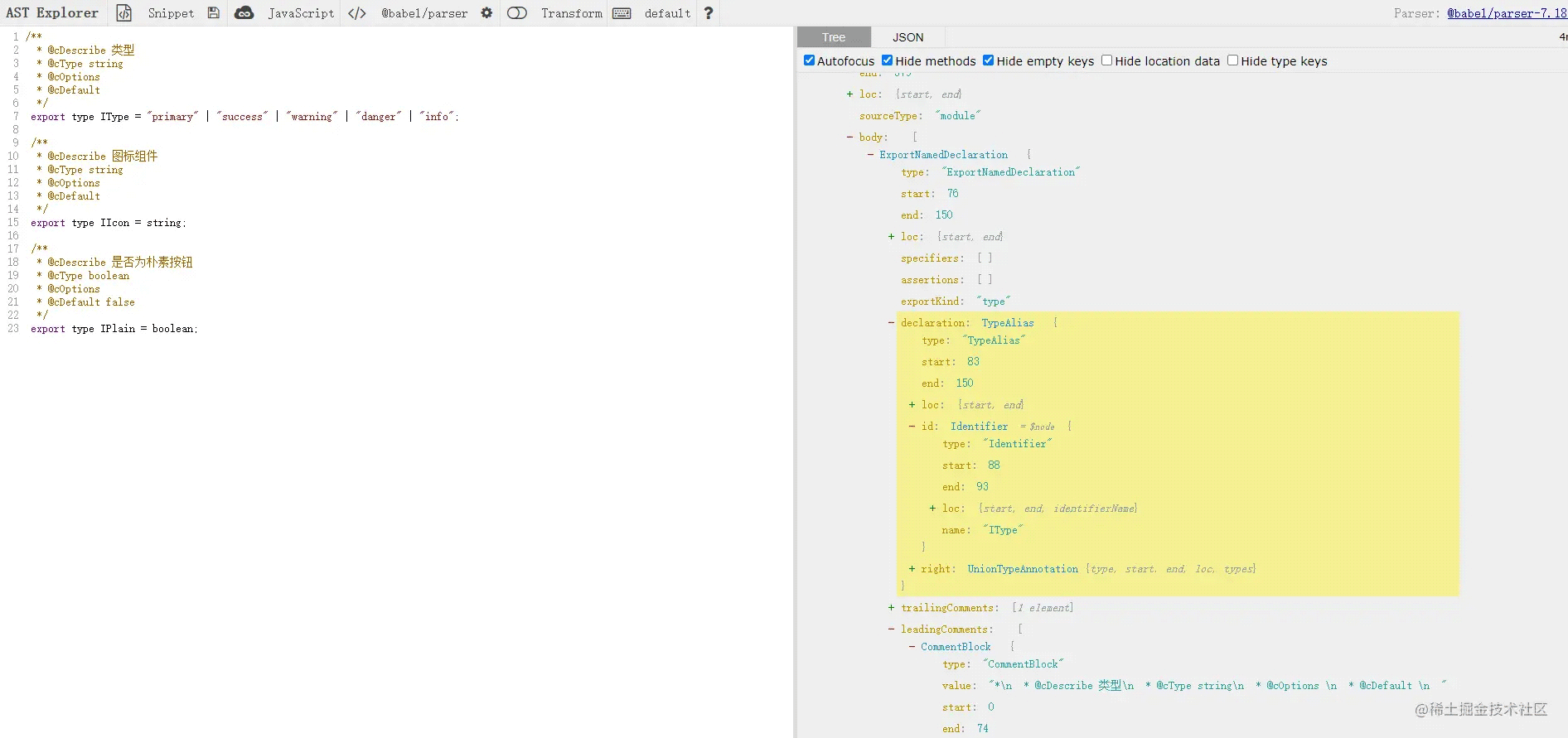
2.4 AST分析详解:
- 通过在AST explorer的源码分析,我们在Babel中可以通过遍历
ExportNamedDeclaration(命名导出声明); - 在
leadingComments数组中可以取出所有注释文本的集合,在Babel处理时我们需要依次处理每一块注释后增加标记来避免重复处理; - 在
(path.node.declaration as t.TypeAlias).id.name中取属性名称;
将注释文本通过doctrine模块解析为对象后和属性名合并对转换Markdown所需要的所有数据~
2.5 插件开发过程:
2.5.1 定义Comment、ApiTable类型对象:
type Comment =
| {
describe: string;
type: any;
options?: any;
default?: any;
}
| undefined;
type ApiTable = {
attributeName: any;
attributeDescribe: any;
attributeType: any;
attributeOptions: any;
attributeDefault: any;
};
2.5.2 插件主逻辑分析:
- pre:初始化存放apidoc容器,避免在存放时找不到容器;
- visitor:解析源码并获取组织MD内容数据暂存到apidoc中;
- post:取出所有的apidoc内容解析并输出到本地文件中;
export default declare(
(api: BabelAPI, options: Record<string, any>, dirname: string) => {
api.assertVersion(7);
return {
name: "auto-attr-doc",
pre(this: PluginPass, file: BabelFile) {
this.set("api-doc", []);
},
visitor: {
ExportNamedDeclaration(
path: NodePath<t.ExportNamedDeclaration>,
state: PluginPass
) {
const apidoc = state.get("api-doc");
// 处理 path.node.leadingComments 中未处理的数据后塞到apidoc中
state.set("api-doc", apidoc);
},
},
post(this: PluginPass, file: BabelFile) {
const apidoc = this.get("api-doc");
const output = generateMD(apidoc);
const root = path.parse(file.opts.filename || "./").dir;
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(root, "api-doc.md"), output, {
encoding: "utf-8",
});
},
} as PluginObj<PluginPass>;
}
);
2.5.3 主逻辑实现:
leadingComments数组会在依次访问ExportNamedDeclaration时不停增加,我们在处理掉当前索引的对象后增加一个处理过的标记skip,下次循环直接跳过;
通过parseComment函数解析后的对象可以通过tags数组获取到所有的注释项目,通过对应的title得到对应description内容;
在往apidoc存放数据时需要处理属性名称符合一定的规则,并将apidoc对象存放到原容器中;
{
ExportNamedDeclaration(
path: NodePath<t.ExportNamedDeclaration>,
state: PluginPass
) {
const apidoc = state.get("api-doc");
let _comment: Comment = undefined;
path.node.leadingComments?.forEach((comment) => {
if (!Reflect.has(comment, "skip")) {
const tags = parseComment(comment.value)?.tags;
_comment = {
describe:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cDescribe")?.description || "",
type: tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cType")?.description || "",
options:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cOptions")?.description || "",
default:
tags?.find((v) => v.title === "cDefault")?.description || "",
};
Reflect.set(comment, "skip", true);
}
});
apidoc.push({
attributeName: (path.node.declaration as t.TypeAlias).id.name.substr(1).toLocaleLowerCase(),
attributeDescribe: _comment!.describe,
attributeType: _comment!.type,
attributeOptions: _comment!.options,
attributeDefault: _comment!.default,
} as ApiTable);
state.set("api-doc", apidoc);
},
}
2.5.4 注释解析函数:
const parseComment = (comment: string) => {
if (!comment) {
return;
}
return doctrine.parse(comment, {
unwrap: true,
});
};
2.5.5 Markdown表格拼装:
const generateMD = (apidoc: Array<ApiTable>) => {
let raw = `| 属性名 | 说明 | 类型 | 可选值 | 默认值 |\n| ------ | ---- | ---- | ----- | ----- |\n`;
apidoc.forEach((item) => {
raw += `| ${item.attributeName} | ${item.attributeDescribe} | ${item.attributeType} | ${item.attributeOptions} | ${item.attributeDefault} |\n`;
});
return raw;
};
2.5.6生成结果展示~
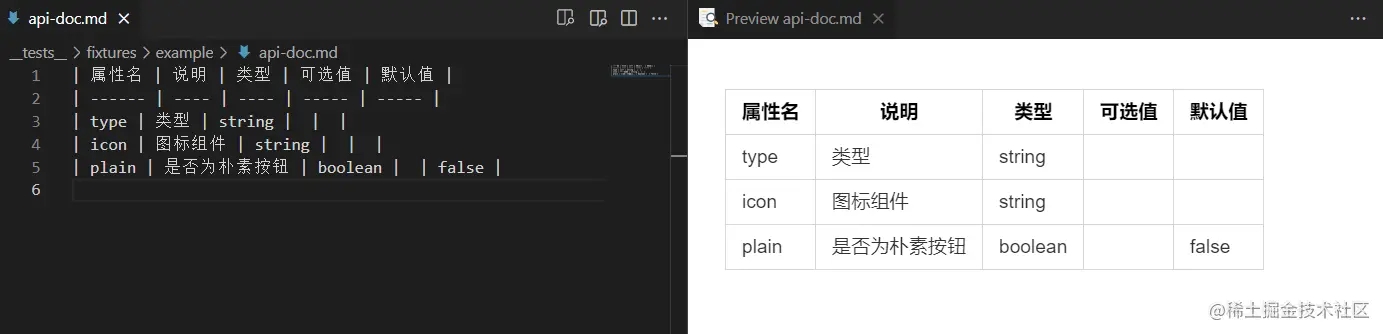
3. 总结
插件生成目前基本功能完成,注释解析可以通过Babel的插件选项来定义作为一个扩展方向,MD文件的生成可以通过对应工具转换,更多的输出文件类型也可以作为扩展方向,欢迎喜欢玩转Babel的小伙伴一起交流交流~
已推送至GitHub https://github.com/OSpoon/awesome-examples
以上就是Babel自动生成Attribute文档实现详解的详细内容,更多关于Babel生成Attribute文档的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

