SpringBoot 错误处理机制与自定义错误处理实现详解
【1】SpringBoot的默认错误处理
① 浏览器访问

请求头如下:

② 使用“PostMan”访问
{
"timestamp": 1529479254647,
"status": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "No message available",
"path": "/aaa1"
}
请求头如下:

总结:如果是浏览器访问,则SpringBoot默认返回错误页面;如果是其他客户端访问,则默认返回JSON数据。
【2】默认错误处理原理
SpringBoot默认配置了许多xxxAutoConfiguration,这里我们找ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration。
其注册部分组件如下:
① DefaultErrorAttributes
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
跟踪其源码如下:
public class DefaultErrorAttributes
implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered {
private static final String ERROR_ATTRIBUTE = DefaultErrorAttributes.class.getName()
+ ".ERROR";
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
storeErrorAttributes(request, ex);
return null;
}
private void storeErrorAttributes(HttpServletRequest request, Exception ex) {
request.setAttribute(ERROR_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes,
boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
return errorAttributes;
}
private void addStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes,
RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
Integer status = getAttribute(requestAttributes,
"javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (status == null) {
errorAttributes.put("status", 999);
errorAttributes.put("error", "None");
return;
}
errorAttributes.put("status", status);
try {
errorAttributes.put("error", HttpStatus.valueOf(status).getReasonPhrase());
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Unable to obtain a reason
errorAttributes.put("error", "Http Status " + status);
}
}
private void addErrorDetails(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes,
RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Throwable error = getError(requestAttributes);
if (error != null) {
while (error instanceof ServletException && error.getCause() != null) {
error = ((ServletException) error).getCause();
}
errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName());
addErrorMessage(errorAttributes, error);
if (includeStackTrace) {
addStackTrace(errorAttributes, error);
}
}
Object message = getAttribute(requestAttributes, "javax.servlet.error.message");
if ((!StringUtils.isEmpty(message) || errorAttributes.get("message") == null)
&& !(error instanceof BindingResult)) {
errorAttributes.put("message",
StringUtils.isEmpty(message) ? "No message available" : message);
}
}
private void addErrorMessage(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, Throwable error) {
BindingResult result = extractBindingResult(error);
if (result == null) {
errorAttributes.put("message", error.getMessage());
return;
}
if (result.getErrorCount() > 0) {
errorAttributes.put("errors", result.getAllErrors());
errorAttributes.put("message",
"Validation failed for object='" + result.getObjectName()
+ "'. Error count: " + result.getErrorCount());
}
else {
errorAttributes.put("message", "No errors");
}
}
private BindingResult extractBindingResult(Throwable error) {
if (error instanceof BindingResult) {
return (BindingResult) error;
}
if (error instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
return ((MethodArgumentNotValidException) error).getBindingResult();
}
return null;
}
private void addStackTrace(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes, Throwable error) {
StringWriter stackTrace = new StringWriter();
error.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(stackTrace));
stackTrace.flush();
errorAttributes.put("trace", stackTrace.toString());
}
private void addPath(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes,
RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
String path = getAttribute(requestAttributes, "javax.servlet.error.request_uri");
if (path != null) {
errorAttributes.put("path", path);
}
}
@Override
public Throwable getError(RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
Throwable exception = getAttribute(requestAttributes, ERROR_ATTRIBUTE);
if (exception == null) {
exception = getAttribute(requestAttributes, "javax.servlet.error.exception");
}
return exception;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> T getAttribute(RequestAttributes requestAttributes, String name) {
return (T) requestAttributes.getAttribute(name, RequestAttributes.SCOPE_REQUEST);
}
}
即,填充错误数据!
② BasicErrorController
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
this.errorViewResolvers);
}
跟踪其源码:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
//产生html类型的数据;浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理
@RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面;包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView == null ? new ModelAndView("error", model) : modelAndView);
}
//产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理;
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>>(body, status);
}
//...
}
其中 resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);方法跟踪如下:
public abstract class AbstractErrorController implements ErrorController {
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
//拿到所有的错误视图解析器
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
//...
}
③ ErrorPageCustomizer
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer() {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties);
}
跟踪其源码:
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.properties.getServletPrefix()
+ this.properties.getError().getPath());
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);
}
//getPath()->go on
/**
* Path of the error controller.
*/
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
即,系统出现错误以后来到error请求进行处理(web.xml注册的错误页面规则)。
④ DefaultErrorViewResolver
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext,
this.resourceProperties);
}
跟踪其源码:
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered {
private static final Map<Series, String> SERIES_VIEWS;
//错误状态码
static {
Map<Series, String> views = new HashMap<Series, String>();
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
//...
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
// 这里如果没有拿到精确状态码(如404)的视图,则尝试拿4XX(或5XX)的视图
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面? error/404||error/4xx
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
//模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址就用模板引擎解析
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders
.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//模板引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404.html
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//从静态资源文件夹下面找错误页面
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}
总结如下:
一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误,ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则),就会来到/error请求,然后被BasicErrorController处理返回ModelAndView或者JSON。
【3】定制错误响应
① 定制错误响应页面
1)有模板引擎的情况下
error/状态码–将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的error文件夹下,发生此状态码的错误就会来到 对应的页面。
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html)。
如下图所示:

页面能获取的信息;
timestamp:时间戳
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
2)没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找。
3)以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面。
WebMVCAutoConfiguration源码如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.error.whitelabel", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@Conditional(ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class)
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final SpelView defaultErrorView = new SpelView(
"<html><body><h1>Whitelabel Error Page</h1>"
+ "<p>This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.</p>"
+ "<div id='created'>${timestamp}</div>"
+ "<div>There was an unexpected error (type=${error}, status=${status}).</div>"
+ "<div>${message}</div></body></html>");
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}
// If the user adds @EnableWebMvc then the bean name view resolver from
// WebMvcAutoConfiguration disappears, so add it back in to avoid disappointment.
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(BeanNameViewResolver.class)
public BeanNameViewResolver beanNameViewResolver() {
BeanNameViewResolver resolver = new BeanNameViewResolver();
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10);
return resolver;
}
}
② 定制错误响应数据
第一种,使用SpringMVC的异常处理器
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
//浏览器客户端返回的都是json
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","user.notexist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
这样无论浏览器还是PostMan返回的都是JSON!
第二种,转发到/error请求进行自适应效果处理
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx
/**
* Integer statusCode = (Integer) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
*/
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user.notexist");
map.put("message","用户出错啦");
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
}
但是此时没有将自定义 code message传过去!
第三种,注册MyErrorAttributes继承自DefaultErrorAttributes(推荐)
从第【2】部分(默认错误处理原理)中知道错误数据都是通过DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes()方法获取,如下所示:
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes,
boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
return errorAttributes;
}
我们可以编写一个MyErrorAttributes继承自DefaultErrorAttributes重写其getErrorAttributes方法将我们的错误数据添加进去。
示例如下:
//给容器中加入我们自己定义的ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
//返回值的map就是页面和json能获取的所有字段
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) {
//DefaultErrorAttributes的错误数据
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company","SpringBoot");
//我们的异常处理器携带的数据
Map<String,Object> ext = (Map<String, Object>) requestAttributes.getAttribute("ext", 0);
map.put("ext",ext);
return map;
}
}
异常处理器修改如下:
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx
/**
* Integer statusCode = (Integer) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
*/
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user.notexist");
map.put("message","用户出错啦");
//将自定义错误数据放入request中
request.setAttribute("ext",map);
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
}
5xx.html页面代码如下:
//...
<main role="main" class="col-md-9 ml-sm-auto col-lg-10 pt-3 px-4">
<h1>status:[[${status}]]</h1>
<h2>timestamp:[[${timestamp}]]</h2>
<h2>exception:[[${exception}]]</h2>
<h2>message:[[${message}]]</h2>
<h2>ext:[[${ext.code}]]</h2>
<h2>ext:[[${ext.message}]]</h2>
</main>
//...
浏览器测试效果如下:
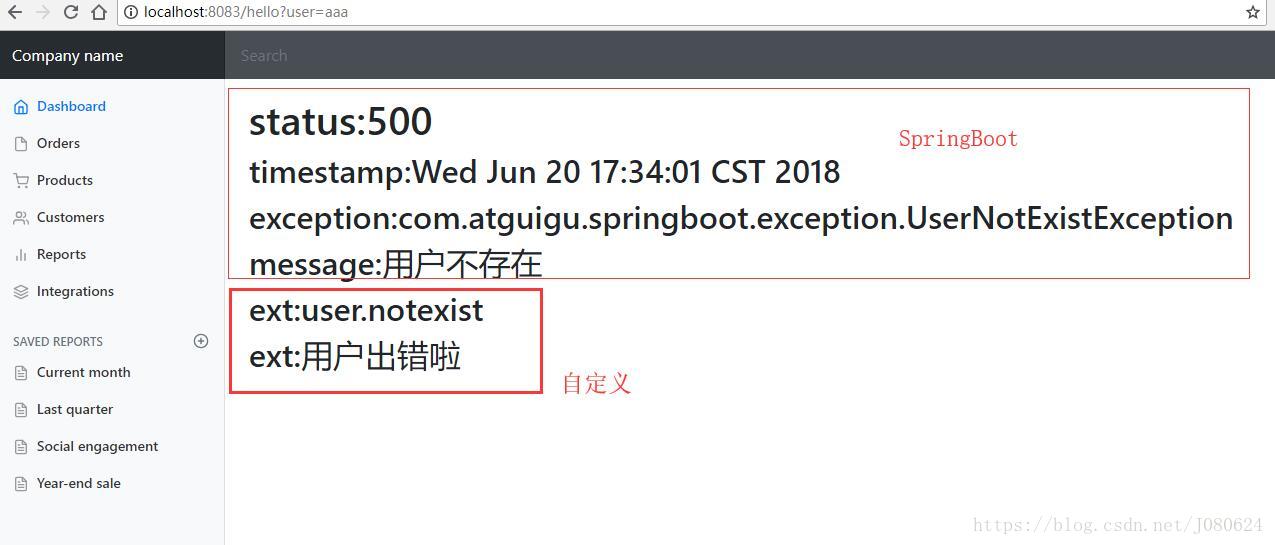
Postman测试效果如下:

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

