浅谈JSP是如何编译成servlet并提供服务的
目录
- 概述
- 源码分析
概述
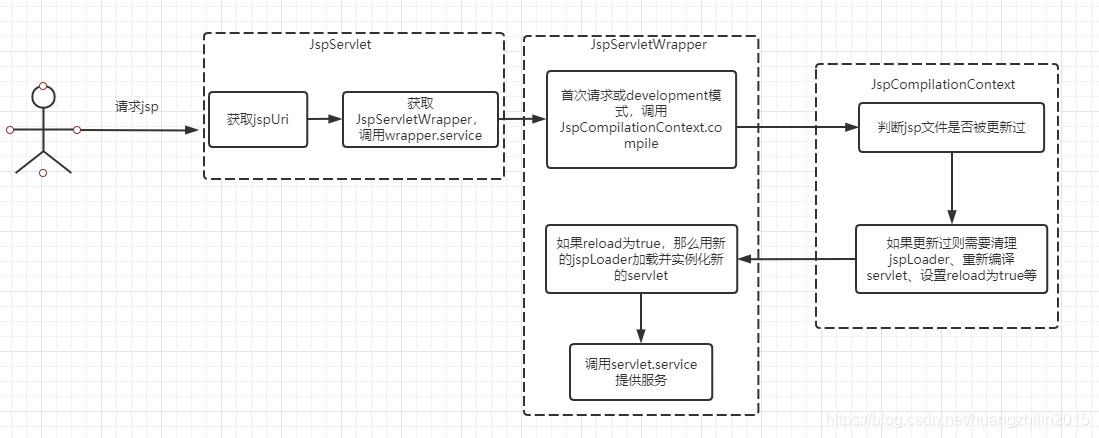
服务端对外提供JSP请求服务的是JspServlet,继承自HttpServlet。核心服务入口在service方法,大体流程如下:
- 首先获取请求的jspUri,如果客户端发起请求:https://xxx.xx.com/jsp/test.jsp,那么获取到的jspUri为:/jsp/test.jsp
- 然后查看缓存(Map结构)中是否包含该jspUri的JspServletWrapper,如果没有就需要创建一个JspServletWrapper并且缓存起来,并调用JspServletWrapper的service方法
- 如果为development模式,或者首次请求,那么就需要执行JspCompilationContext.compile() 方法
- 在JspCompilationContext.compile方法中,会根据jsp文件的lastModified判断文件是否已经被更新(out dated),如果被更新过了,就需要删除之前生成的相关文件,然后将jspLoader置空(后面需要加载的时候如果jspLoader为空,就会创建一个新的jspLoader),调用Compiler.compile方法生成servlet,设置reload为true(默认为true),后面会根据reload参数判断是否需要重新加载该servlet
- 调用JspServletWrapper.getServlet方法获取最终提供服务的servlet,这个过程会根据reload参数看是否需要重载servlet,如果需要重载,那么就会获取jspLoader实例化一个新的servlet(如果前面发现jsp文件过期,那么此时获取的jspLoader为空,则会创建一个新的jspLoader),并且设置reload为false
- 调用servlet的service方法提供服务,如果servlet实现了SingleThreadModel接口,那么会用synchronized做同步控制
源码分析
首先看JspServlet的核心逻辑,主要是获取jspUri和获取JspServletWrapper,分别是入口service方法和serviceJspFile方法,代码如下(部分):
/**
* 获取jspUri,然后调用serviceJspFile方法
*/
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
String jspUri = this.jspFile;
String pathInfo;
if (jspUri == null) {
pathInfo = (String)request.getAttribute(Constants.JSP_FILE);
if (pathInfo != null) {
jspUri = pathInfo;
request.removeAttribute(Constants.JSP_FILE);
}
}
if (jspUri == null) {
jspUri = (String)request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.include.servlet_path");
if (jspUri != null) {
pathInfo = (String)request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.include.path_info");
if (pathInfo != null) {
jspUri = jspUri + pathInfo;
}
} else {
jspUri = request.getServletPath();
pathInfo = request.getPathInfo();
if (pathInfo != null) {
jspUri = jspUri + pathInfo;
}
}
}
boolean precompile = this.preCompile(request);
this.serviceJspFile(request, response, jspUri, precompile);
}
/**
* 主要获取JspServletWrapper,然后调用JspServletWrapper.service方法
*/
private void serviceJspFile(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, String jspUri, boolean precompile) throws ServletException, IOException {
JspServletWrapper wrapper = this.rctxt.getWrapper(jspUri);
if (wrapper == null) {
synchronized(this) {
wrapper = this.rctxt.getWrapper(jspUri);
if (wrapper == null) {
if (null == this.context.getResource(jspUri)) {
this.handleMissingResource(request, response, jspUri);
return;
}
wrapper = new JspServletWrapper(this.config, this.options, jspUri, this.rctxt);
this.rctxt.addWrapper(jspUri, wrapper);
}
}
}
try {
//核心服务方法
wrapper.service(request, response, precompile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException var8) {
this.handleMissingResource(request, response, jspUri);
}
}
然后进入JspServletWrapper.service方法(部分代码):
//注意这个reload是volatile修饰的
private volatile boolean reload = true;
public void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, boolean precompile) throws ServletException, IOException, FileNotFoundException {
Servlet servlet;
try {
if (this.ctxt.isRemoved()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.jspUri);
}
//判断development模式和firstTime(首次请求)
if (!this.options.getDevelopment() && !this.firstTime) {
if (this.compileException != null) {
throw this.compileException;
}
} else {
synchronized (this) {
this.firstTime = false;
//调用JspCompilationContext.compile方法
this.ctxt.compile();
}
}
//获取最终提供服务的servlet
servlet = this.getServlet();
if (precompile) {
return;
}
}
try {
//根据是否实现SingleThreadModel决定是否需要做同步控制
if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) {
synchronized (this) {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
}
}
这里主要看JspCompilationContext.complie方法:
public void compile() throws JasperException, FileNotFoundException {
this.createCompiler();
if (this.jspCompiler.isOutDated()) {
if (this.isRemoved()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(this.jspUri);
}
try {
//清楚文件数据
this.jspCompiler.removeGeneratedFiles();
//置空jspLoader,现在置null,后面就会创建一个新的JspLoader
this.jspLoader = null;
//根据jsp生成servlet的逻辑,实现主要有AntCompiler和JDTCompiler,默认JDTCompiler
this.jspCompiler.compile();
//设置reload为true,后面根据reload参数判断是否需要重新加载
this.jsw.setReload(true);
this.jsw.setCompilationException((JasperException) null);
}
}
}
要注意对于isOutDated方法的判断,并不是简单地每次请求都检查jsp文件是否更新,而是有一个间隔时间,如果此次检查更新的时间在上一次检查更新+间隔时间之内,也就是没有超过间隔时间,那么就不会去检查jsp文件的更新。这就是我们说的jsp热更新延时生效,isOutDated是Compiler的方法,如下(部分代码):
public boolean isOutDated(boolean checkClass) {
if (this.jsw != null && this.ctxt.getOptions().getModificationTestInterval() > 0) {
//getModificationTestInterval就是检查最短间隔时间,单位为秒
if (this.jsw.getLastModificationTest() + (long)(this.ctxt.getOptions().getModificationTestInterval() * 1000) > System.currentTimeMillis()) {
return false;
}
this.jsw.setLastModificationTest(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
Long jspRealLastModified = this.ctxt.getLastModified(this.ctxt.getJspFile());
if (jspRealLastModified < 0L) {
return true;
} else {
long targetLastModified = 0L;
File targetFile;
if (checkClass) {
targetFile = new File(this.ctxt.getClassFileName());
} else {
targetFile = new File(this.ctxt.getServletJavaFileName());
}
if (!targetFile.exists()) {
return true;
} else {
targetLastModified = targetFile.lastModified();
if (checkClass && this.jsw != null) {
this.jsw.setServletClassLastModifiedTime(targetLastModified);
}
if (targetLastModified != jspRealLastModified) {
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug("Compiler: outdated: " + targetFile + " " + targetLastModified);
}
return true;
} else if (this.jsw == null) {
return false;
}
}
}
另外,这里还涉及到JSP的编译工作,编译工作主要由org.apache.jasper.compiler.Compiler编译器负责,Compiler是一个抽象类,apache-jsp中提供了两种实现:AntCompiler和JDTCompiler,默认使用的编译器为JDTCompiler。
最后回到JspServletWrapper.getServlet方法:
private volatile boolean reload = true;
public Servlet getServlet() throws ServletException {
//reload是被volatile修饰的一个boolean变量
//这里进行双重检测
if (this.reload) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.reload) {
//需要重载
this.destroy();
Servlet servlet;
try {
InstanceManager instanceManager = InstanceManagerFactory.getInstanceManager(this.config);
//创建一个新的serlvet实例对象,注意这里的getJspLoader方法
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(this.ctxt.getFQCN(), this.ctxt.getJspLoader());
} catch (Exception var6) {
Throwable t = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(var6);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
throw new JasperException(t);
}
servlet.init(this.config);
if (!this.firstTime) {
this.ctxt.getRuntimeContext().incrementJspReloadCount();
}
this.theServlet = servlet;
this.reload = false;
}
}
}
return this.theServlet;
}
可以看到,方法中使用了双重检测机制判断是否需要重载,reload参数由volatile修饰保证可见性。在创建新的servlet实例的时候,classLoader是通过JspCompilationContext.getJspLoader方法获取的,看看这个方法的逻辑:
public ClassLoader getJspLoader() {
if (this.jspLoader == null) {
this.jspLoader = new JasperLoader(new URL[]{this.baseUrl}, this.getClassLoader(), this.rctxt.getPermissionCollection());
}
return this.jspLoader;
}
在前面JspCompilationContext.complie的逻辑中,如果检测到jsp文件被更新过(过期),那么jspLoader会被设置为null,此时就会创建一个新的jspLoader(JasperLoader),然后使用新的loader加载新的servlet,以完成jsp的热更新,老的classloader在之后会被GC直接回收。
到此这篇关于浅谈JSP是如何编译成servlet并提供服务的的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JSP编译成servlet内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

