C++回溯算法广度优先搜索举例分析
目录
- 迷宫问题
- N叉树的层序遍历
- 腐烂的橘子
- 单词接龙
- 打开转盘锁
迷宫问题
假设有一个迷宫,里面有障碍物,迷宫用二维矩阵表示,标记为0的地方表示可以通过,标记为1的地方表示障碍物,不能通过。现在给一个迷宫出口,让你判断是否可以从入口进来之后,走出迷宫,每次可以向任意方向走。

代码实现:
namespace BFS {
struct pair {
int _x;
int _y;
pair(int x, int y)
:_x(x)
, _y(y)
{}
};
bool mapBFS(vector<vector<int>> mat, int sx, int sy, int ex, int ey)
{
int row = mat.size();
int col = mat[0].size();
queue<pair> q;
q.push(pair(sx, sy));
vector<vector<int>> book(row, vector<int>(col, 0));
book[sx][sy] = 1;
int nextP[4][2] = { { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 } };
while (!q.empty())
{
pair curPos = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curPos._x == ex && curPos._y == ey)
return true;
//一个点的所有可能延伸的点
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int curX = curPos._x + nextP[i][0];
int curY = curPos._y + nextP[i][1];
if (curX < 0 || curX >= row || curY < 0 || curY >= col)
continue;
//没有走过且不是障碍物
if (mat[curX][curY] == 0 && book[curX][curY] == 0)
{
book[curX][curY] = 1;
//保存新的位置
q.push(pair(curX, curY));
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<vector<int>> mat{ {0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0} };
int sx, sy, ex, ey;
cin >> sx >> sy >> ex >> ey;
cout << BFS::mapBFS(mat, sx, sy, ex, ey);
return 0;
}
N叉树的层序遍历
问题描述:
给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。 树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔(参见示例)。
代码实现:
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(!root)
return result;
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
//获取队列中的元素个数
int sz = q.size();
vector<int> rowV;
while(sz--)
{
//保存当前元素在同一行
Node* node = q.front();
q.pop();
rowV.push_back(node->val);
//当前元素的孩子结点入队
for(auto e : node->children)
{
q.push(e);
}
}
result.push_back(rowV);
}
return result;
}
};
腐烂的橘子
问题描述:
在给定的网格中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
值 0 代表空单元格;
值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,任何与腐烂的橘子(在 4 个正方向上)相邻的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1。

本题可以先找到所有的腐烂橘子入队,用第一批带出新一批腐烂的橘子。 每一批橘子都会在一分钟之内腐烂,所以此题可以转化为求BFS执行的大循环的次数。这里的step的更新需要有一个标记,只有新的腐烂的橘子加入,step才++ 最后BFS执行完,说明所有可以被腐烂的都完成了,再去遍历grid,如果还有值为1的,说明没有办法全部腐烂,返回-1,如果没有,则返回step
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int step = 0;
int row = grid.size();
int col = grid[0].size();
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
//把所有腐烂的橘子入队
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 2)
q.push(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
static int nextP[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0 ,1}};
while(!q.empty()){
int sz = q.size();
bool flag = false;
while(sz--){
pair curPos = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int curX = curPos.first + nextP[i][0];
int curY = curPos.second + nextP[i][1];
if(curX < 0 || curX >= row || curY < 0 || curY >= col)
continue;
if(grid[curX][curY] == 1){
flag = true;
grid[curX][curY] = 2;
q.push(make_pair(curX, curY));
}
}
}
if(flag)
++step;
}
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1)
return -1;
}
}
return step;
}
};
单词接龙
问题描述:
字典 wordList 中从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
序列中第一个单词是 beginWord 。
序列中最后一个单词是 endWord 。
每次转换只能改变一个字母。
转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典 wordList 中的单词。
给你两个单词 beginWord 和 endWord 和一个字典 wordList ,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 中的 单词数目 。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
示例 1:
输入:beginWord = “hit”, endWord = “cog”, wordList = [“hot”,“dot”,“dog”,“lot”,“log”,“cog”]
输出:5
解释:一个最短转换序列是 “hit” -> “hot” -> “dot” -> “dog” -> “cog”, 返回它的长度 5。
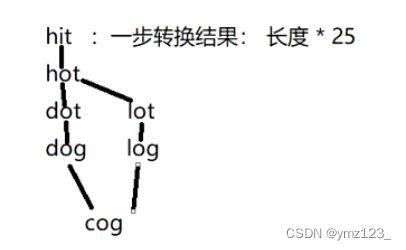
1.通过BFS,首先用beginWord带出转换一个字符之后所有可能的结果
2.每一步都要把队列中上一步添加的所有单词转换一遍,最短的转换肯定在这些单词中,所有这些词的转换只能算一次转换,因为都是上一步转换出来的,这里对于每个单词的每个位置都可以用26个字母进行转换,所以一个单词一次转换的可能有:单词的长度*25
3.把转换成功的新词入队,进行下一步的转换
4.最后整个转换的长度就和BFS执行的次数相同
需要判断单词有没有被搜索过,是一个查询的过程,可以用哈希表
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
int step = 1;
unordered_set<string> book;
unordered_set<string> dict;
book.insert(beginWord);
for(string& ch : wordList)
dict.insert(ch);
queue<string> q;
q.push(beginWord);
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
while(size--){
string curStr = q.front();
q.pop();
if(curStr == endWord)
return step;
for(int i = 0; i < curStr.size(); i++){
string str1 = curStr;
for(char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ++ch){
str1[i] = ch;
//判断新的单词是否在词典中,且没被搜索过
if(dict.find(str1) != dict.end()
&& book.find(str1) == book.end()){
q.push(str1);
book.insert(str1);
}
}
}
}
++step;
}
return 0;
}
};
打开转盘锁
问题描述:
你有一个带有四个圆形拨轮的转盘锁。每个拨轮都有10个数字: ‘0', ‘1', ‘2', ‘3', ‘4', ‘5', ‘6', ‘7', ‘8', ‘9' 。每个拨轮可以自由旋转:例如把 ‘9' 变为 ‘0',‘0' 变为 ‘9' 。每次旋转都只能旋转一个拨轮的一位数字。
锁的初始数字为 ‘0000' ,一个代表四个拨轮的数字的字符串。
列表 deadends 包含了一组死亡数字,一旦拨轮的数字和列表里的任何一个元素相同,这个锁将会被永久锁定,无法再被旋转。
字符串 target 代表可以解锁的数字,你需要给出解锁需要的最小旋转次数,如果无论如何不能解锁,返回 -1 。
深度优先不适合此题,递归深度太大,会导致栈溢出。
本题的密码为4位密码,每位密码可以通过拨动一次进行改变,注意这里的数的回环以及拨动的方向拨动方向:向前,向后。
回环:如果当前是9,0时,向前,向后拨动需要变成最小最大,而不是简单的自加自减。
0000一步旋转后的结果有:
0001 0009 0010 0090 0100 0900 1000 9000
代码实现:
class Solution {
public:
int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) {
unordered_set<string> deaddict(deadends.begin(), deadends.end());
//如果0000在死亡数字中,则永远也到不了
if(deaddict.find("0000") != deaddict.end())
return -1;
queue<string> q;
q.push("0000");
//添加标记,已经搜索过的字符不再搜索
unordered_set<string> book;
book.insert("0000");
int step = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int size = q.size();
while(size--){
string curStr = q.front();
q.pop();
if(curStr == target)
return step;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
string s1 = curStr;
string s2 = curStr;
//向前或向后旋转
s1[i] = s1[i] =='0' ? '9' : --s1[i];
s2[i] = s2[i] =='9' ? '0' : ++s2[i];
if(deaddict.find(s1) == deaddict.end()
&& book.find(s1) == book.end()){
q.push(s1);
book.insert(s1);
}
if(deaddict.find(s2) == deaddict.end()
&& book.find(s2) == book.end()){
q.push(s2);
book.insert(s2);
}
}
}
++step;
}
return -1;
}
};
到此这篇关于C++回溯算法广度优先搜索举例分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ 回溯算法 内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

