elasticsearch索引index之engine读写控制结构实现
目录
- engine的实现结构
- Engine类的方法:
- 如index方法的实现:
- 总结
engine的实现结构
elasticsearch对于索引中的数据操作如读写get等接口都封装在engine中,同时engine还封装了索引的读写控制,如流量、错误处理等。engine是离lucene最近的一部分。
engine的实现结构如下所示:
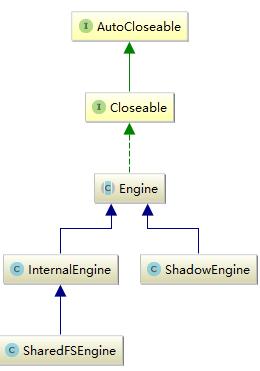
engine接口有三个实现类,主要逻辑都在InternalEngine中。
ShadowEngine之实现了engine接口的部分读方法,主要用于对于索引的读操作。
shardFSEngine在InternalEngine的基础上实现了recovery方法,它的功能跟InternalEngine基本相同只是它的recovery过程有区别,不会对Translog和index进行快照存储。
Engine类定义了一些index操作的主要方法和内部类,方法如create,index等。内部类如index,delete等。这些方法的实现是在子类中,这些方法的参数是这些内部类。
Engine类的方法:
public abstract void create(Create create) throws EngineException;
public abstract void index(Index index) throws EngineException;
public abstract void delete(Delete delete) throws EngineException;
public abstract void delete(DeleteByQuery delete) throws EngineException;
这些抽象方法都在子类中实现,它们的参数都是一类,这些都是Engine的内部类,这些内部类类似于实体类,没有相关逻辑只是由很多filed及get方法构成。如Create和Index都继承自IndexOperation,它们所有信息都存储到IndexOperation的相关Field中,IndexOperation如下所示:
public static abstract class IndexingOperation implements Operation {
private final DocumentMapper docMapper;
private final Term uid;
private final ParsedDocument doc;
private long version;
private final VersionType versionType;
private final Origin origin;
private final boolean canHaveDuplicates;
private final long startTime;
private long endTime;
………………
}
无论是Index还是Create,相关数据和配置都在doc中,根据doc和docMapper就能够获取本次操作的所有信息,另外的一些字段如version,uid都是在类初始化时构建。这样传给实际方法的是一个class,在方法内部根据需求获取到相应的数据
如index方法的实现:
private void innerIndex(Index index) throws IOException {
synchronized (dirtyLock(index.uid())) {
final long currentVersion;
VersionValue versionValue = versionMap.getUnderLock(index.uid().bytes());
if (versionValue == null) {
currentVersion = loadCurrentVersionFromIndex(index.uid());
} else {
if (engineConfig.isEnableGcDeletes() && versionValue.delete() && (engineConfig.getThreadPool().estimatedTimeInMillis() - versionValue.time()) > engineConfig.getGcDeletesInMillis()) {
currentVersion = Versions.NOT_FOUND; // deleted, and GC
} else {
currentVersion = versionValue.version();
}
}
long updatedVersion;
long expectedVersion = index.version();
if (index.versionType().isVersionConflictForWrites(currentVersion, expectedVersion)) {
if (index.origin() == Operation.Origin.RECOVERY) {
return;
} else {
throw new VersionConflictEngineException(shardId, index.type(), index.id(), currentVersion, expectedVersion);
}
}
updatedVersion = index.versionType().updateVersion(currentVersion, expectedVersion);
index.updateVersion(updatedVersion);
if (currentVersion == Versions.NOT_FOUND) {
// document does not exists, we can optimize for create
index.created(true);
if (index.docs().size() > 1) {
indexWriter.addDocuments(index.docs(), index.analyzer());
} else {
indexWriter.addDocument(index.docs().get(0), index.analyzer());
}
} else {
if (versionValue != null) {
index.created(versionValue.delete()); // we have a delete which is not GC'ed...
}
if (index.docs().size() > 1) {
indexWriter.updateDocuments(index.uid(), index.docs(), index.analyzer());//获取IndexOperation中doc中字段更新索引
} else {
indexWriter.updateDocument(index.uid(), index.docs().get(0), index.analyzer());
}
}
Translog.Location translogLocation = translog.add(new Translog.Index(index));//写translog
versionMap.putUnderLock(index.uid().bytes(), new VersionValue(updatedVersion, translogLocation));
indexingService.postIndexUnderLock(index);
}
}
这就是Engine中create、index这些方法的实现方式。后面分析索引过程中会有更加详细说明。Engine中还有获取索引状态(元数据)及索引操作的方法如merge。这些方法也是在子类中调用lucene的相关接口,跟create,index,get很类似。因为没有深入Engine的方法实现,因此这里的分析比较简单,后面的分析会涉及这里面很多方法。
总结
这里只是从结构上对indexEngine进行了简单说明,它里面的方法是es对lucene索引操作方法的封装,只是增加了一下处理方面的逻辑如写translog,异常处理等。它的操作对象是shard,es所有对shard的写操作都是通过Engine来实现,后面的分析会有所体现。
以上就是elasticsearch索引index之engine读写控制结构实现的详细内容,更多关于elasticsearch索引index engine读写控制的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

