vue-cli3 项目从搭建优化到docker部署的方法
1. 创建一个vue项目
相信大部分人都已经知道怎么创建项目的,可以跳过这一节,看下一节。
1.1 安装@vue/cli
# 全局安装 vue-cli脚手架 npm install -g @vue/cli
等待安装完成后开始下一步
1.2 初始化项目
vue create vue-cli3-project
(1)选择一个预设
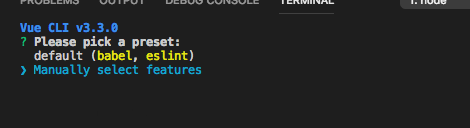
可以选择默认预设,默认预设包含了 babel , eslint
我们选择更多功能 Manually select features
回车后来到选择插件
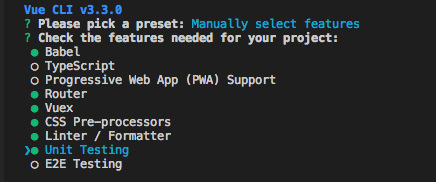
(2)插件选择
这边选择了(Babel、Router、Vuex、Css预处理器、Linter / Formatter 格式检查、Unit测试框架)
(3)路由模式选择
是否使用 history 模式的路由 (Yes)

(4)选择一个css预处理器 (Sass/SCSS)

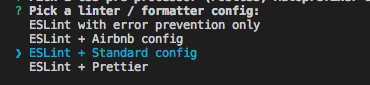
(5)选择一个eslint配置
这边选择 ESLint + Standard config ,个人比较喜欢这个代码规范
(6)选择什么时候进行 eslint 校验
选择(Lint on save)保存是检查
如果你正在使用的vscode编辑器的话,可以配置eslint插件进行代码自动格式化

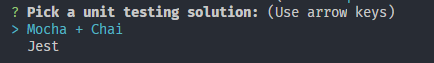
7. 选择测试框架 (Mocha + Chai)
8. 选择将这些配置文件写入到什么地方 (In dedicated config files)
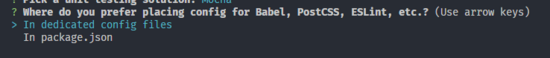
9. 是否保存这份预设配置?(y)
选是的话,下次创建一个vue项目,可以直接使用这个预设文件,而无需再进行配置。

等待依赖完成

2. 全局组件自动注册
在 components 目录下创建一个 global 目录,里面放置一些需要全局注册的组件。
index.js 作用只要是引入 main.vue ,导出组件对象
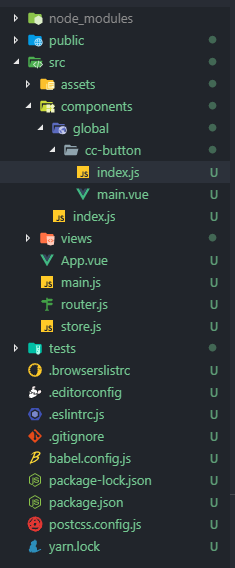
在 components 中创建一个 index.js,用来扫描全局对象并自动注册。
// components/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
// 自动加载 global 目录下的 .js 结尾的文件
const componentsContext = require.context('./global', true, /\.js$/)
componentsContext.keys().forEach(component => {
const componentConfig = componentsContext(component)
/**
* 兼容 import export 和 require module.export 两种规范
*/
const ctrl = componentConfig.default || componentConfig
Vue.component(ctrl.name, ctrl)
})
最后在入口文件 main.js 中导入这个 index.js 中就可以了
3.路由自动引入
在 Vue 项目中使用路由,相信想熟的人已经很熟悉怎么使用了,要新增一个页面的话,需要到路由配置中配置该页面的信息。
如果页面越来越多的话,那么如何让我们的路由更简洁呢?
3.1 拆分路由
根据不同的业务模块进行拆分路由
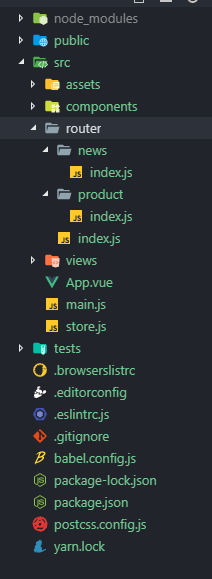
在每个子模块中导出一个路由配置数组
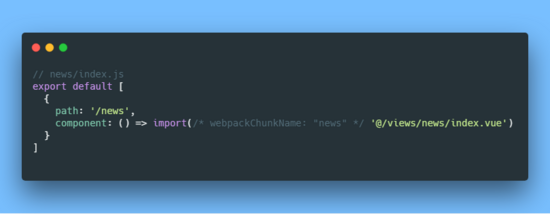
在根 index.js 中导入所有子模块
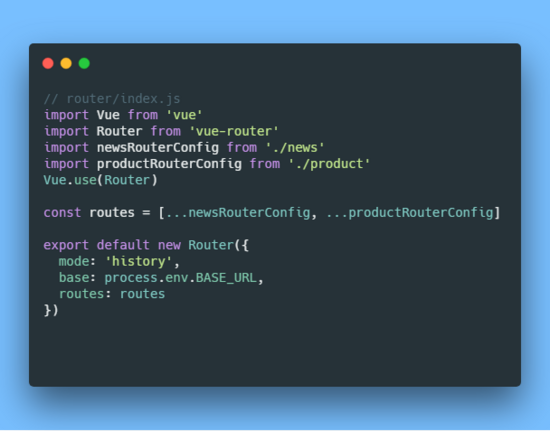
3.2 自动扫描子模块路由并导入
当我们的业务越来越庞大,每次新增业务模块的时候,我们都要在路由下面新增一个子路由模块,然后在 index.js 中导入。
那么如何简化这种操作呢?
通过上面的自动扫描全局组件注册,我们也可以实现自动扫描子模块路由并导入

4. 通过node来生成组件
作为前端开发者,放着 node 这么好用的东西如果不能运用起来,岂不是很浪费?

虽然我们通过上面已经实现了组件的自动注册,不过每次新建组件的时候,都要创建一个目录,然后新增一个 .vue 文件,然后写 template 、 script 、 style 这些东西,然后新建一个 index.js
、导出vue组件、虽然有插件能实现自动补全,但还是很麻烦有木有。
那么我们能不能通过 node 来帮助我们干这些事情呢?只要告诉 node 帮我生成的组件名称就行了。其它的事情让 node 来干

4.1 通过node来生成组件
安装一下 chalk ,这个插件能让我们的控制台输出语句有各种颜色区分
npm install chalk --save-dev
在根目录中创建一个 scripts 文件夹,
新增一个 generateComponent.js 文件,放置生成组件的代码、
新增一个 template.js 文件,放置组件模板的代码
template.js
// template.js
module.exports = {
vueTemplate: compoenntName => {
return `<template>
<div class="${compoenntName}">
${compoenntName}组件
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: '${compoenntName}'
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.${compoenntName} {
}
</style>
`
},
entryTemplate: `import Main from './main.vue'
export default Main`
}
generateComponent.js`
// generateComponent.js`
const chalk = require('chalk')
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const resolve = (...file) => path.resolve(__dirname, ...file)
const log = message => console.log(chalk.green(`${message}`))
const successLog = message => console.log(chalk.blue(`${message}`))
const errorLog = error => console.log(chalk.red(`${error}`))
const { vueTemplate, entryTemplate } = require('./template')
const generateFile = (path, data) => {
if (fs.existsSync(path)) {
errorLog(`${path}文件已存在`)
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.writeFile(path, data, 'utf8', err => {
if (err) {
errorLog(err.message)
reject(err)
} else {
resolve(true)
}
})
})
}
log('请输入要生成的组件名称、如需生成全局组件,请加 global/ 前缀')
let componentName = ''
process.stdin.on('data', async chunk => {
const inputName = String(chunk).trim().toString()
/**
* 组件目录路径
*/
const componentDirectory = resolve('../src/components', inputName)
/**
* vue组件路径
*/
const componentVueName = resolve(componentDirectory, 'main.vue')
/**
* 入口文件路径
*/
const entryComponentName = resolve(componentDirectory, 'index.js')
const hasComponentDirectory = fs.existsSync(componentDirectory)
if (hasComponentDirectory) {
errorLog(`${inputName}组件目录已存在,请重新输入`)
return
} else {
log(`正在生成 component 目录 ${componentDirectory}`)
await dotExistDirectoryCreate(componentDirectory)
// fs.mkdirSync(componentDirectory);
}
try {
if (inputName.includes('/')) {
const inputArr = inputName.split('/')
componentName = inputArr[inputArr.length - 1]
} else {
componentName = inputName
}
log(`正在生成 vue 文件 ${componentVueName}`)
await generateFile(componentVueName, vueTemplate(componentName))
log(`正在生成 entry 文件 ${entryComponentName}`)
await generateFile(entryComponentName, entryTemplate)
successLog('生成成功')
} catch (e) {
errorLog(e.message)
}
process.stdin.emit('end')
})
process.stdin.on('end', () => {
log('exit')
process.exit()
})
function dotExistDirectoryCreate (directory) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
mkdirs(directory, function () {
resolve(true)
})
})
}
// 递归创建目录
function mkdirs (directory, callback) {
var exists = fs.existsSync(directory)
if (exists) {
callback()
} else {
mkdirs(path.dirname(directory), function () {
fs.mkdirSync(directory)
callback()
})
}
}
配置package.json
"new:comp": "node ./scripts/generateComponent"
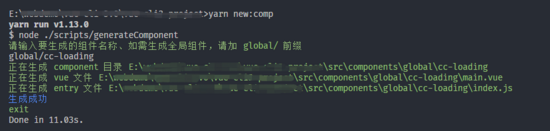
执行
如果使用 npm 的话 就是 npm run new:comp
如果使用 yarn 的话 就是 yarn new:comp
4.2 通过node来生成页面组件
通过上面的逻辑代码我们可以通过 node 来生成组件了,那么也可以举一反三来生成页面组件。只需稍微修改一下生成组件代码的逻辑。 在 scripts 目录下新建一个 generateView.js 文件
// generateView.js
const chalk = require('chalk')
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const resolve = (...file) => path.resolve(__dirname, ...file)
const log = message => console.log(chalk.green(`${message}`))
const successLog = message => console.log(chalk.blue(`${message}`))
const errorLog = error => console.log(chalk.red(`${error}`))
const { vueTemplate } = require('./template')
const generateFile = (path, data) => {
if (fs.existsSync(path)) {
errorLog(`${path}文件已存在`)
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.writeFile(path, data, 'utf8', err => {
if (err) {
errorLog(err.message)
reject(err)
} else {
resolve(true)
}
})
})
}
log('请输入要生成的页面组件名称、会生成在 views/目录下')
let componentName = ''
process.stdin.on('data', async chunk => {
const inputName = String(chunk).trim().toString()
/**
* Vue页面组件路径
*/
let componentVueName = resolve('../src/views', inputName)
// 如果不是以 .vue 结尾的话,自动加上
if (!componentVueName.endsWith('.vue')) {
componentVueName += '.vue'
}
/**
* vue组件目录路径
*/
const componentDirectory = path.dirname(componentVueName)
const hasComponentExists = fs.existsSync(componentVueName)
if (hasComponentExists) {
errorLog(`${inputName}页面组件已存在,请重新输入`)
return
} else {
log(`正在生成 component 目录 ${componentDirectory}`)
await dotExistDirectoryCreate(componentDirectory)
}
try {
if (inputName.includes('/')) {
const inputArr = inputName.split('/')
componentName = inputArr[inputArr.length - 1]
} else {
componentName = inputName
}
log(`正在生成 vue 文件 ${componentVueName}`)
await generateFile(componentVueName, vueTemplate(componentName))
successLog('生成成功')
} catch (e) {
errorLog(e.message)
}
process.stdin.emit('end')
})
process.stdin.on('end', () => {
log('exit')
process.exit()
})
function dotExistDirectoryCreate (directory) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
mkdirs(directory, function () {
resolve(true)
})
})
}
// 递归创建目录
function mkdirs (directory, callback) {
var exists = fs.existsSync(directory)
if (exists) {
callback()
} else {
mkdirs(path.dirname(directory), function () {
fs.mkdirSync(directory)
callback()
})
}
}
配置package.json 新增一个 scripts 脚本
"new:view": "node ./scripts/generateView"
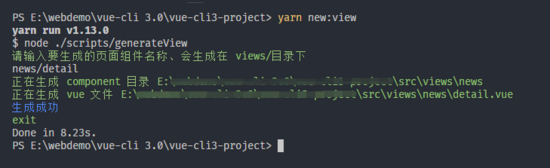
执行
如果使用 npm 的话 就是 npm run new:view
如果使用 yarn 的话 就是 yarn new:view
5. axios封装 安装 axios
npm install axios --save // or yarn add axios
5.1 配置不同的环境
在根目录新建三个环境变量文件
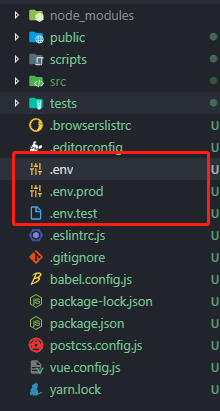
分别输入不同的地址, 比如 dev 就写 dev 的api地址、 test 就写 test的api地址
# // .env NODE_ENV = "development" BASE_URL = https://easy-mock.com/mock/5c4c50b9888ef15de01bec2c/api
接着在根目录中新建一个 vue.config.js
// vue.config.js
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
// 这里是对环境的配置,不同环境对应不同的BASE_URL,以便axios的请求地址不同
config.plugin('define').tap(args => {
args[0]['process.env'].BASE_URL = JSON.stringify(process.env.BASE_URL)
return args
})
}
}
然后在 src 目录下新建一个 api 文件夹,创建一个 index.js 用来配置 axios 的配置信息
// src/api/index.js
import axios from 'axios'
import router from '../router'
import { Message } from 'element-ui'
const service = axios.create({
// 设置超时时间
timeout: 60000,
baseURL: process.env.BASE_URL
})
// post请求的时候,我们需要加上一个请求头,所以可以在这里进行一个默认的设置
// 即设置post的请求头为application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8
service.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8''
export default service
5.2 请求响应封装
import axios from 'axios'
import router from '../router'
import { Message } from 'element-ui'
const service = axios.create({
// 设置超时时间
timeout: 60000,
baseURL: process.env.BASE_URL
})
/**
* 请求前拦截
* 用于处理需要在请求前的操作
*/
service.interceptors.request.use(config => {
const token = localStorage.getItem('token')
if (token) {
config.headers['Authorization'] = token
}
return config
}, (error) => {
return Promise.reject(error)
})
/**
* 请求响应拦截
* 用于处理需要在请求返回后的操作
*/
service.interceptors.response.use(response => {
const responseCode = response.status
// 如果返回的状态码为200,说明接口请求成功,可以正常拿到数据
// 否则的话抛出错误
if (responseCode === 200) {
return Promise.resolve(response)
} else {
return Promise.reject(response)
}
}, error => {
// 服务器返回不是 2 开头的情况,会进入这个回调
// 可以根据后端返回的状态码进行不同的操作
const responseCode = error.response.status
switch (responseCode) {
// 401:未登录
case 401:
// 跳转登录页
router.replace({
path: '/login',
query: {
redirect: router.currentRoute.fullPath
}
})
break
// 403: token过期
case 403:
// 弹出错误信息
Message({
type: 'error',
message: '登录信息过期,请重新登录'
})
// 清除token
localStorage.removeItem('token')
// 跳转登录页面,并将要浏览的页面fullPath传过去,登录成功后跳转需要访问的页面
setTimeout(() => {
router.replace({
path: '/login',
query: {
redirect: router.currentRoute.fullPath
}
})
}, 1000)
break
// 404请求不存在
case 404:
Message({
message: '网络请求不存在',
type: 'error'
})
break
// 其他错误,直接抛出错误提示
default:
Message({
message: error.response.data.message,
type: 'error'
})
}
return Promise.reject(error)
})
export default service
Message 方法是 element-ui 提供的一个消息提示组件、大家可以根据自己的消息提示组件进行替换
5.3 断网处理
在响应拦截中添加处理逻辑
service.interceptors.response.use(response => {
const responseCode = response.status
// 如果返回的状态码为200,说明接口请求成功,可以正常拿到数据
// 否则的话抛出错误
if (responseCode === 200) {
return Promise.resolve(response.data)
} else {
return Promise.reject(response)
}
}, error => {
// 断网 或者 请求超时 状态
if (!error.response) {
// 请求超时状态
if (error.message.includes('timeout')) {
console.log('超时了')
Message.error('请求超时,请检查网络是否连接正常')
} else {
// 可以展示断网组件
console.log('断网了')
Message.error('请求失败,请检查网络是否已连接')
}
return
}
// 省略其它代码 ······
return Promise.reject(error)
})
5.4 封装图片上传
// src/api/index.js
export const uploadFile = formData => {
const res = service.request({
method: 'post',
url: '/upload',
data: formData,
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'multipart/form-data' }
})
return res
}
调用
async uploadFile (e) {
const file = document.getElementById('file').files[0]
const formdata = new FormData()
formdata.append('file', file)
await uploadFile(formdata)
}
5.5 请求 显示 Loading 效果
let loading = null
service.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// 在请求先展示加载框
loading = Loading.service({
text: '正在加载中......'
})
// 省略其它代码 ······
return config
}, (error) => {
return Promise.reject(error)
})
service.interceptors.response.use(response => {
// 请求响应后关闭加载框
if (loading) {
loading.close()
}
// 省略其它代码 ······
}, error => {
// 请求响应后关闭加载框
if (loading) {
loading.close()
}
// 省略其它代码 ······
return Promise.reject(error)
})
6. 巧用 Mixins

6.1 封装 store 公用方法
假设有这样一个场景,我们通过 vuex 封装了获取新闻列表的 function
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import { getNewsList } from '../api/news'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const types = {
NEWS_LIST: 'NEWS_LIST'
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
[types.NEWS_LIST]: []
},
mutations: {
[types.NEWS_LIST]: (state, res) => {
state[types.NEWS_LIST] = res
}
},
actions: {
[types.NEWS_LIST]: async ({ commit }, params) => {
const res = await getNewsList(params)
return commit(types.NEWS_LIST, res)
}
},
getters: {
getNewsResponse (state) {
return state[types.NEWS_LIST]
}
}
})
然后在新闻列表页,我们通过 mapAction 、 mapGetters 来调用 Action 和 getters 我们需要写上这些代码
import { mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['getNewsResponse'])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['NEWS_LIST'])
}
在假设,在另一个页面又需要重新调用获取新闻列表的接口,我们又要在写一遍上面的代码对吧?
复制粘贴就是干有木有?
如果接口突然加了一个参数,那岂不是每个要用到这个接口的代码都得加这个参数。
复制粘贴一时爽,需求一改你就爽

既然是重复的代码,我们肯定要复用,这时候 Vue 提供的 Mixin 就起了大作用了
封装 news-mixin.js 在 src 下创建一个 mixins 目录,用来管理所有的mixins 新建一个 news-mixin.js
import { mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['getNewsResponse'])
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['NEWS_LIST'])
}
}
然后在需要用到的组件中引入这个 mixin ,就能直接调用这个方法了。不管多少个页面,只要引入这个 mixin ,直接就能使用。
需求一改的话,也只需要修改这个 mixin 文件
// news/index.vue
import Vue from 'vue'
import newsMixin from '@/mixins/news-mixin'
export default {
name: 'news',
mixins: [newsMixin],
data () {
return {}
},
async created () {
await this.NEWS_LIST()
console.log(this.getNewsResponse)
}
}
6.2 扩展
除了封装 vuex 的公用方法,其实还有很多的东西也能做封装。例如: 分页对象 , 表格数据 , 公用方法 、等等就不一一举例了。可以看github
在多个地方经常使用,就可以考虑封装成 mixin ,不过请写好注释哦。不然就会有人在背后骂你了!!你懂的~~
7. 优化
7.1 gzip压缩
安装 compression-webpack-plugin 插件
npm install compression-webpack-plugin --save-dev // or yarn add compression-webpack-plugin --dev
在 vue.config.js 中添加配置
// vue.config.js
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
// 这里是对环境的配置,不同环境对应不同的BASE_URL,以便axios的请求地址不同
config.plugin('define').tap(args => {
args[0]['process.env'].BASE_URL = JSON.stringify(process.env.BASE_URL)
return args
})
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') {
// #region 启用GZip压缩
config
.plugin('compression')
.use(CompressionPlugin, {
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp('\\.(' + ['js', 'css'].join('|') + ')$'),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8,
cache: true
})
.tap(args => { })
// #endregion
}
}
}
npm run build 后能看到生成 .gz 文件就OK了。如果你的服务器使用nginx的话,nginx也需要配置开启 GZIP 、下面会讲到如何在 nginx 中开启 GZIP
7.2 第三方库引用cdn
对于 vue 、 vue-router 、 vuex 、 axios 和 element-ui 等等这些不经常改动的库、我们让 webpack 不对他们进行打包,通过 cdn 引入,可以减少代码的大小、也可以减少服务器的带宽,更能把这些文件缓存到客户端,客户端加载的会更快。
配置 vue.config.js
const CompressionPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
chainWebpack: config => {
// 省略其它代码 ······
// #region 忽略生成环境打包的文件
var externals = {
vue: 'Vue',
axios: 'axios',
'element-ui': 'ELEMENT',
'vue-router': 'VueRouter',
vuex: 'Vuex'
}
config.externals(externals)
const cdn = {
css: [
// element-ui css
'//unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
],
js: [
// vue
'//cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.5.22/vue.min.js',
// vue-router
'//cdn.staticfile.org/vue-router/3.0.2/vue-router.min.js',
// vuex
'//cdn.staticfile.org/vuex/3.1.0/vuex.min.js',
// axios
'//cdn.staticfile.org/axios/0.19.0-beta.1/axios.min.js',
// element-ui js
'//unpkg.com/element-ui/lib/index.js'
]
}
config.plugin('html')
.tap(args => {
args[0].cdn = cdn
return args
})
// #endregion
}
}
}
修改 index.html
<!--public/index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<% if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production') { %>
<% for(var css of htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.css) { %>
<link href="<%=css%>" rel="preload" as="style">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="<%=css%>" as="style">
<% } %>
<% for(var js of htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js) { %>
<link href="<%=js%>" rel="preload" as="script">
<script src="<%=js%>"></script>
<% } %>
<% } %>
<title>vue-cli3-project</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but vue-cli3-project doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
7.3 全站cdn
我们已经把第三方库使用 cdn 替代了,那么我们 build 后生成的 js , css 之类的文件能否也用 cdn 呢?

申请自己的cdn域名
要想把自己的资源上传到 cdn 上,前提是得有自己的 cdn 域名,如果没有的话,可以到七牛云官网上注册申请一个
- 注册七牛云账号
- 到七牛云对象存储模块中新建存储空间
- 输入存储空间信息

确定创建
创建成功后会跳转到这个存储空间的控制台页面
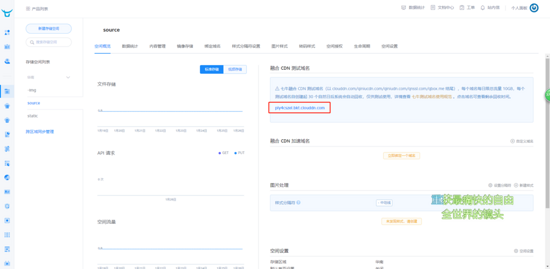
其中有个域名就是你的测试域名
我们可以在内容管理那上传我们的 js 、 css 之类的文件、不过我们的文件那么多,一个一个上传明显不合理。要你你也不干。
这时候,这些批量又重复的操作应该由我们的 node 出马,让我们来通过 node 来批量上传我们的资源文件
将生成的js、css资源上传到七牛cdn
在七牛云官网的文档中心有介绍如何通过 node 上传文件、感兴趣的人可以自己去研究一下。
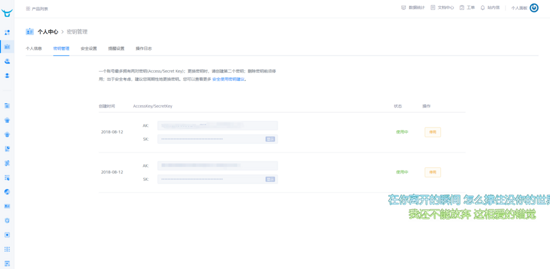
查看 AccessKey 和 SecretKey ,在你的个人面板 -> 秘钥管理 ,这两个秘钥待会会用到
安装需要的插件
npm install qiniu glob mime --save-dev
在 scripts 目录下创建一个 upcdn.js 文件
// /scripts/upcdn.js
const qiniu = require('qiniu')
const glob = require('glob')
const mime = require('mime')
const path = require('path')
const isWindow = /^win/.test(process.platform)
let pre = path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist/') + (isWindow ? '\\' : '')
const files = glob.sync(
`${path.join(
__dirname,
'../dist/**/*.?(js|css|map|png|jpg|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot)'
)}`
)
pre = pre.replace(/\\/g, '/')
const options = {
scope: 'source' // 空间对象名称
}
var config = {
qiniu: {
accessKey: '', // 个人中心 秘钥管理里的 AccessKey
secretKey: '', // 个人中心 秘钥管理里的 SecretKey
bucket: options.scope,
domain: 'http://ply4cszel.bkt.clouddn.com'
}
}
var accessKey = config.qiniu.accessKey
var secretKey = config.qiniu.secretKey
var mac = new qiniu.auth.digest.Mac(accessKey, secretKey)
var putPolicy = new qiniu.rs.PutPolicy(options)
var uploadToken = putPolicy.uploadToken(mac)
var cf = new qiniu.conf.Config({
zone: qiniu.zone.Zone_z2
})
var formUploader = new qiniu.form_up.FormUploader(cf)
async function uploadFileCDN (files) {
files.map(async file => {
const key = getFileKey(pre, file)
try {
await uploadFIle(key, file)
console.log(`上传成功 key: ${key}`)
} catch (err) {
console.log('error', err)
}
})
}
async function uploadFIle (key, localFile) {
const extname = path.extname(localFile)
const mimeName = mime.getType(extname)
const putExtra = new qiniu.form_up.PutExtra({ mimeType: mimeName })
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
formUploader.putFile(uploadToken, key, localFile, putExtra, function (
respErr,
respBody,
respInfo
) {
if (respErr) {
reject(respErr)
}
resolve({ respBody, respInfo })
})
})
}
function getFileKey (pre, file) {
if (file.indexOf(pre) > -1) {
const key = file.split(pre)[1]
return key.startsWith('/') ? key.substring(1) : key
}
return file
}
(async () => {
console.time('上传文件到cdn')
await uploadFileCDN(files)
console.timeEnd('上传文件到cdn')
})()
修改 publicPath
修改 vue.config.js 的配置信息,让其 publicPath 指向我们 cdn 的域名
const IS_PROD = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const cdnDomian = 'http://ply4cszel.bkt.clouddn.com'
module.exports = {
publicPath: IS_PROD ? cdnDomian : '/',
// 省略其它代码 ·······
}
修改package.json配置
修改package.json配置,使我们 build 完成后自动上传资源文件到 cdn服务器
"build": "vue-cli-service build --mode prod && node ./scripts/upcdn.js",
运行查看效果
npm run build
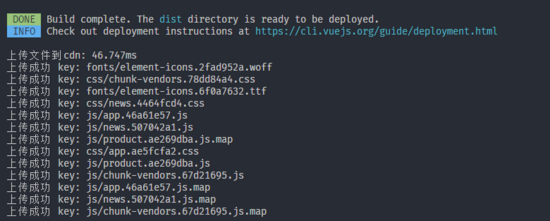
然后到你的 cdn
控制台的内容管理看看文件是否已经上传成功

8. docker部署
这边使用的是 centOS7 环境,不过使用的是不同的系统,可以参考一下其它系统的安装方法
8.1 安装docker 更新软件库
yum update -y
安装docker
yum install docker
启动docker服务
service docker start
安装docker-compose
// 安装epel源 yum install -y epel-release // 安装docker-compose yum install docker-compose
8.2 编写docker-compose.yaml
version: '2.1' services: nginx: restart: always image: nginx volumes: #~ /var/local/nginx/nginx.conf为本机目录, /etc/nginx为容器目录 - /var/local/nginx/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #~ /var/local/app/dist 为本机 build 后的dist目录, /usr/src/app为容器目录, - /var/local/app/dist:/usr/src/app ports: - 80:80 privileged: true
8.3 编写 nginx.conf 配置
#user nobody;
worker_processes 2;
#工作模式及连接数上线
events {
worker_connections 1024; #单个工作进程 处理进程的最大并发数
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,对于普通应用,
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
# 开启GZIP
gzip on;
# # 监听 80 端口,转发请求到 3000 端口
server {
#监听端口
listen 80;
#编码格式
charset utf-8;
# 前端静态文件资源
location / {
root /usr/src/app;
index index.html index.htm;
try_files $uri $uri/ @rewrites;
}
# 配置如果匹配不到资源,将url指向 index.html, 在 vue-router 的 history 模式下使用,就不会显示404
location @rewrites {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html last;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
8.4 执行 docker-compose
docker-compose -d up

8.5 docker + jenkins 自动化部署
使用 docker + jenkins 能实现代码提交到github后自动部署环境、这个要讲起来内容太多,有兴趣的可以看我这一篇文章
从零搭建docker+jenkins+node.js自动化部署环境
扩展
使用pm2自动化部署node项目
通过vue-cli3构建一个SSR应用程序
项目地址 vue-cli3-project欢迎 star
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

