spring-cloud Sleuth的使用方法
一直没弄明白sleuth的tracerContext是如何创建和传递的,闲来无事研究了一下。由于对sleuth的源码不熟悉,准备通过debug brave.Tracer的nextId()方法,查看方法调用栈来找来龙去脉。
首先创建两个service A和B,记作srvA、srvB,在srvA中添加testA controller,sevB中添加testB controller,testA中通过Feign调用testB。

先看当用户通过浏览器调用srvA的时候,srvA是作为server的。
configuration:
TraceWebServletAutoConfiguration==>TracingFilter
TraceHttpAutoConfiguration==>HttpTracing
TraceAutoConfiguration==>Tracing
SleuthLogAutoConfiguration.Slf4jConfiguration==>CurrentTraceContext
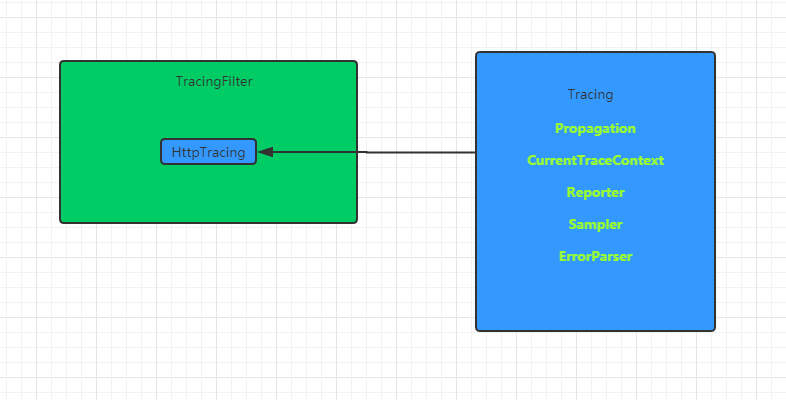
配置中,TracingFilter在实例化时需要一个HttpTracing:
public static Filter create(HttpTracing httpTracing) {
return new TracingFilter(httpTracing);
}
//Servlet运行时类
final ServletRuntime servlet = ServletRuntime.get();
//Slf4jCurrentTraceContext
final CurrentTraceContext currentTraceContext;
final Tracer tracer;
final HttpServerHandler<HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse> handler;
//TraceContext的数据提取器
final TraceContext.Extractor<HttpServletRequest> extractor;
TracingFilter(HttpTracing httpTracing) {
tracer = httpTracing.tracing().tracer();
currentTraceContext = httpTracing.tracing().currentTraceContext();
handler = HttpServerHandler.create(httpTracing, ADAPTER);
extractor = httpTracing.tracing().propagation().extractor(GETTER);
}
HttpTracing Builder模式构造时接收一个Tracing:
Tracing tracing;
//客户端span解析器
HttpClientParser clientParser;
String serverName;
//服务端span解析器
HttpServerParser serverParser;
HttpSampler clientSampler, serverSampler;
Builder(Tracing tracing) {
if (tracing == null) throw new NullPointerException("tracing == null");
final ErrorParser errorParser = tracing.errorParser();
this.tracing = tracing;
this.serverName = "";
// override to re-use any custom error parser from the tracing component
this.clientParser = new HttpClientParser() {
@Override protected ErrorParser errorParser() {
return errorParser;
}
};
this.serverParser = new HttpServerParser() {
@Override protected ErrorParser errorParser() {
return errorParser;
}
};
this.clientSampler = HttpSampler.TRACE_ID;
this.serverSampler(HttpSampler.TRACE_ID);
}
Tracing实例化:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
// NOTE: stable bean name as might be used outside sleuth
Tracing tracing(@Value("${spring.zipkin.service.name:${spring.application.name:default}}") String serviceName,
Propagation.Factory factory,
CurrentTraceContext currentTraceContext,
Reporter<zipkin2.Span> reporter,
Sampler sampler,
ErrorParser errorParser,
SleuthProperties sleuthProperties
) {
return Tracing.newBuilder()
.sampler(sampler)
.errorParser(errorParser)
.localServiceName(serviceName)
//ExtraFieldPropagation.Factory
.propagationFactory(factory)
.currentTraceContext(currentTraceContext)
.spanReporter(adjustedReporter(reporter))
.traceId128Bit(sleuthProperties.isTraceId128())
.supportsJoin(sleuthProperties.isSupportsJoin())
.build();
}
下面看TracingFilter的doFilter:
Span span = handler.handleReceive(extractor, httpRequest);
// Add attributes for explicit access to customization or span context
request.setAttribute(SpanCustomizer.class.getName(), span.customizer());
request.setAttribute(TraceContext.class.getName(), span.context());
Throwable error = null;
Scope scope = currentTraceContext.newScope(span.context());
try {
// any downstream code can see Tracer.currentSpan() or use Tracer.currentSpanCustomizer()
chain.doFilter(httpRequest, httpResponse);
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException | Error e) {
error = e;
throw e;
} finally {
scope.close();
if (servlet.isAsync(httpRequest)) { // we don't have the actual response, handle later
servlet.handleAsync(handler, httpRequest, httpResponse, span);
} else { // we have a synchronous response, so we can finish the span
handler.handleSend(ADAPTER.adaptResponse(httpRequest, httpResponse), error, span);
}
}
}
在SleuthLogAutoConfiguration中如果有slfj的包,则注入CurrentTraceContext:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(MDC.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SleuthSlf4jProperties.class)
protected static class Slf4jConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.sleuth.log.slf4j.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CurrentTraceContext slf4jSpanLogger() {
return Slf4jCurrentTraceContext.create();
}
...
}
Slf4jCurrentTraceContext中,delegate就是CurrentTraceContext.Default.inheritable():
public static final class Default extends CurrentTraceContext {
static final ThreadLocal<TraceContext> DEFAULT = new ThreadLocal<>();
// Inheritable as Brave 3's ThreadLocalServerClientAndLocalSpanState was inheritable
static final InheritableThreadLocal<TraceContext> INHERITABLE = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
final ThreadLocal<TraceContext> local;
//静态方法create,local对象为ThreadLocal类型
/** Uses a non-inheritable static thread local */
public static CurrentTraceContext create() {
return new Default(DEFAULT);
}
//local对象为InheritableThreadLocal类型
//官方文档指出,inheritable方法在线程池的环境中需谨慎使用,可能会取出错误的TraceContext,这样会导致Span等信息会记录并关联到错误的traceId上
/**
* Uses an inheritable static thread local which allows arbitrary calls to {@link
* Thread#start()} to automatically inherit this context. This feature is available as it is was
* the default in Brave 3, because some users couldn't control threads in their applications.
*
* <p>This can be a problem in scenarios such as thread pool expansion, leading to data being
* recorded in the wrong span, or spans with the wrong parent. If you are impacted by this,
* switch to {@link #create()}.
*/
public static CurrentTraceContext inheritable() {
return new Default(INHERITABLE);
}
Default(ThreadLocal<TraceContext> local) {
if (local == null) throw new NullPointerException("local == null");
this.local = local;
}
@Override public TraceContext get() {
return local.get();
}
//替换当前TraceContext,close方法将之前的TraceContext设置回去
//Scope接口继承了Closeable接口,在try中使用会自动调用close方法,为了避免用户忘记close方法,还提供了Runnable,Callable,Executor,ExecutorService包装方法
@Override public Scope newScope(@Nullable TraceContext currentSpan) {
final TraceContext previous = local.get();
local.set(currentSpan);
class DefaultCurrentTraceContextScope implements Scope {
@Override public void close() {
local.set(previous);
}
}
return new DefaultCurrentTraceContextScope();
}
}
Slf4jCurrentTraceContext的delegate使用的就是一个InheritableThreadLocal,InheritableThreadLocal在创建子线程的时候,会将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals继承下来。这样就实现了TraceContext在父子线程中的传递。
看一下CurrentTraceContext的maybeScope:
//返回一个新的scope,如果当前scope就是传入的scope,返回一个空scope
public Scope maybeScope(@Nullable TraceContext currentSpan) {
//获取当前TraceContext
TraceContext currentScope = get();
//如果传入的TraceContext为空,且当前TraceContext为空返回空scope
if (currentSpan == null) {
if (currentScope == null) return Scope.NOOP;
return newScope(null);
}
return currentSpan.equals(currentScope) ? Scope.NOOP : newScope(currentSpan);
}
TracingFilter中HttpServerHandler解析Request:请输入代码
2.srvA请求到servB时作为Client。
TraceLoadBalancerFeignClient-->LoadBalancerFeignClient-->FeignLoadBalancer-->LazyTracingFeignClient-->Client
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

