Tensorflow加载模型实现图像分类识别流程详解
目录
- 前言
- 正文
- VGG19网络介绍
- 总结
前言
深度学习框架在市面上有很多。比如Theano、Caffe、CNTK、MXnet 、Tensorflow等。今天讲解的就是主角Tensorflow。Tensorflow的前身是Google大脑项目的一个分布式机器学习训练框架,它是一个十分基础且集成度很高的系统,它的目标就是为研究超大型规模的视觉项目,后面延申到各个领域。Tensorflow 在2015年正式开源,开源的一个月内就收获到1w多的starts,这足以说明Tensorflow的优越性以及Google的影响力。在Api方面Tensorflow为了满足绝大部分的开发者需求,这也是Google的一贯作风,集成了Java、Go、Python、C++等编程语言。
正文
图像识别是一件很有趣的事,话不多说,咱们先了解下特征提取VGG in Tensorflow。官网地址:VGG in TensorFlow · Davi Frossard。
VGG 是牛津大学的 K. Simonyan 和 A. Zisserman 在论文“Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition”中提出的卷积神经网络模型。该模型在 ImageNet 中实现了 92.7% 的 top-5 测试准确率,这是一个包含 1000 个类别的超过 1400 万张图像的数据集。 在这篇简短的文章中,我们提供了 VGG16 的实现以及从原始 Caffe 模型转换为 TensorFlow 的权重。这句话是VGGNet官方的介绍,直接从它提供的数字可以看出来,它的识别率是十分高的,是不是很激动,动起手来吧。
开发步骤分4步,如下所示:
a) 依赖加载
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import os import scipy.io import scipy.misc from imagenet_classes import class_names
b)定义卷积、池化等函数
def _conv_layer(input,weight,bias):
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input,weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
return tf.nn.bias_add(conv,bias)
def _pool_layer(input):
return tf.nn.max_pool(input,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
def preprocess(image,mean_pixel):
'''简单预处理,全部图片减去平均值'''
return image-mean_pixel
def unprocess(image,mean_pixel):
return image+mean_pixel
c)图像的读取以及保存
def imread(path):
return scipy.misc.imread(path)
def imsave(image,path):
img = np.clip(image,0,255).astype(np.int8)
scipy.misc.imsave(path,image)
d) 定义网络结构,这里使用的是VGG19
def net(data_path,input_image,sess=None):
"""
读取VGG模型参数,搭建VGG网络
:param data_path: VGG模型文件位置
:param input_image: 输入测试图像
:return:
"""
layers = (
'conv1_1', 'conv1_2', 'pool1',
'conv2_1', 'conv2_2', 'pool2',
'conv3_1', 'conv3_2', 'conv3_3','conv3_4', 'pool3',
'conv4_1', 'conv4_2', 'conv4_3','conv4_4', 'pool4',
'conv5_1', 'conv5_2', 'conv5_3','conv5_4', 'pool5',
'fc1' , 'fc2' , 'fc3' ,
'softmax'
)
data = scipy.io.loadmat(data_path)
mean = data["normalization"][0][0][0][0][0]
input_image = np.array([preprocess(input_image, mean)]).astype(np.float32)#去除平均值
net = {}
current = input_image
net["src_image"] = tf.constant(current) # 存储数据
count = 0 #计数存储
for i in range(43):
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("relu"):
continue
if str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0])[:4] == ("pool"):
current = _pool_layer(current)
elif str(data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]) == ("softmax"):
current = tf.nn.softmax(current)
elif i == (37):
shape = int(np.prod(current.get_shape()[1:]))
current = tf.reshape(current, [-1, shape])
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[-1,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == (39):
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels,[4096,4096])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(current,kernels),bias))
elif i == 41:
kernels, bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
kernels = np.reshape(kernels, [4096, 1000])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)
current = tf.add(tf.matmul(current, kernels), bias)
else:
kernels,bias = data['layers'][0][i][0][0][0][0]
#注意VGG存储方式为[,]
#kernels = np.transpose(kernels,[1,0,2,3])
bias = bias.reshape(-1)#降低维度
current = tf.nn.relu(_conv_layer(current,kernels,bias))
net[layers[count]] = current #存储数据
count += 1
return net, mean
e)加载模型进行识别
if __name__ == '__main__':
VGG_PATH = "./one/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat"
IMG_PATH = './one/3.jpg'
input_image =imread(IMG_PATH)
shape = (1, input_image.shape[0], input_image.shape[1], input_image.shape[2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
image = tf.placeholder('float', shape=shape)
nets, mean_pixel, all_layers= net(VGG_PATH, image)
input_image_pre=np.array([preprocess(input_image,mean_pixel)])
layers = all_layers
for i , layer in enumerate(layers):
print("[%d/%d] %s" % (i+1,len(layers),layers))
features = nets[layer].eval(feed_dict={image:input_image_pre})
print("Type of 'feature' is ",type(features))
print("Shape of 'features' is %s" % (features.shape,))
if 1:
plt.figure(i+1,figsize=(10,5))
plt.matshow(features[0,:,:,0],cmap=plt.cm.gray,fignum=i+1)
plt.title(""+layer)
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
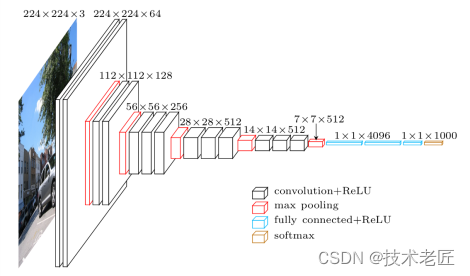
VGG19网络介绍
VGG19 的宏观架构如图所示。我们在 TensorFlow 中的文件 vgg19.py 中对其进行编码。请注意,我们包含一个预处理层,它采用像素值在 0-255 范围内的 RGB 图像并减去平均图像值(在整个 ImageNet 训练集上计算)。
总结
Tensorflow是一款十分不错的深度学习框架,它在工业上得到的十分的认可并进行了实践。因此,如果你还在犹豫生产落地使用框架,不要犹豫啦。VGGNet家族是一个十分优秀的网络结构,它在处理特征提取过程中,也是得到了很多公司和研究学者的认可,比较著名的有VGG16、VGG19等。
到此这篇关于Tensorflow加载模型实现图像分类识别流程详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Tensorflow图像分类识别内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

