vue3 keepalive源码解析解决线上问题
目录
- 引言
- 1、keepalive功能
- 2、keepalive使用场景
- 3、在项目中的使用过程
- 4、vue3 keepalive源码调试
- 5、vue3 keealive源码粗浅分析
- 6、总结
引言
- 1、通过本文可以了解到vue3 keepalive功能
- 2、通过本文可以了解到vue3 keepalive使用场景
- 3、通过本文可以学习到vue3 keepalive真实的使用过程
- 4、通过本文可以学习vue3 keepalive源码调试
- 5、通过本文可以学习到vue3 keepalive源码的精简分析
1、keepalive功能
- keepalive是vue3中的一个全局组件
- keepalive 本身不会渲染出来,也不会出现在dom节点当中,但是它会被渲染为vnode,通过vnode可以跟踪到keepalive中的cache和keys,当然也是在开发环境才可以,build打包以后没有暴露到vnode中(这个还要再确认一下)
- keepalive 最重要的功能就是缓存组件
- keepalive 通过LRU缓存淘汰策略来更新组件缓存,可以更有效的利用内存,防止内存溢出,源代码中的最大缓存数max为10,也就是10个组件之后,就开始淘汰最先被缓存的组件了
2、keepalive使用场景
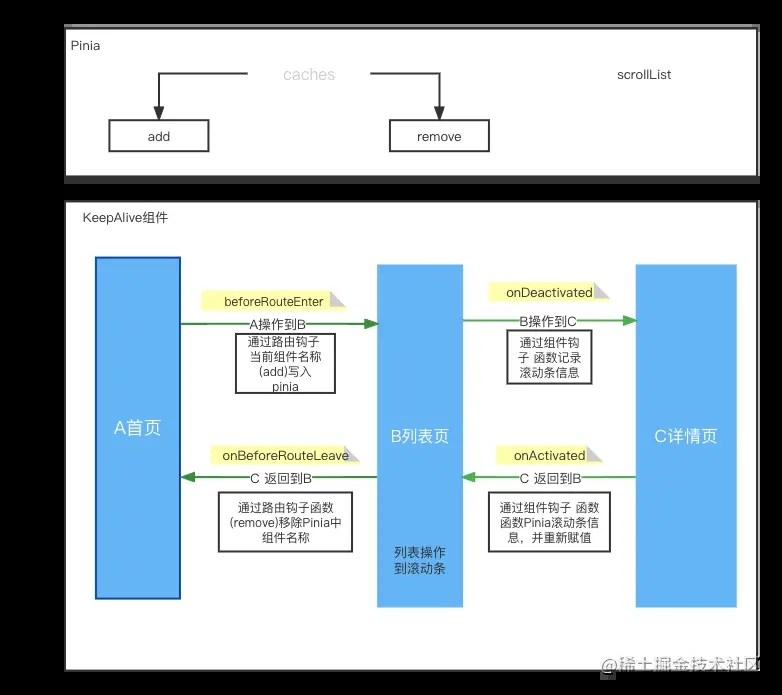
- 这里先假设一个场景: A页面是首页=====> B页面列表页面(需要缓存的页面)=======> C 详情页 由C详情页到到B页面的时候,要返回到B的缓存页面,包括页面的基础数据和列表的滚动条位置信息 如果由B页面返回到A页面,则需要将B的缓存页清空
- 上述另外一个场景:进入页面直接缓存,然后就结束了,这个比较简单本文就不讨论了
3、在项目中的使用过程
keepalive组件总共有三个参数
- include:可传字符串、正则表达式、数组,名称匹配成功的组件会被缓存
- exclude:可传字符串、正则表达式、数组,名称匹配成功的组件不会被缓存
- max:可传数字,限制缓存组件的最大数量,默认为10
首先在App.vue根代码中添加引入keepalive组件,通过这里可以发现,我这里缓存的相当于整个页面,当然你也可以进行更细粒度的控制页面当中的某个区域组件
<template>
<router-view v-slot="{ Component }">
<keep-alive :include="keepAliveCache">
<component :is="Component" :key="$route.name" />
</keep-alive>
</router-view>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { computed } from "vue";
import { useKeepAliverStore } from "@/store";
const useStore = useKeepAliverStore();
const keepAliveCache = computed(() => {
return useStore.caches;
});
</script>
通过App.vue可以发现,通过pinia(也就是vue2中使用的vuex)保存要缓存的页面组件, 来处理include缓存,和保存页面组件中的滚动条信息数据
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useKeepAliverStore = defineStore("useKeepAliverStore", {
state: () => ({
caches: [] as any,
scrollList: new Map(), // 缓存页面组件如果又滚动条的高度
}),
actions: {
add(name: string) {
this.caches.push(name);
},
remove(name: string) {
console.log(this.caches, 'this.caches')
this.caches = this.caches.filter((item: any) => item !== name);
console.log(this.caches, 'this.caches')
},
clear() {
this.caches = []
}
}
});
组件路由刚刚切换时,通过beforeRouteEnter将组件写入include, 此时组件生命周期还没开始。如果都已经开始执行组件生命周期了,再写入就意义了。
所以这个钩子函数就不能写在setup中,要单独提出来写。当然你也可以换成路由的其他钩子函数处理beforeEach,但这里面使用的话,好像使用不了pinia,这个还需要进一步研究一下。
import { useRoute, useRouter, onBeforeRouteLeave } from "vue-router";
import { useKeepAliverStore } from "@/store";
const useStore = useKeepAliverStore()
export default {
name:"record-month",
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
next(vm => {
if(from.name === 'Home' && to.name === 'record-month') {
useStore.add(to.name)
}
});
}
}
</script>
组件路由离开时判断,是否要移出缓存,这个钩子就直接写在setup中就可以了。
onBeforeRouteLeave((to, from) => {
console.log(to.name, "onBeforeRouteLeave");
if (to.name === "new-detection-detail") {
console.log(to, from, "进入详情页面不做处理");
} else {
useStore.remove(from.name)
console.log(to, from, "删除组件缓存");
}
});
在keepalive两个钩子函数中进行处理scroll位置的缓存,onActivated中获取缓存中的位置, onDeactivated记录位置到缓存
onActivated(() => {
if(useStore.scrollList.get(routeName)) {
const top = useStore.scrollList.get(routeName)
refList.value.setScrollTop(Number(top))
}
});
onDeactivated(() => {
const top = refList.value.getScrollTop()
useStore.scrollList.set(routeName, top)
});
这里定义一个方法,设置scrollTop使用了原生javascript的api
const setScrollTop = (value: any) => {
const dom = document.querySelector('.van-pull-refresh')
dom!.scrollTop = value
}
同时高度怎么获取要先注册scroll事件,然后通过getScrollTop 获取当前滚动条的位置进行保存即可
onMounted(() => {
scrollDom.value = document.querySelector('.van-pull-refresh') as HTMLElement
const throttledFun = useThrottleFn(() => {
console.log(scrollDom.value?.scrollTop, 'addEventListener')
state.scrollTop = scrollDom.value!.scrollTop
}, 500)
if(scrollDom.value) {
scrollDom.value.addEventListener('scroll',throttledFun)
}
})
const getScrollTop = () => {
console.log('scrollDom.vaue', scrollDom.value?.scrollTop)
return state.scrollTop
}
上面注册scroll事件中使用了一个useThrottleFn,这个类库是@vueuse/core中提供的,其中封装了很多工具都非常不错,用兴趣的可以研究研究
https://vueuse.org/shared/usethrottlefn/#usethrottlefn
此时也可以查看找到实例的vnode查找到keepalive,是在keepalive紧挨着的子组件里
const instance = getCurrentInstance()
console.log(instance.vnode.parent) // 这里便是keepalive组件vnode
// 如果是在开发环境中可以查看到cache对象
instance.vnode.parent.__v_cache
// vue源码中,在dev环境对cache进行暴露,生产环境是看不到的
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
;(instance as any).__v_cache = cache
}
4、vue3 keepalive源码调试
1、克隆代码
git clone git@github.com:vuejs/core.git
2、安装依赖
pnpm i
3、如果不能使用pnpm,可以先通过npm安装一下
npm i pnpm -g
4、安装完成以后,找到根目录package.json文件中的scripts
// 在dev命令后添加 --source-map是从已转换的代码,映射到原始的源文件
"dev": "node scripts/dev.js --sourcemap"
参考 https://www.jb51.net/article/154583.htm
5、执行pnpm run dev则会build vue源码
pnpm run dev
//则会出现以下,代表成功了(2022年5月27日),后期vue源代码作者可能会更新,相应的提示可能发生变更,请注意一下
> @3.2.36 dev H:\github\sourceCode\core
> node scripts/dev.js --sourcemap
watching: packages\vue\dist\vue.global.js
//到..\..\core\packages\vue\dist便可以看到编译成功,以及可以查看到examples样例demo页面
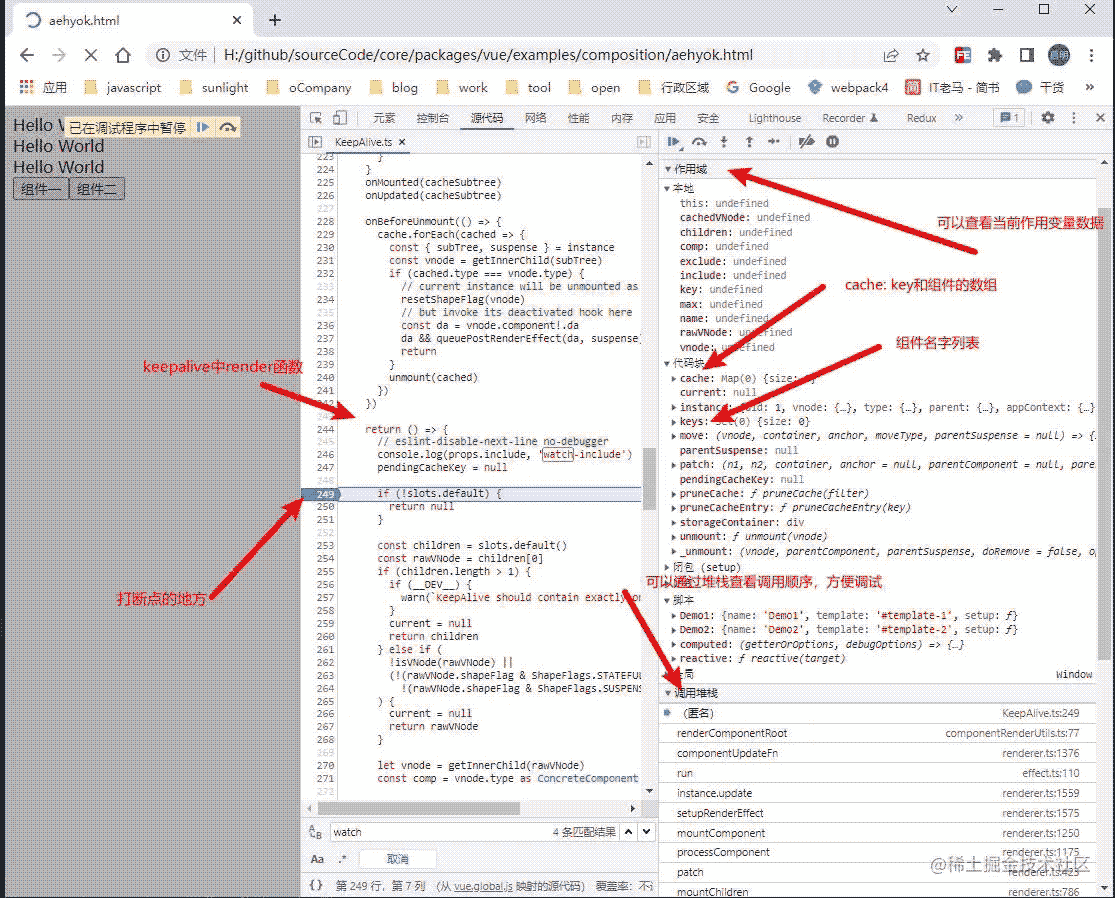
6、然后在 ....\core\packages\vue\examples\composition中添加一个aehyok.html文件,将如下代码进行拷贝,然后通过chrome浏览器打开,F12,找到源代码的Tab页面,通过快捷键Ctrl+ P 输入KeepAlive便可以找到这个组件,然后通过左侧行标右键就可以添加断点,进行调试,也可以通过右侧的【调用堆栈】进行快速跳转代码进行调试。
<script src="../../dist/vue.global.js"></script>
<script type="text/x-template" id="template-1">
<div>template-1</div>
<div>template-1</div>
</script>
<script type="text/x-template" id="template-2">
<div>template-2</div>
<div>template-2</div>
</script>
<script>
const { reactive, computed } = Vue
const Demo1 = {
name: 'Demo1',
template: '#template-1',
setup(props) {
}
}
const Demo2 = {
name: 'Demo2',
template: '#template-2',
setup(props) {
}
}
</script>
<!-- App template (in DOM) -->
<div id="demo">
<div>Hello World</div>
<div>Hello World</div>
<div>Hello World</div>
<button @click="changeClick(1)">组件一</button>
<button @click="changeClick(2)">组件二</button>
<keep-alive :include="includeCache">
<component :is="componentCache" :key="componentName" v-if="componentName" />
</keep-alive>
</div>
<!-- App script -->
<script>
Vue.createApp({
components: {
Demo1,
Demo2
},
data: () => ({
includeCache: [],
componentCache: '',
componentName: '',
}),
methods:{
changeClick(type) {
if(type === 1) {
if(!this.includeCache.includes('Demo1')) {
this.includeCache.push('Demo1')
}
console.log(this.includeCache, '000')
this.componentCache = Demo1
this.componentName = 'Demo1'
}
if(type === 2) {
if(!this.includeCache.includes('Demo2')) {
this.includeCache.push('Demo2')
}
console.log(this.includeCache, '2222')
this.componentName = 'Demo2'
this.componentCache = Demo2
}
}
}
}).mount('#demo')
</script>
7、调试源码发现 keepalive中的render函数(或者说时setup中的return 函数)在子组件切换时就会去执行,变更逻辑缓存
- 第一次进入页面初始化keepalive组件会执行一次,
- 然后点击组件一,再次执行render函数
- 然后点击组件二,会再次执行render函数
8、调试截图说明
9、调试操作,小视频观看
5、vue3 keealive源码粗浅分析
通过查看vue3 KeepAlive.ts源码,源码路径:https://github.com/vuejs/core/blob/main/packages/runtime-core/src/components/KeepAlive.ts
// 在setup初始化中,先获取keepalive实例
// getCurrentInstance() 可以获取当前组件的实例
const instance = getCurrentInstance()!
// KeepAlive communicates with the instantiated renderer via the
// ctx where the renderer passes in its internals,
// and the KeepAlive instance exposes activate/deactivate implementations.
// The whole point of this is to avoid importing KeepAlive directly in the
// renderer to facilitate tree-shaking.
const sharedContext = instance.ctx as KeepAliveContext
// if the internal renderer is not registered, it indicates that this is server-side rendering,
// for KeepAlive, we just need to render its children
/// SSR 判断,暂时可以忽略掉即可。
if (__SSR__ && !sharedContext.renderer) {
return () => {
const children = slots.default && slots.default()
return children && children.length === 1 ? children[0] : children
}
}
// 通过Map存储缓存vnode,
// 通过Set存储缓存的key(在外面设置的key,或者vnode的type)
const cache: Cache = new Map()
const keys: Keys = new Set()
let current: VNode | null = null
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
;(instance as any).__v_cache = cache
}
const parentSuspense = instance.suspense
const {
renderer: {
p: patch,
m: move,
um: _unmount,
o: { createElement }
}
} = sharedContext
// 创建了隐藏容器
const storageContainer = createElement('div')
// 在实例上注册两个钩子函数 activate, deactivate
sharedContext.activate = (vnode, container, anchor, isSVG, optimized) => {
const instance = vnode.component!
move(vnode, container, anchor, MoveType.ENTER, parentSuspense)
// in case props have changed
patch(
instance.vnode,
vnode,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
vnode.slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
instance.isDeactivated = false
if (instance.a) {
invokeArrayFns(instance.a)
}
const vnodeHook = vnode.props && vnode.props.onVnodeMounted
if (vnodeHook) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, instance.parent, vnode)
}
}, parentSuspense)
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
// Update components tree
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
}
sharedContext.deactivate = (vnode: VNode) => {
const instance = vnode.component!
move(vnode, storageContainer, null, MoveType.LEAVE, parentSuspense)
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
if (instance.da) {
invokeArrayFns(instance.da)
}
const vnodeHook = vnode.props && vnode.props.onVnodeUnmounted
if (vnodeHook) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, instance.parent, vnode)
}
instance.isDeactivated = true
}, parentSuspense)
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
// Update components tree
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
}
// 组件卸载
function unmount(vnode: VNode) {
// reset the shapeFlag so it can be properly unmounted
resetShapeFlag(vnode)
_unmount(vnode, instance, parentSuspense, true)
}
// 定义 include和exclude变化时,对缓存进行动态处理
function pruneCache(filter?: (name: string) => boolean) {
cache.forEach((vnode, key) => {
const name = getComponentName(vnode.type as ConcreteComponent)
if (name && (!filter || !filter(name))) {
pruneCacheEntry(key)
}
})
}
function pruneCacheEntry(key: CacheKey) {
const cached = cache.get(key) as VNode
if (!current || cached.type !== current.type) {
unmount(cached)
} else if (current) {
// current active instance should no longer be kept-alive.
// we can't unmount it now but it might be later, so reset its flag now.
resetShapeFlag(current)
}
cache.delete(key)
keys.delete(key)
}
// 可以发现通过include 可以配置被显示的组件,
// 当然也可以设置exclude来配置不被显示的组件,
// 组件切换时随时控制缓存
watch(
() => [props.include, props.exclude],
([include, exclude]) => {
include && pruneCache(name => matches(include, name))
exclude && pruneCache(name => !matches(exclude, name))
},
// prune post-render after `current` has been updated
{ flush: 'post', deep: true }
)
// 定义当前组件Key
// cache sub tree after render
let pendingCacheKey: CacheKey | null = null
// 这是一个重要的方法,设置缓存
const cacheSubtree = () => {
// fix #1621, the pendingCacheKey could be 0
if (pendingCacheKey != null) {
cache.set(pendingCacheKey, getInnerChild(instance.subTree))
}
}
onMounted(cacheSubtree)
onUpdated(cacheSubtree)
// 组件卸载的时候,对缓存列表进行循环判断处理
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
cache.forEach(cached => {
const { subTree, suspense } = instance
const vnode = getInnerChild(subTree)
if (cached.type === vnode.type) {
// current instance will be unmounted as part of keep-alive's unmount
resetShapeFlag(vnode)
// but invoke its deactivated hook here
const da = vnode.component!.da
da && queuePostRenderEffect(da, suspense)
return
}
unmount(cached)
})
})
// 同时在keepAlive组件setup生命周期中,return () => {} 渲染的时候,对组件进行判断逻辑处理,同样对include和exclude判断渲染。
// 判断keepalive组件中的子组件,如果大于1个的话,直接警告处理了
// 另外如果渲染的不是虚拟dom(vNode),则直接返回渲染即可。
return () => {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-debugger
console.log(props.include, 'watch-include')
pendingCacheKey = null
if (!slots.default) {
return null
}
const children = slots.default()
const rawVNode = children[0]
if (children.length > 1) {
if (__DEV__) {
warn(`KeepAlive should contain exactly one component child.`)
}
current = null
return children
} else if (
!isVNode(rawVNode) ||
(!(rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) &&
!(rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE))
) {
current = null
return rawVNode
}
// 接下来处理时Vnode虚拟dom的情况,先获取vnode
let vnode = getInnerChild(rawVNode)
// 节点类型
const comp = vnode.type as ConcreteComponent
// for async components, name check should be based in its loaded
// inner component if available
// 获取组件名称
const name = getComponentName(
isAsyncWrapper(vnode)
? (vnode.type as ComponentOptions).__asyncResolved || {}
: comp
)
//这个算是最熟悉的通过props传递进行的参数,进行解构
const { include, exclude, max } = props
// include判断 组件名称如果没有设置, 或者组件名称不在include中,
// exclude判断 组件名称有了,或者匹配了
// 对以上两种情况都不进行缓存处理,直接返回当前vnode虚拟dom即可。
if (
(include && (!name || !matches(include, name))) ||
(exclude && name && matches(exclude, name))
) {
current = vnode
return rawVNode
}
// 接下来开始处理有缓存或者要缓存的了
// 先获取一下vnode的key设置,然后看看cache缓存中是否存在
const key = vnode.key == null ? comp : vnode.key
const cachedVNode = cache.get(key)
// 这一段可以忽略了,好像时ssContent相关,暂时不管了,没看明白??
// clone vnode if it's reused because we are going to mutate it
if (vnode.el) {
vnode = cloneVNode(vnode)
if (rawVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
rawVNode.ssContent = vnode
}
}
// 上面判断了,如果没有设置key,则使用vNode的type作为key值
pendingCacheKey = key
//判断上面缓存中是否存在vNode
// if 存在的话,就将缓存中的vnode复制给当前的vnode
// 同时还判断了组件是否为过渡组件 transition,如果是的话 需要注册过渡组件的钩子
// 同时先删除key,然后再重新添加key
// else 不存在的话,就添加到缓存即可
// 并且要判断一下max最大缓存的数量是否超过了,超过了,则通过淘汰LPR算法,删除最旧的一个缓存
// 最后又判断了一下是否为Suspense。也是vue3新增的高阶组件。
if (cachedVNode) {
// copy over mounted state
vnode.el = cachedVNode.el
vnode.component = cachedVNode.component
if (vnode.transition) {
// recursively update transition hooks on subTree
setTransitionHooks(vnode, vnode.transition!)
}
// avoid vnode being mounted as fresh
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE
// make this key the freshest
keys.delete(key)
keys.add(key)
} else {
keys.add(key)
// prune oldest entry
if (max && keys.size > parseInt(max as string, 10)) {
pruneCacheEntry(keys.values().next().value)
}
}
// avoid vnode being unmounted
vnode.shapeFlag |= ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE
current = vnode
return isSuspense(rawVNode.type) ? rawVNode : vnode
6、总结
通过这次查看vue3 keepalive源码发现,其实也没那么难,当然这次查看源代码也只是粗略查看,并没有看的那么细,主要还是先解决问题。动动手调试一下,有时候真的就是不逼一下自己都不知道自己有多么的优秀。原来我也能稍微看看源代码了。以后有空可以多看看vue3源代码,学习一下vue3的精髓。了解vue3更为细节的一些知识点。
本文涉及到的代码后续会整理到该代码仓库中
https://github.com/aehyok/vue-qiankun
最后自己每天工作中的笔记记录仓库,主要以文章链接和问题处理方案为主
https://github.com/aehyok/2022
以上就是vue3 keepalive源码解析解决线上问题的详细内容,更多关于vue3 keepalive的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

