RocketMQ存储文件的实现
RocketMQ存储路径默认是${ROCKRTMQ_HOME}/store,主要存储消息、主题对应的消息队列的索引等。
1、概述
查看其目录文件

commitlog:消息的存储目录config:运行期间一些配置信息
consumequeue:消息消费队列存储目录index:消息索引文件存储目录abort:如果存在abort文件说明Broker非正常关闭,该文件默认启动时创建,正常退出时删除checkpoint:文件检测点。存储commitlog文件最后一次刷盘时间戳、consumequeue最后一次刷盘时间、index索引文件最后一次刷盘时间戳。
2、文件简介
2.1、commitlog文件
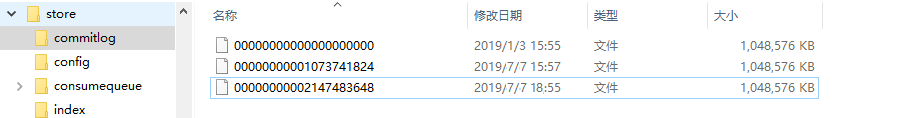
commitlog文件的存储地址:$HOME\store\commitlog${fileName},每个文件的大小默认1G =102410241024,commitlog的文件名fileName,名字长度为20位,左边补零,剩余为起始偏移量;比如00000000000000000000代表了第一个文件,起始偏移量为0,文件大小为1G=1073741824;当这个文件满了,第二个文件名字为00000000001073741824,起始偏移量为1073741824,以此类推,第三个文件名字为00000000002147483648,起始偏移量为2147483648 ,消息存储的时候会顺序写入文件,当文件满了,写入下一个文件。
commitlog目录下的文件主要存储消息,每条消息的长度不同,查看其存储的逻辑视图,每条消息的前面4个字节存储该条消息的总长度。

文件的消息单元存储详细信息
| 编号 | 字段简称 | 字段大小(字节) | 字段含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | msgSize | 4 | 代表这个消息的大小 |
| 2 | MAGICCODE | 4 | MAGICCODE = daa320a7 |
| 3 | BODY CRC | 4 | 消息体BODY CRC 当broker重启recover时会校验 |
| 4 | queueId | 4 | |
| 5 | flag | 4 | |
| 6 | QUEUEOFFSET | 8 | 这个值是个自增值不是真正的consume queue的偏移量,可以代表这个consumeQueue队列或者tranStateTable队列中消息的个数,若是非事务消息或者commit事务消息,可以通过这个值查找到consumeQueue中数据,QUEUEOFFSET * 20才是偏移地址;若是PREPARED或者Rollback事务,则可以通过该值从tranStateTable中查找数据 |
| 7 | PHYSICALOFFSET | 8 | 代表消息在commitLog中的物理起始地址偏移量 |
| 8 | SYSFLAG | 4 | 指明消息是事物事物状态等消息特征,二进制为四个字节从右往左数:当4个字节均为0(值为0)时表示非事务消息;当第1个字节为1(值为1)时表示表示消息是压缩的(Compressed);当第2个字节为1(值为2)表示多消息(MultiTags);当第3个字节为1(值为4)时表示prepared消息;当第4个字节为1(值为8)时表示commit消息;当第3/4个字节均为1时(值为12)时表示rollback消息;当第3/4个字节均为0时表示非事务消息 |
| 9 | BORNTIMESTAMP | 8 | 消息产生端(producer)的时间戳 |
| 10 | BORNHOST | 8 | 消息产生端(producer)地址(address:port) |
| 11 | STORETIMESTAMP | 8 | 消息在broker存储时间 |
| 12 | STOREHOSTADDRESS | 8 | 消息存储到broker的地址(address:port) |
| 13 | RECONSUMETIMES | 8 | 消息被某个订阅组重新消费了几次(订阅组之间独立计数),因为重试消息发送到了topic名字为%retry%groupName的队列queueId=0的队列中去了,成功消费一次记录为0; |
| 14 | PreparedTransaction Offset | 8 | 表示是prepared状态的事物消息 |
| 15 | messagebodyLength | 4 | 消息体大小值 |
| 16 | messagebody | bodyLength | 消息体内容 |
| 17 | topicLength | 1 | topic名称内容大小 |
| 18 | topic | topicLength | topic的内容值 |
| 19 | propertiesLength | 2 | 属性值大小 |
| 20 | properties | propertiesLength | propertiesLength大小的属性数据 |
2.2、consumequeue
RocketMQ基于主题订阅模式实现消息的消费,消费者关心的是主题下的所有消息。
但是由于不同的主题的消息不连续的存储在commitlog文件中,如果只是检索该消息文件可想而知会有多慢,为了提高效率,对应的主题的队列建立了索引文件,为了加快消息的检索和节省磁盘空间,每一个consumequeue条目存储了消息的关键信息commitog文件中的偏移量、消息长度、tag的hashcode值。

查看目录结构:
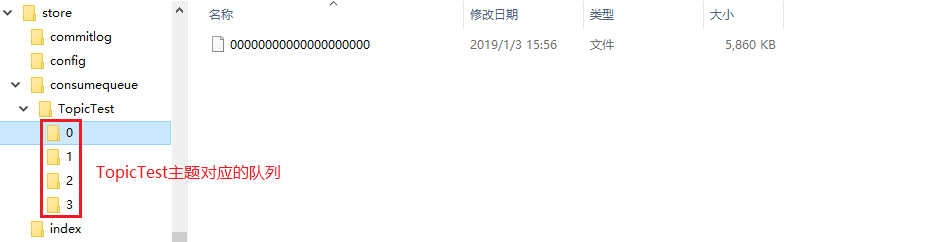
单个consumequeue文件中默认包含30万个条目,每个条目20个字节,所以每个文件的大小是固定的20w x 20字节,单个consumequeue文件可认为是一个数组,下标即为逻辑偏移量,消息的消费进度存储的偏移量即逻辑偏移量。
2.3、IndexFile
IndexFile:用于为生成的索引文件提供访问服务,通过消息Key值查询消息真正的实体内容。在实际的物理存储上,文件名则是以创建时的时间戳命名的,固定的单个IndexFile文件大小约为400M,一个IndexFile可以保存 2000W个索引;
2.3.1、IndexFile结构分析
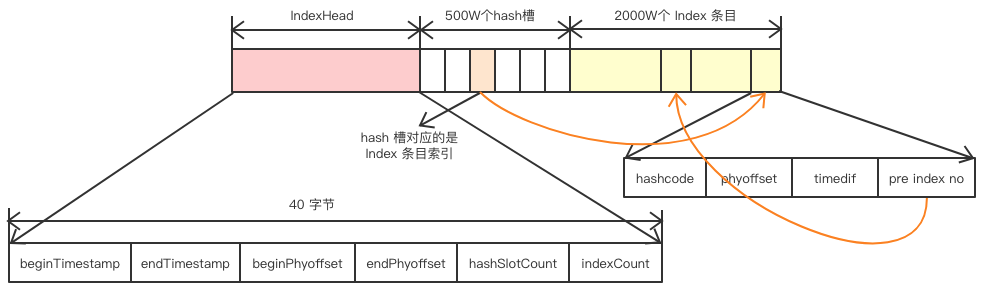
IndexHead 数据: beginTimestamp:该索引文件包含消息的最小存储时间 endTimestamp:该索引文件包含消息的最大存储时间 beginPhyoffset:该索引文件中包含消息的最小物理偏移量(commitlog 文件偏移量) endPhyoffset:该索引文件中包含消息的最大物理偏移量(commitlog 文件偏移量) hashSlotCount:hashslot个数,并不是 hash 槽使用的个数,在这里意义不大, indexCount:已使用的 Index 条目个数
Hash 槽: 一个 IndexFile 默认包含 500W 个 Hash 槽,每个 Hash 槽存储的是落在该 Hash 槽的 hashcode 最新的 Index 的索引
Index 条目列表 hashcode:key 的 hashcode phyoffset:消息对应的物理偏移量 timedif:该消息存储时间与第一条消息的时间戳的差值,小于 0 表示该消息无效 preIndexNo:该条目的前一条记录的 Index 索引,hash 冲突时,根据该值构建链表结构
2.3.2、IndexFile条目存储
RocketMQ将消息索引键与消息的偏移量映射关系写入IndexFile中,其核心的实现方法是public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp);参数含义分别是消息的索引、消息的物理偏移量、消息的存储时间。
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) {
//判断当前的条目数是否大于最大的允许的条目数
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() < this.indexNum) {
//获取KEY的hash值(正整数)
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
//计算hash槽的下标
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
//获取hash槽的物理地址
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos, hashSlotSize,
// false);
//获取hash槽中存储的数据
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
//判断值是否小于等于0或者 大于当前索引文件的最大条目
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()) {
slotValue = invalidIndex;
}
//计算当前消息存储时间与第一条消息时间戳的时间差
long timeDiff = storeTimestamp - this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp();
//秒
timeDiff = timeDiff / 1000;
if (this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() <= 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
} else if (timeDiff > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
timeDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else if (timeDiff < 0) {
timeDiff = 0;
}
//计算条目的物理地址 = 索引头部大小(40字节) + hash槽的大小(4字节)*槽的数量(500w) + 当前索引最大条目的个数*每index的大小(20字节)
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
//依次存入 key的hash值(4字节)+消息的物理偏移量(8字节)+消息存储时间戳和index文件的时间戳差(4字节)+当前hash槽的值(4字节)
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
//存储当前index中包含的条目数量存入hash槽中,覆盖原先hash槽的值
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
//更新文件索引的头信息,hash槽的总数、index条目的总数、最后消息的物理偏移量、最后消息的存储时间
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("putKey exception, Key: " + key + " KeyHashCode: " + key.hashCode(), e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
}
} else {
log.warn("Over index file capacity: index count = " + this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
+ "; index max num = " + this.indexNum);
}
return false;
}
以上详细了分析了IndexFile条目存储的业务逻辑
2.3.3、通过KEY查找消息

DefaultMessageStore类中的
public QueryMessageResult queryMessage(String topic, String key, int maxNum, long begin, long end)
中其核心方法是
QueryOffsetResult queryOffsetResult = this.indexService.queryOffset(topic, key, maxNum, begin, lastQueryMsgTime);
获取消息的物理存储地址,通过偏移量去commitLog中获取消息集。
public QueryOffsetResult queryOffset(String topic, String key, int maxNum, long begin, long end)
核心方法又是IndexFile类中的
public void selectPhyOffset(final List<Long> phyOffsets, final String key, final int maxNum, final long begin, final long end, boolean lock)
方法
public void selectPhyOffset(final List<Long> phyOffsets, final String key, final int maxNum,
final long begin, final long end, boolean lock) {
if (this.mappedFile.hold()) {
//获取key的hash信息
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
//获取hash槽的下标
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
//获取hash槽的物理地址
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
FileLock fileLock = null;
try {
if (lock) {
// fileLock = this.fileChannel.lock(absSlotPos,
// hashSlotSize, true);
}
//获取hash槽的值
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
// if (fileLock != null) {
// fileLock.release();
// fileLock = null;
// }
//判断值是否小于等于0或者 大于当前索引文件的最大条目
if (slotValue <= invalidIndex || slotValue > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
} else {
for (int nextIndexToRead = slotValue; ; ) {
if (phyOffsets.size() >= maxNum) {
break;
}
//计算条目的物理地址 = 索引头部大小(40字节) + hash槽的大小(4字节)*槽的数量(500w) + 当前索引最大条目的个数*每index的大小(20字节)
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ nextIndexToRead * indexSize;
//获取key的hash值
int keyHashRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos);
//获取消息的物理偏移量
long phyOffsetRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getLong(absIndexPos + 4);
//获取当前消息的存储时间戳与index文件的时间戳差值
long timeDiff = (long) this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8);
//获取前一个条目的信息(链表结构)
int prevIndexRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4);
if (timeDiff < 0) {
break;
}
timeDiff *= 1000L;
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
//判断该消息是否在查询的区间
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
//判断key的hash值是否相等并且在查询的时间区间内
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) {
//加入到物理偏移量的List中
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}
if (prevIndexRead <= invalidIndex
|| prevIndexRead > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| prevIndexRead == nextIndexToRead || timeRead < begin) {
break;
}
//继续前一个条目信息获取进行匹配
nextIndexToRead = prevIndexRead;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("selectPhyOffset exception ", e);
} finally {
if (fileLock != null) {
try {
fileLock.release();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Failed to release the lock", e);
}
}
this.mappedFile.release();
}
}
}
1、根据查询的 key 的 hashcode%slotNum 得到具体的槽的位置( slotNum 是一个索引文件里面包含的最大槽的数目,例如图中所示 slotNum=5000000)。
2、根据 slotValue( slot 位置对应的值)查找到索引项列表的最后一项(倒序排列, slotValue 总是指向最新的一个 索引项)。
3、遍历索引项列表返回查询时间范围内的结果集(默认一次最大返回的 32 条记彔)
4、Hash 冲突;寻找 key 的 slot 位置时相当于执行了两次散列函数,一次 key 的 hash,一次 key 的 hash 值取模,因此返里存在两次冲突的情况;第一种, key 的 hash 不同但模数相同,此时查询的时候会在比较一次key 的hash 值(每个索引项保存了 key 的 hash 值),过滤掉 hash 值不相等的项。第二种, hash 值相等但 key 不等,出于性能的考虑冲突的检测放到客户端处理( key 的原始值是存储在消息文件中的,避免对数据文件的解析),客户端比较一次消息体的 key 是否相同
2.4、checkpoint
checkpoint文件的作用是记录commitlog、consumequeue、index文件的刷盘时间点,文件固定长度4k,其中只用了该文件的前24个字节。查看其存储格式

physicMsgTimestamp:commitlog文件刷盘时间点
logicsMsgTimestamp:消息的消费队列文件刷盘时间点
indexMsgTimestamp:索引文件刷盘时间点
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。

