springboot 基于Tomcat容器的自启动流程分析
Springboot 内置了Tomcat的容器,我们今天来说一下Springboot的自启动流程。
一、Spring通过注解导入Bean大体可分为四种方式,我们主要来说以下Import的两种实现方法:
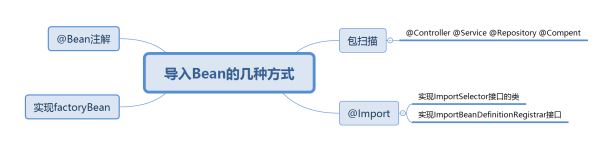
1、通过实现ImportSerlector接口,实现Bean加载:
public class TestServiceImpl {
public void testImpl() {
System.out.println("我是通过importSelector导入进来的service");
}
}
public class TestService implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.ycdhz.service.TestServiceImpl"};
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(value = {TestService.class})
public class TestConfig {
}
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private TestServiceImpl testServiceImpl;
@RequestMapping("testImpl")
public String testTuling() {
testServiceImpl.testImpl();
return "Ok";
}
}
2、 通过实现ImportSerlector接口,实现Bean加载:
public class TestService {
public TestService() {
System.out.println("我是通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar导入进来的组件");
}
}
public class TestImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义一个BeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(TestService.class);
//把自定义的bean定义导入到容器中
registry.registerBeanDefinition("testService",beanDefinition);
}
}
@Configuration
@Import(TestImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)
public class TestConfig {
}
二、 Springboot启动过程中会自动装配
我们从spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.6.RELEASE.jar下搜索到Tomcat的相关配置,发现有两个自动装配类,分别包含了三个定制器(面向对象的单一职责原则),还有一个工厂类。

2.1、TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer:定制Servlet和Reactive服务器通用的Tomcat特定功能。
public class TomcatWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties properties = this.serverProperties;
ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcatProperties = properties.getTomcat();
PropertyMapper propertyMapper = PropertyMapper.get();
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getBasedir).whenNonNull()
.to(factory::setBaseDirectory);
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getBackgroundProcessorDelay).whenNonNull()
.as(Duration::getSeconds).as(Long::intValue)
.to(factory::setBackgroundProcessorDelay);
customizeRemoteIpValve(factory);
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxThreads).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxThreads) -> customizeMaxThreads(factory,
tomcatProperties.getMaxThreads()));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMinSpareThreads).when(this::isPositive)
.to((minSpareThreads) -> customizeMinThreads(factory, minSpareThreads));
propertyMapper.from(() -> determineMaxHttpHeaderSize()).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxHttpHeaderSize) -> customizeMaxHttpHeaderSize(factory,
maxHttpHeaderSize));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxHttpPostSize)
.when((maxHttpPostSize) -> maxHttpPostSize != 0)
.to((maxHttpPostSize) -> customizeMaxHttpPostSize(factory,
maxHttpPostSize));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getAccesslog)
.when(ServerProperties.Tomcat.Accesslog::isEnabled)
.to((enabled) -> customizeAccessLog(factory));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getUriEncoding).whenNonNull()
.to(factory::setUriEncoding);
propertyMapper.from(properties::getConnectionTimeout).whenNonNull()
.to((connectionTimeout) -> customizeConnectionTimeout(factory,
connectionTimeout));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getMaxConnections).when(this::isPositive)
.to((maxConnections) -> customizeMaxConnections(factory, maxConnections));
propertyMapper.from(tomcatProperties::getAcceptCount).when(this::isPositive)
.to((acceptCount) -> customizeAcceptCount(factory, acceptCount));
customizeStaticResources(factory);
customizeErrorReportValve(properties.getError(), factory);
}
}
2.2、ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer:WebServerFactoryCustomizer 将ServerProperties属性应用于Tomcat web服务器。
public class ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer implements
WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
PropertyMapper map = PropertyMapper.get().alwaysApplyingWhenNonNull();
map.from(this.serverProperties::getPort).to(factory::setPort);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getAddress).to(factory::setAddress);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextPath)
.to(factory::setContextPath);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getApplicationDisplayName)
.to(factory::setDisplayName);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getSession).to(factory::setSession);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getSsl).to(factory::setSsl);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getJsp).to(factory::setJsp);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getCompression).to(factory::setCompression);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getHttp2).to(factory::setHttp2);
map.from(this.serverProperties::getServerHeader).to(factory::setServerHeader);
map.from(this.serverProperties.getServlet()::getContextParameters)
.to(factory::setInitParameters);
}
}
2.3、ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer :WebServerFactoryCustomizer 将ServerProperties属性应用于Tomcat web服务器。
public class TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer
implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<TomcatServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
@Override
public void customize(TomcatServletWebServerFactory factory) {
ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcatProperties = this.serverProperties.getTomcat();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(tomcatProperties.getAdditionalTldSkipPatterns())) {
factory.getTldSkipPatterns()
.addAll(tomcatProperties.getAdditionalTldSkipPatterns());
}
if (tomcatProperties.getRedirectContextRoot() != null) {
customizeRedirectContextRoot(factory,
tomcatProperties.getRedirectContextRoot());
}
if (tomcatProperties.getUseRelativeRedirects() != null) {
customizeUseRelativeRedirects(factory,
tomcatProperties.getUseRelativeRedirects());
}
}
}
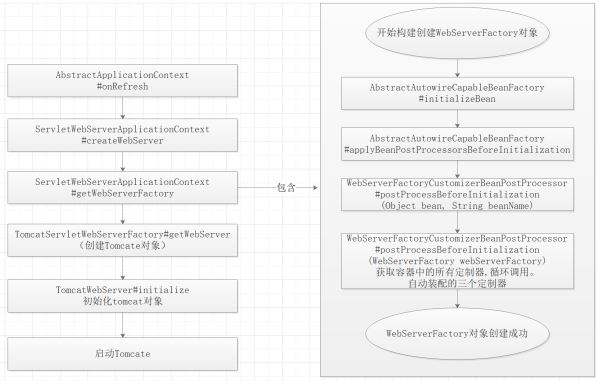
三、有了TomcatServletWebServerFactory,相当于有了Spring加载的入口
通过AbstractApplicationContext#onReFresh()在IOC 容器中的带动tomcat启动,然后在接着执行 ioc容器的其他步骤。
我们通过断点可以观察Tomcat加载的整个生命周期,以及三个定制器的加载过程。
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
//设置是否自动启动
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
//创建Tomcat引擎
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//刷新上下文
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//准备启动
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
TomcatWebServer.logger
.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource())
&& Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(),
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}
备注: 在这个过程中我们需要了解Bean的生命周期,Tomcat的三个定制器均在BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar(Bean后置处理器)过程中加载;
构造方法-->Bean后置处理器Before-->InitializingBean-->init-method-->Bean后置处理器After
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//构造方法
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
......
return exposedObject;
}
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Bean后置处理器Before
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Bean后置处理器After
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
总结
到此这篇关于springboot 基于Tomcat容器的自启动流程分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot tomcat自启动内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

