Spring Boot 自定义starter的示例代码
SpringBoot 个人感觉特点:
1)众多库的集合(各种Starter),方便快速构建应用系统。
2)自动配置spring(通过AutoConfiguration机制),简化配置,也方便扩展新的Starter。
3)内嵌web容器,无需WAR部署。
创建一个用maven构建的springboot项目
pom文件配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xjw.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>hellostarter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>hello-spring-boot-starter</name>
<description>测试自定义starter</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
定义一个pojo用来接收properties中配置的信息
package com.xjw;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
public class HelloServiceProperteis {
private String msg;
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties:用来标识这个pojo是一个用来接收指定前缀的资源配置值
prefix:表示在配置文件中配置项前缀[/code]
编写一个Service用来对外提供服务
package com.xjw;
public class HelloService {
private String msg;
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello " + msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
配置一个pojo用来读取上面配置的HelloServiceProperteis
package com.xjw;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HelloServiceProperteis.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(HelloService.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "hello", value = "enable", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HelloAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloServiceProperteis helloServiceProperteis;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HelloService.class)
public HelloService helloService() {
HelloService helloService = new HelloService();
helloService.setMsg(helloServiceProperteis.getMsg());
return helloService;
}
}
@Configuration:标识此类为一个spring配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HelloServiceProperteis.class):启动配置文件,value用来指定我们要启用的配置类,可以有多个,多个时我们可以这么写value={xxProperties1.class,xxProperteis2.class....}
@ConditionalOnClass(HelloService.class):表示当classPath下存在HelloService.class文件时改配置文件类才有效
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "hello", value = "enable", matchIfMissing = true):表示只有我们的配置文件是否配置了以hello为前缀的资源项值,并且在该资源项值为enable,如果没有配置我们默认设置为enable[/code]
最后在src/main/resources 文件夹下新建文件夹 META-INF,在新建的META-INF文件夹下新建spring.factories
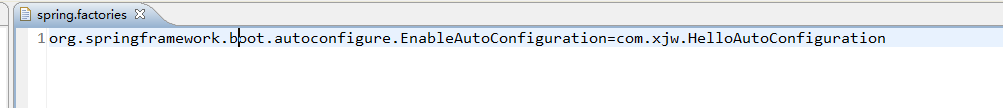
在新建的spring.factories文件中配置自动启动类为我们之前编写的HelloAutoConfiguration 类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.xjw.HelloAutoConfiguration
然后就可以在其他的spring-boot项目中使用我们刚刚新建的starter了,我们来测试一下
在新建一个spring-boot项目,pom.xml配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xjw.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>hellostarter.test</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>hello-spring-boot-starter-test</name>
<description>测试自定义starter</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xjw.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>hellostarter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
然后我们直接在咋们的启动类中中尝试使用以下我们上面定义的starter提供的HelloService:
package com.xjw;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloSpringBootStarterTestApplication {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return helloService.sayHello();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloSpringBootStarterTestApplication.class, args);
}
}
接着我们修改测试项目中的application.properteis,加入如下配置:
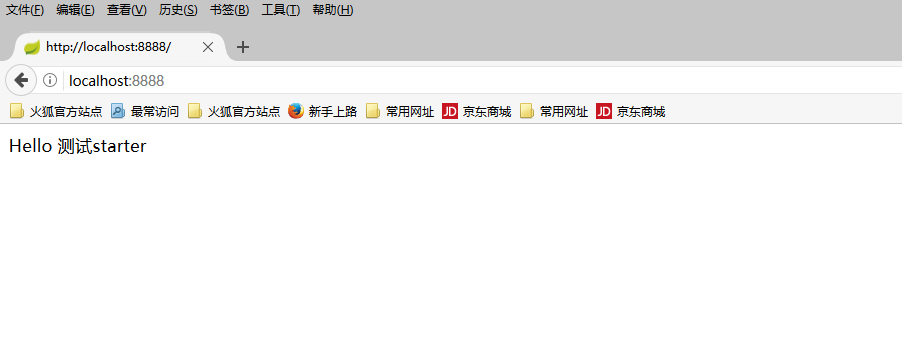
debug=true server.port=8888 #hello=enable hello.msg=测试starter
最后启动项目,观察控制台输出的内容中依赖的starter,从Positive matches下我们可以看到有这么一句:
HelloAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'com.xjw.HelloService'; @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnProperty (hello.enable) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
或者我们打开项目依赖树也能找到我们的starter ,这说明spring已经自动的启动了我们的starter了,打开浏览器输入地址:http://localhost:8888/将会看到如下结果
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

