Java集合 LinkedList的原理及使用详解
LinkedList和ArrayList一样是集合List的实现类,虽然较之ArrayList,其使用场景并不多,但同样有用到的时候,那么接下来,我们来认识一下它。
一. 定义一个LinkedList
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> tempList = new ArrayList<>();
tempList.add("牛魔王");
tempList.add("蛟魔王");
tempList.add("鹏魔王");
tempList.add("狮驼王");
tempList.add("猕猴王");
tempList.add("禺贼王");
tempList.add("美猴王");
List<String> stringList2 = new LinkedList<>(tempList);
}
上面代码中采用了两种方式来定义LinkedList,可以定义一个空集合,也可以传递已有的集合,将其转化为LinkedList。我们看一下源码
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
}
LinkedList继承了AbstractSequentialList类,实现了List接口,AbstractSequentialList中已经实现了很多方法,如get(int index)、set(int index, E element)、add(int index, E element) 和 remove(int index),这些方法是我们集合操作时使用最多的,不过这些方法在LinkedList中都已经被重写了,而抽象方法在LinkedList中有了具体实现。因此我们回到LinkedList类
LinkedList类中定义了三个变量
- size:集合的长度
- first:双向链表头部节点
- last:双向链表尾部节点
针对first变量和last变量,我们看到是Node类的实体,这是一个静态内部类,关于静态内部类的讲解,我们在static五大应用场景一章已经有说明
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
我们知道LinkedList是通过双向链表实现的,而双向链表就是通过Node类来体现的,类中通过item变量保存了当前节点的值,通过next变量指向下一个节点,通过prev变量指向上一个节点。
二. LinkedList常用方法
1. get(int index)
我们知道随机读取元素不是LinkedList所擅长的,读取效率比起ArrayList也低得多,那么我来看一下为什么
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* 返回一个指定索引的非空节点.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
从上述代码中我们可以看到get(int index)方法是通过node(int index)来实现的,它的实现机制是:
比较传入的索引参数index与集合长度size/2,如果是index小,那么从第一个顺序循环,直到找到为止;如果index大,那么从最后一个倒序循环,直到找到为止。也就是说越靠近中间的元素,调用get(int index方法遍历的次数越多,效率也就越低,而且随着集合的越来越大,get(int index)执行性能也会指数级降低。因此在使用LinkedList的时候,我们不建议使用这种方式读取数据,可以使用getFirst(),getLast()方法,将直接用到类中的first和last变量。
2. add(E e) 和 add(int index, E element)
大家都在说LinkedList插入、删除操作效率比较高,以stringList.add(“猪八戒”)为例来看到底发生了什么?
在LinkedList中我们找到add(E e)方法的源码
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 设置元素e为最后一个元素
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
很好理解:
情况1:假如stringList为空,那么添加进来的node就是first,也是last,这个node的prev和next都为null;

情况2:假如stringList不为空,那么添加进来的node就是last,node的prev指向以前的最后一个元素,node的next为null;同时以前的最后一个元素的next.
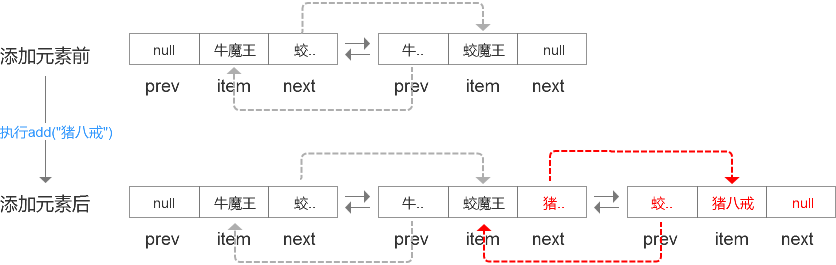
而如果通过stringList.add(1, “猪八戒”)这种方式将元素添加到集合中呢?
//在指定位置添加一个元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* 在一个非空节点前插入一个元素
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
其实从代码中看到和add(E e)的代码实现没有本质区别,都是通过新建一个Node实体,同时指定其prev和next来实现,不同点在于需要调用node(int index)通过传入的index来定位到要插入的位置,这个也是比较耗时的,参考上面的get(int index)方法。
其实看到这里,大家也都明白了。
LinkedList插入效率高是相对的,因为它省去了ArrayList插入数据可能的数组扩容和数据元素移动时所造成的开销,但数据扩容和数据元素移动却并不是时时刻刻都在发生的。
3. remove(Object o) 和 remove(int index)
这里removeFirst()和removeLast()就不多说了,会用到类中定义的first和last变量,非常简单,我们看一下remove(Object o) 和 remove(int index)源码
//删除某个对象
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//删除某个位置的元素
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//删除某节点,并将该节点的上一个节点(如果有)和下一个节点(如果有)关联起来
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
其实实现都非常简单,先找到要删除的节点,remove(Object o)方法遍历整个集合,通过 == 或 equals方法进行判断;remove(int index)通过node(index)方法。
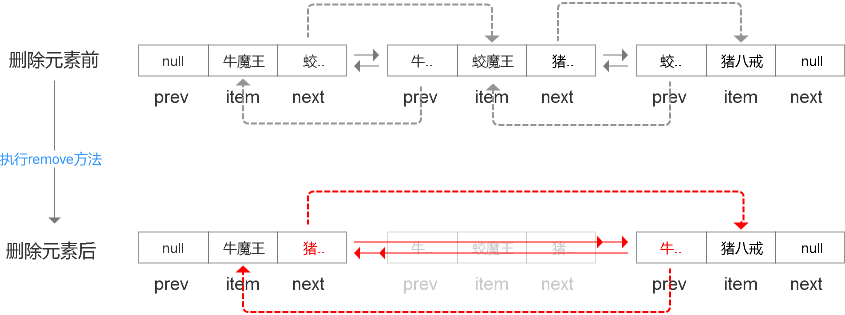
4. LinkedList遍历
我们主要列举一下三种常用的遍历方式,
普通for循环,增强for循环,Iterator迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = getLinkedList();
//通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
listByNormalFor(list);
//通过增强for循环遍历LinkedList
listByStrengThenFor(list);
//通过快迭代器遍历LinkedList
listByIterator(list);
}
/**
* 构建一个LinkedList集合,包含元素50000个
* @return
*/
private static LinkedList<Integer> getLinkedList() {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++){
list.add(i);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void listByNormalFor(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
list.get(i);
}
// 记录用时
long interval = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("listByNormalFor:" + interval + " ms");
}
/**
* 通过增强for循环遍历LinkedList
* @param list
*/
public static void listByStrengThenFor(LinkedList<Integer> list){
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Integer i : list) { }
// 记录用时
long interval = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("listByStrengThenFor:" + interval + " ms");
}
/**
* 通过快迭代器遍历LinkedList
*/
private static void listByIterator(LinkedList<Integer> list) {
// 记录开始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(Iterator iter = list.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
iter.next();
}
// 记录用时
long interval = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("listByIterator:" + interval + " ms");
}
执行结果如下:
listByNormalFor:1067 ms
listByStrengThenFor:3 ms
listByIterator:2 ms
通过普通for循环随机访问的方式执行时间远远大于迭代器访问方式,这个我们可以理解,在前面的get(int index)方法中已经有过说明,那么为什么增强for循环能做到迭代器遍历差不多的效率?
通过反编译工具后得到如下代码
public static void listByStrengThenFor(LinkedList<Integer> list)
{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Integer localInteger;
for (Iterator localIterator = list.iterator(); localIterator.hasNext();
localInteger = (Integer)localIterator.next()) {}
long interval = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
System.out.println("listByStrengThenFor:" + interval + " ms");
}
很明显了,增强for循环遍历时也调用了迭代器Iterator,不过多了一个赋值的过程。
还有类似于pollFirst(),pollLast()取值后删除的方法也能达到部分的遍历效果。
三. 总结
本文基于java8从定义一个LinkList入手,逐步展开,从源码角度分析LinkedList双向链表的结构是如何构建的,同时针对其常用方法进行分析,包括get,add,remove以及常用的遍历方法,并简单的说明了它的插入、删除操作为何相对高效,而取值操作性能相对较低,若有不对之处,请批评指正,望共同进步,谢谢!
到此这篇关于Java集合 LinkedList的原理及使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java LinkedList内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

