Spring Cloud + Nacos + Seata整合过程(分布式事务解决方案)
目录
- 一、简介
- 二、seata-server部署
- 1、官网下载
- 2、解压到本地
- 3、修改配置文件
- 4、seata数据库初始化
- 5、业务数据库
- 6、启动seata-server
- 三、微服务项目集成Seata
- 1、引入依赖
- 2、配置文件
一、简介
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于在微服务架构下提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。
2019 年 1 月,阿里巴巴中间件团队发起了开源项目 Fescar(Fast & EaSy Commit And Rollback),和社区一起共建开源分布式事务解决方案。Fescar 的愿景是让分布式事务的使用像本地事务的使用一样,简单和高效,并逐步解决开发者们遇到的分布式事务方面的所有难题。
Fescar 开源后,蚂蚁金服加入 Fescar 社区参与共建,并在 Fescar 0.4.0 版本中贡献了 TCC 模式。
为了打造更中立、更开放、生态更加丰富的分布式事务开源社区,经过社区核心成员的投票,大家决定对 Fescar 进行品牌升级,并更名为 Seata,意为:Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture,是一套一站式分布式事务解决方案。

二、seata-server部署
1、官网下载
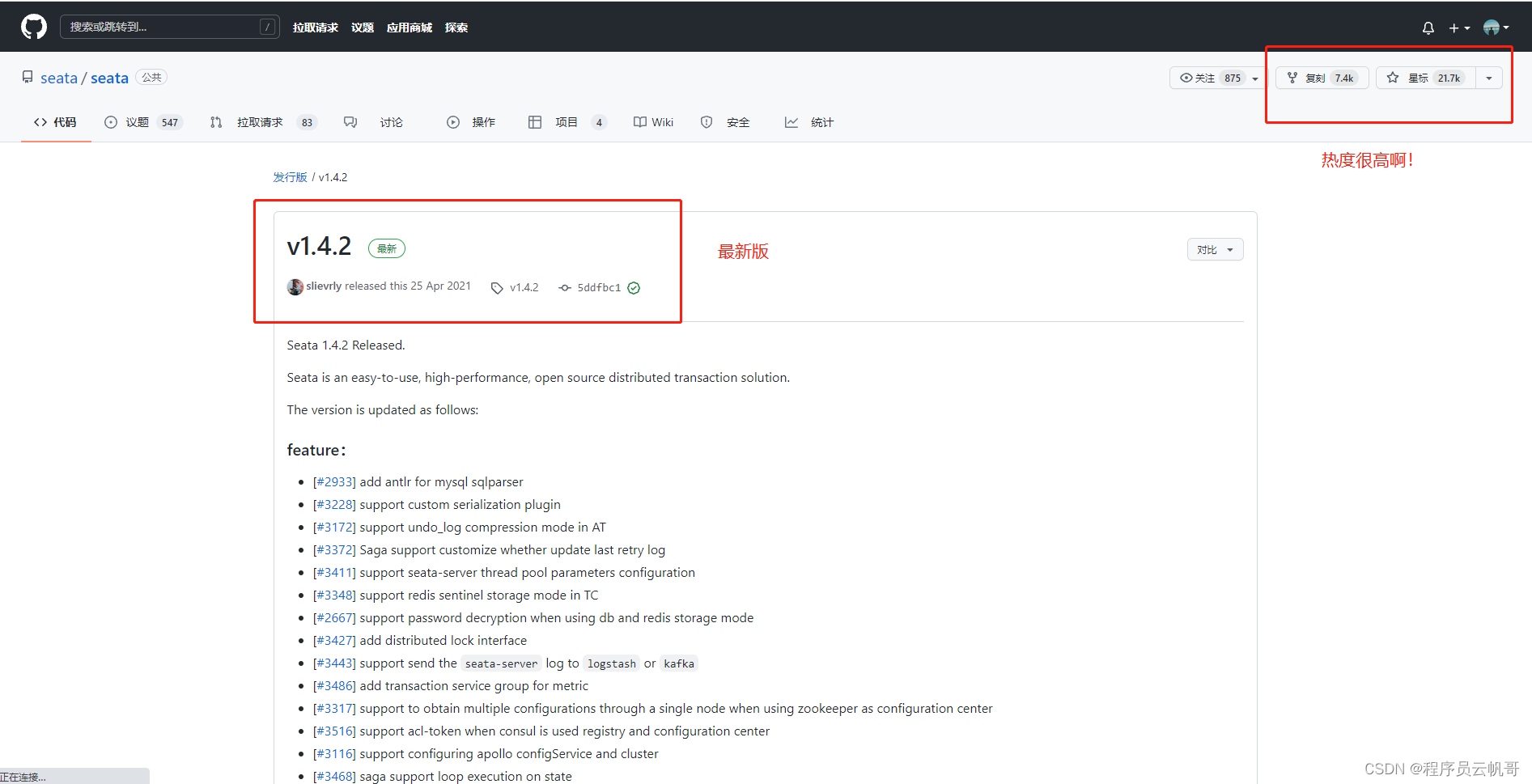
我们可以看到Seata的github star数有2万多,说明还是热门的!
我们下载最新版本v1.4.2 https://github.com/seata/seata/releases/download/v1.4.2/seata-server-1.4.2.zip
2、解压到本地

3、修改配置文件
第一步,修改conf/registry.conf,重点修改nacos配置。
registry {
# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofa
type = "nacos"
nacos {
application = "seata-server"
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
namespace = ""
cluster = "default"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
}
......
config {
# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3
type = "nacos"
nacos {
serverAddr = "127.0.0.1:8848"
namespace = ""
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
username = "nacos"
password = "nacos"
dataId = "seataServer.properties"
}
}
最新!现在支持配置dataId,就可以把所有配置放里面。(其他地方的博客还在说,去下载config.txt、nacos-config.sh,然后执行跑到nacos上去,过时了!多关注nacos版本更新)

第二步,在Nacos上新增seataServer.properties

里面的内容:
#For details about configuration items, see https://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/user/configurations.html #Transport configuration, for client and server transport.type=TCP transport.server=NIO transport.heartbeat=true transport.enableTmClientBatchSendRequest=false transport.enableRmClientBatchSendRequest=true transport.enableTcServerBatchSendResponse=false transport.rpcRmRequestTimeout=30000 transport.rpcTmRequestTimeout=30000 transport.rpcTcRequestTimeout=30000 transport.threadFactory.bossThreadPrefix=NettyBoss transport.threadFactory.workerThreadPrefix=NettyServerNIOWorker transport.threadFactory.serverExecutorThreadPrefix=NettyServerBizHandler transport.threadFactory.shareBossWorker=false transport.threadFactory.clientSelectorThreadPrefix=NettyClientSelector transport.threadFactory.clientSelectorThreadSize=1 transport.threadFactory.clientWorkerThreadPrefix=NettyClientWorkerThread transport.threadFactory.bossThreadSize=1 transport.threadFactory.workerThreadSize=default transport.shutdown.wait=3 transport.serialization=seata transport.compressor=none #Transaction routing rules configuration, only for the client service.vgroupMapping.default_tx_group=default #If you use a registry, you can ignore it service.default.grouplist=127.0.0.1:8091 service.enableDegrade=false service.disableGlobalTransaction=false #Transaction rule configuration, only for the client client.rm.asyncCommitBufferLimit=10000 client.rm.lock.retryInterval=10 client.rm.lock.retryTimes=30 client.rm.lock.retryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict=true client.rm.reportRetryCount=5 client.rm.tableMetaCheckEnable=false client.rm.tableMetaCheckerInterval=60000 client.rm.sqlParserType=druid client.rm.reportSuccessEnable=false client.rm.sagaBranchRegisterEnable=false client.rm.sagaJsonParser=fastjson client.rm.tccActionInterceptorOrder=-2147482648 client.tm.commitRetryCount=5 client.tm.rollbackRetryCount=5 client.tm.defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout=60000 client.tm.degradeCheck=false client.tm.degradeCheckAllowTimes=10 client.tm.degradeCheckPeriod=2000 client.tm.interceptorOrder=-2147482648 client.undo.dataValidation=true client.undo.logSerialization=jackson client.undo.onlyCareUpdateColumns=true server.undo.logSaveDays=7 server.undo.logDeletePeriod=86400000 client.undo.logTable=undo_log client.undo.compress.enable=true client.undo.compress.type=zip client.undo.compress.threshold=64k #For TCC transaction mode tcc.fence.logTableName=tcc_fence_log tcc.fence.cleanPeriod=1h #Log rule configuration, for client and server log.exceptionRate=100 #Transaction storage configuration, only for the server. The file, DB, and redis configuration values are optional. store.mode=db store.lock.mode=file store.session.mode=file #Used for password encryption store.publicKey= #If `store.mode,store.lock.mode,store.session.mode` are not equal to `file`, you can remove the configuration block. store.file.dir=file_store/data store.file.maxBranchSessionSize=16384 store.file.maxGlobalSessionSize=512 store.file.fileWriteBufferCacheSize=16384 store.file.flushDiskMode=async store.file.sessionReloadReadSize=100 #These configurations are required if the `store mode` is `db`. If `store.mode,store.lock.mode,store.session.mode` are not equal to `db`, you can remove the configuration block. store.db.datasource=druid store.db.dbType=mysql store.db.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver store.db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata?useUnicode=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true store.db.user=root store.db.password=root store.db.minConn=5 store.db.maxConn=30 store.db.globalTable=global_table store.db.branchTable=branch_table store.db.distributedLockTable=distributed_lock store.db.queryLimit=100 store.db.lockTable=lock_table store.db.maxWait=5000 #These configurations are required if the `store mode` is `redis`. If `store.mode,store.lock.mode,store.session.mode` are not equal to `redis`, you can remove the configuration block. store.redis.mode=single store.redis.single.host=127.0.0.1 store.redis.single.port=6379 store.redis.sentinel.masterName= store.redis.sentinel.sentinelHosts= store.redis.maxConn=10 store.redis.minConn=1 store.redis.maxTotal=100 store.redis.database=0 store.redis.password= store.redis.queryLimit=100 #Transaction rule configuration, only for the server server.recovery.committingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.asynCommittingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.rollbackingRetryPeriod=1000 server.recovery.timeoutRetryPeriod=1000 server.maxCommitRetryTimeout=-1 server.maxRollbackRetryTimeout=-1 server.rollbackRetryTimeoutUnlockEnable=false server.distributedLockExpireTime=10000 server.session.branchAsyncQueueSize=5000 server.session.enableBranchAsyncRemove=true #Metrics configuration, only for the server metrics.enabled=false metrics.registryType=compact metrics.exporterList=prometheus metrics.exporterPrometheusPort=9898
第三步,修改file.conf,修改为db模式,并连接MySQL
## transaction log store, only used in seata-server
store {
## store mode: file、db、redis
mode = "db"
......
## database store property
db {
## the implement of javax.sql.DataSource, such as DruidDataSource(druid)/BasicDataSource(dbcp)/HikariDataSource(hikari) etc.
datasource = "druid"
## mysql/oracle/postgresql/h2/oceanbase etc.
dbType = "mysql"
driverClassName = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
## if using mysql to store the data, recommend add rewriteBatchedStatements=true in jdbc connection param
url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata?rewriteBatchedStatements=true"
user = "root"
password = "root"
minConn = 5
maxConn = 100
globalTable = "global_table"
branchTable = "branch_table"
lockTable = "lock_table"
queryLimit = 100
maxWait = 5000
}
}
4、seata数据库初始化
-- -------------------------------- The script used when storeMode is 'db' --------------------------------
-- the table to store GlobalSession data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `global_table`
(
`xid` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
`transaction_id` BIGINT,
`status` TINYINT NOT NULL,
`application_id` VARCHAR(32),
`transaction_service_group` VARCHAR(32),
`transaction_name` VARCHAR(128),
`timeout` INT,
`begin_time` BIGINT,
`application_data` VARCHAR(2000),
`gmt_create` DATETIME,
`gmt_modified` DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY (`xid`),
KEY `idx_status_gmt_modified` (`status` , `gmt_modified`),
KEY `idx_transaction_id` (`transaction_id`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8;
-- the table to store BranchSession data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `branch_table`
`branch_id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`xid` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
`transaction_id` BIGINT,
`resource_group_id` VARCHAR(32),
`resource_id` VARCHAR(256),
`branch_type` VARCHAR(8),
`status` TINYINT,
`client_id` VARCHAR(64),
`application_data` VARCHAR(2000),
`gmt_create` DATETIME(6),
`gmt_modified` DATETIME(6),
PRIMARY KEY (`branch_id`),
KEY `idx_xid` (`xid`)
-- the table to store lock data
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `lock_table`
`row_key` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
`xid` VARCHAR(128),
`transaction_id` BIGINT,
`branch_id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
`resource_id` VARCHAR(256),
`table_name` VARCHAR(32),
`pk` VARCHAR(36),
`status` TINYINT NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '0:locked ,1:rollbacking',
`gmt_create` DATETIME,
`gmt_modified` DATETIME,
PRIMARY KEY (`row_key`),
KEY `idx_status` (`status`),
KEY `idx_branch_id` (`branch_id`)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `distributed_lock`
`lock_key` CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`lock_value` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
`expire` BIGINT,
primary key (`lock_key`)
DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4;
INSERT INTO `distributed_lock` (lock_key, lock_value, expire) VALUES ('HandleAllSession', ' ', 0);
5、业务数据库
在每个需要开启seata事务操作的业务数据库下都需要建立此表。
undo_log:回滚日志表。
--日志文件表--
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `undo_log`
(
`branch_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT 'branch transaction id',
`xid` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL COMMENT 'global transaction id',
`context` VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL COMMENT 'undo_log context,such as serialization',
`rollback_info` LONGBLOB NOT NULL COMMENT 'rollback info',
`log_status` INT(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '0:normal status,1:defense status',
`log_created` DATETIME(6) NOT NULL COMMENT 'create datetime',
`log_modified` DATETIME(6) NOT NULL COMMENT 'modify datetime',
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`, `branch_id`)
) ENGINE = INNODB
AUTO_INCREMENT = 1
DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8 COMMENT ='AT transaction mode undo table';
6、启动seata-server
双击启动bin目录下的seata-server.bat。(linux系统的启动seata-server.sh)

启动成功后,端口是8091。我们也可以在nacos上看到服务注册上来了。

三、微服务项目集成Seata
1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seata</artifactId>
<version>2021.1</version>
<exclusions>
<!-- 排除依赖 指定版本和服务器端一致 -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-all</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-all</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2</version>
</dependency>
版本号根据自己的项目需要。
2、配置文件
# 分布式事务配置
seata:
enabled: true
enable-auto-data-source-proxy: true #是否开启数据源自动代理,默认为true
tx-service-group: default_tx_group #要与配置文件中的vgroupMapping一致
registry:
type: nacos
nacos:
application: seata-server
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
group: SEATA_GROUP
config:
type: nacos
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
group: SEATA_GROUP
dataId: seataServer.properties
到这里配置就结束了,赶紧在项目里面用起来吧!如有遇到搭建问题,可以阅读Seata官方文档或者我们一起探讨。
到此这篇关于Spring Cloud + Nacos + Seata整合过程(分布式事务解决方案)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Cloud + Nacos + Seata整合内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

