一文搞懂Codec2解码组件
目录
- 1 前言
- 2 组件的创建
- 3 组件接口
- 4 组件运行原理
- 5 小结
1 前言
在本篇中,我们将关注Codec 2.0以下几个问题:
1.从顶而下,一个解码组件是如何创建的
2.组件的接口有哪些,分别是什么含义
3.组件是如何运行的,输入与输出的数据流是怎样的
2 组件的创建
CCodec在allocate中,通过CreateComponentByName创建了具体的解码组件。
//android/frameworks/av/media/codec2/sfplguin/CCodec.cpp
void CCodec::allocate(const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &codecInfo) {
...
AString componentName = codecInfo->getCodecName();
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client;
// set up preferred component store to access vendor store parameters
//从CCodec调用到component是通过HAL层服务的,默认谷歌的原生服务为
//android.hardware.media.c2@IComponentStore/software,默认厂商的服务为
//android.hardware.media.c2@IComponentStore/default,在android小机shell中通过lshal|grep media可以查询
//到正在运行的codec2服务,如果厂商已支持codec2,则可以查询到default服务。如果CCodec中能够创建到default
//服务,则可以将该服务设置为Preferred Codec2 ComponentStore,也就是将其作为目标组件。
client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService("default");
if (client) {
ALOGI("setting up '%s' as default (vendor) store", client->getServiceName().c_str());
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(
std::make_shared<Codec2ClientInterfaceWrapper>(client));
}
//创建具体的解码组件或者编码组件,譬如c2.android.avc.decoder
//所有omx与codec2的编解码组件支持列表可以在libstagefright/data目录下的xml中查询得到,它们的加载与
//排序情况可以在libstagefright/MediaCodecList.cpp中追踪
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> comp =
Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
componentName.c_str(),
mClientListener,
&client);
...
ALOGI("Created component [%s]", componentName.c_str());
mChannel->setComponent(comp);
auto setAllocated = [this, comp, client] {
Mutexed<State>::Locked state(mState);
if (state->get() != ALLOCATING) {
state->set(RELEASED);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
state->set(ALLOCATED);
state->comp = comp;
mClient = client;
return OK;
};
...
// initialize config here in case setParameters is called prior to configure
Mutexed<Config>::Locked config(mConfig);
status_t err = config->initialize(mClient, comp);
...
config->queryConfiguration(comp);
mCallback->onComponentAllocated(componentName.c_str());
}
继续追踪Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName接口。
//android/frameworks/av/media/codec2/hidl/client/client.cpp
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>
Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
const char* componentName,
const std::shared_ptr<Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client>* owner,
size_t numberOfAttempts) {
std::string key{"create:"};
key.append(componentName);
std::shared_ptr<Component> component;
c2_status_t status = ForAllServices(
key,
numberOfAttempts,
[owner, &component, componentName, &listener](
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> &client)
-> c2_status_t {
//调用Codec2Client类的createComponent接口,获取component
c2_status_t status = client->createComponent(componentName,
listener,
&component);
...
return status;
});
...
return component;
}
追踪Codec2Client类的createComponent接口。
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\client\client.cpp
c2_status_t Codec2Client::createComponent(
const C2String& name,
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Listener>& listener,
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component>* const component) {
c2_status_t status;
sp<Component::HidlListener> hidlListener = new Component::HidlListener{};
hidlListener->base = listener;
//这里的mBase是什么?这里调用的是IComponentStore的createComponent接口
Return<void> transStatus = mBase->createComponent(
name,
hidlListener,
ClientManager::getInstance(),
[&status, component, hidlListener](
Status s,
const sp<IComponent>& c) {
status = static_cast<c2_status_t>(s);
if (status != C2_OK) {
return;
}
*component = std::make_shared<Codec2Client::Component>(c);
hidlListener->component = *component;
});
...
return status;
}
我们先看一下IComponentStore的createComponent接口。
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\1.0\utils\include\codec2\hidl\1.0\ComponentStore.h
struct ComponentStore : public IComponentStore {
ComponentStore(const std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentStore>& store);
virtual ~ComponentStore() = default;
// Methods from ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore.
virtual Return<void> createComponent(
const hidl_string& name,
const sp<IComponentListener>& listener,
const sp<IClientManager>& pool,
createComponent_cb _hidl_cb) override;
virtual Return<void> createInterface(
const hidl_string& name,
createInterface_cb _hidl_cb) override;、
...
}
该接口的实现为:
\\av\media\codec2\hidl\1.0\utils\ComponentStore.cpp
// Methods from ::android::hardware::media::c2::V1_0::IComponentStore
Return<void> ComponentStore::createComponent(
const hidl_string& name,
const sp<IComponentListener>& listener,
const sp<IClientManager>& pool,
createComponent_cb _hidl_cb) {
sp<Component> component;
std::shared_ptr<C2Component> c2component;
//C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent调用
//调用C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent接口,返回的是一个C2Component对象
//譬如,这个对象可以是C2SoftAvcDec Component对象,也可以是VendorHwAvcDec Component对象
Status status = static_cast<Status>(
mStore->createComponent(name, &c2component));
if (status == Status::OK) {
onInterfaceLoaded(c2component->intf());
//把前面创建的C2SoftAvcDec“装载”到Component类中,Client调用Component
//Component内部会调用到C2SoftAvcDec
//Component相当于对原生编解码组件/厂商编解码组件的统一封装
component = new Component(c2component, listener, this, pool);
if (!component) {
status = Status::CORRUPTED;
} else {
reportComponentBirth(component.get());
if (component->status() != C2_OK) {
status = static_cast<Status>(component->status());
} else {
component->initListener(component);
if (component->status() != C2_OK) {
status = static_cast<Status>(component->status());
}
}
}
}
_hidl_cb(status, component);
return Void();
}
关于C2PlatformComponentStore的createComponent调用,它的实现在C2Store.cpp中,它继承于C2ComponentStore类,有几个重要成员对象,ComponentModule,ComponentLoader,有几个重要的接口,listComponents(),createComponent(),createInterface()。ComponentLoader包含ComponentModule对象,而ComponentModule主要提供两个接口,createComponent()与createInterface(),内部也包含着C2ComponentFactory成员以及它的创建与销毁接口,分别是C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc,C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
class C2PlatformComponentStore : public C2ComponentStore {
public:
virtual std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> listComponents() override;
...
virtual c2_status_t createInterface(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> *const interface) override;
virtual c2_status_t createComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *const component) override;
virtual ~C2PlatformComponentStore() override = default;
private:
/**
* An object encapsulating a loaded component module.
*/
struct ComponentModule : public C2ComponentFactory,
public std::enable_shared_from_this<ComponentModule> {
virtual c2_status_t createComponent(
c2_node_id_t id, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *component,
ComponentDeleter deleter = std::default_delete<C2Component>()) override;
virtual c2_status_t createInterface(
c2_node_id_t id, std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> *interface,
InterfaceDeleter deleter = std::default_delete<C2ComponentInterface>()) override;
...
protected:
...
void *mLibHandle; ///< loaded library handle
C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc createFactory; ///< loaded create function
C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc destroyFactory; ///< loaded destroy function
C2ComponentFactory *mComponentFactory; ///< loaded/created component factory
};
/**
* An object encapsulating a loadable component module.
*/
struct ComponentLoader {
/**
* Load the component module.
*
* This method simply returns the component module if it is already currently loaded, or
* attempts to load it if it is not.
*/
c2_status_t fetchModule(std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
c2_status_t res = C2_OK;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> localModule = mModule.lock();
if (localModule == nullptr) {
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>();
res = localModule->init(mLibPath);
if (res == C2_OK) {
mModule = localModule;
}
}
*module = localModule;
return res;
}
/**
* Creates a component loader for a specific library path (or name).
*/
ComponentLoader(std::string libPath)
: mLibPath(libPath) {}
private:
std::weak_ptr<ComponentModule> mModule; ///< weak reference to the loaded module
};
struct Interface : public C2InterfaceHelper {
...
};
/**
* Retrieves the component module for a component.
*/
c2_status_t findComponent(C2String name, std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module);
/**
* Loads each component module and discover its contents.
*/
void visitComponents();
std::map<C2String, ComponentLoader> mComponents; ///< path -> component module
std::map<C2String, C2String> mComponentNameToPath; ///< name -> path
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits>> mComponentList;
...
};
C2PlatformComponentStore::createComponent调用findComponent(name, &module)找到拥有component的ComponentModule,再通过module->createComponent(0, component)调用,找到相应的component。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::createComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<C2Component> *const component) {
// This method SHALL return within 100ms.
component->reset();
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> module;
c2_status_t res = findComponent(name, &module);
if (res == C2_OK) {
// TODO: get a unique node ID
res = module->createComponent(0, component);
}
return res;
}
findComponent(name, &module)有两步,先通过visitComponents()列举出所有可用的components,再调用ComponentLoader的fetchModule(),找到拥有component的ComponentModule。module可以看作是组件,加载某个module,也就是加载对应的组件,module提供的 createComponent()接口就是用来创建具体component的,譬如C2SoftAvcDec。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::findComponent(
C2String name, std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
(*module).reset();
visitComponents();
auto pos = mComponentNameToPath.find(name);
if (pos != mComponentNameToPath.end()) {
return mComponents.at(pos->second).fetchModule(module);
}
return C2_NOT_FOUND;
}
visitComponents()访问mComponents对象(这是一个map对象,将path与component module映射关联,这一映射工作在C2PlatformComponentStore初始化时进行),遍历所有的mComponents,即pathAndLoader对象,如果一个对象的loader能够加载成功,则添加到mComponentNameToPath对象中。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
void C2PlatformComponentStore::visitComponents() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
if (mVisited) {
return;
}
//参考定义 std::map<C2String, ComponentLoader> mComponents; ///< path -> component module
for (auto &pathAndLoader : mComponents) {
const C2String &path = pathAndLoader.first;
ComponentLoader &loader = pathAndLoader.second;
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> module;
if (loader.fetchModule(&module) == C2_OK) {
std::shared_ptr<const C2Component::Traits> traits = module->getTraits();
if (traits) {
mComponentList.push_back(traits);
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(traits->name, path);
for (const C2String &alias : traits->aliases) {
mComponentNameToPath.emplace(alias, path);
}
}
}
}
mVisited = true;
}
loader.fetchModule(&module)这个函数定义在ComponentLoader类中,在这里再贴一次代码。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t fetchModule(std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> *module) {
c2_status_t res = C2_OK;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mMutex);
std::shared_ptr<ComponentModule> localModule = mModule.lock();
if (localModule == nullptr) {
localModule = std::make_shared<ComponentModule>();
res = localModule->init(mLibPath);
if (res == C2_OK) {
mModule = localModule;
}
}
*module = localModule;
return res;
}
对于module,会调用初始化函数,初始化成功就算是fetch到了。初始化作了什么工作,参见C2PlatformComponentStore::ComponentModule::init函数,也就是对编解码库dlopen成功,可获得相应的函数地址,譬如,C2SoftAvcDec.cpp中的C2ComponentFactory* CreateCodec2Factory()与void DestroyCodec2Factory()。当然还有其他,不面面俱道了。
\\av\media\codec2\vndk\C2Store.cpp
c2_status_t C2PlatformComponentStore::ComponentModule::init(
std::string libPath) {
ALOGV("in %s", __func__);
ALOGV("loading dll");
mLibHandle = dlopen(libPath.c_str(), RTLD_NOW|RTLD_NODELETE);
createFactory =
(C2ComponentFactory::CreateCodec2FactoryFunc)dlsym(mLibHandle, "CreateCodec2Factory");
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(createFactory == nullptr,
"createFactory is null in %s", libPath.c_str());
destroyFactory =
(C2ComponentFactory::DestroyCodec2FactoryFunc)dlsym(mLibHandle, "DestroyCodec2Factory");
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(destroyFactory == nullptr,
"destroyFactory is null in %s", libPath.c_str());
mComponentFactory = createFactory();
...
std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> intf;
c2_status_t res = createInterface(0, &intf);
...
return mInit;
}
那么问题来了,为什么谷歌对它自己的codec2插件组C2PlatformComponentStore设计得这么复杂,能不能简化一点。
3 组件接口
在codec2/components目录下,有base, avc, aom, hevc, aac等文件夹,base目录下是SimpleC2Component.cpp与SimpleC2Interface.cpp以及对应的头文件,avc目录下是C2SoftAvcDec.cpp,C2SoftAvcEnc.cpp以及对应的头文件,其他编解码器文件夹亦同样道理。C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等编解码器类都是继承于SimpleC2Component类的,也就是说,SimpleC2Component是components的顶层类,它对接了component类的接口,实现了编解码器的公共流程部分,C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等子类继承SimpleC2Component的一些接口,实现各自的编解码操作。
SimpleC2Component实现的component的接口如下:
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\include\SimpleC2Component.h
// C2Component
// From C2Component
//设置回调
virtual c2_status_t setListener_vb(
const std::shared_ptr<Listener> &listener, c2_blocking_t mayBlock) override;
//送数据到component,数据打包成某种对象,叫C2Work,这个对象很关键,它包含input与output
virtual c2_status_t queue_nb(std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>>* const items) override;
//暂时没有多大用处,不管它
virtual c2_status_t announce_nb(const std::vector<C2WorkOutline> &items) override;
//跳播使用,将当前数据冲刷掉
virtual c2_status_t flush_sm(
flush_mode_t mode, std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>>* const flushedWork) override;
//渲染可用的帧
virtual c2_status_t drain_nb(drain_mode_t mode) override;
virtual c2_status_t start() override;
virtual c2_status_t stop() override;
virtual c2_status_t reset() override;
virtual c2_status_t release() override;
virtual std::shared_ptr<C2ComponentInterface> intf() override;
而C2SoftAvcDec,C2SoftHevcDec等子类继承SimpleC2Component的接口如下:
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\include\SimpleC2Component.h
virtual c2_status_t onInit() = 0;
virtual c2_status_t onStop() = 0;
virtual void onReset() = 0;
virtual void onRelease() = 0;
virtual c2_status_t onFlush_sm() = 0;
//最重要的处理函数,处理的对象是C2Work,它包含着输入输出,交互配置方面的类。
virtual void process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) = 0;
virtual c2_status_t drain(
uint32_t drainMode,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) = 0;
4 组件运行原理
SimpleC2Component有一个成员对象WorkHandler,这个类继承于AHandler,也就是说,SimpleC2Component内部运行一个线程,来自上层的接口调用,都可以发送消息到onMessageReceived中排队处理,譬如初始化、停止、重置、释放以及数据处理等工作,都在队列中排队处理,相应的处理都是调用到子类的实现,譬如,onInit(),onStop(),onReset(),onRelease(),以及processQueue()。
我们可以看一下onMessageReceived的实现。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
void SimpleC2Component::WorkHandler::onMessageReceived(const sp<AMessage> &msg) {
std::shared_ptr<SimpleC2Component> thiz = mThiz.lock();
...
switch (msg->what()) {
case kWhatProcess: {
if (mRunning) {
if (thiz->processQueue()) {
(new AMessage(kWhatProcess, this))->post();
}
} else {
ALOGV("Ignore process message as we're not running");
}
break;
}
case kWhatInit: {
int32_t err = thiz->onInit();
Reply(msg, &err);
[[fallthrough]];
}
case kWhatStart: {
mRunning = true;
break;
}
case kWhatStop: {
int32_t err = thiz->onStop();
Reply(msg, &err);
break;
}
case kWhatReset: {
thiz->onReset();
mRunning = false;
Reply(msg);
break;
}
case kWhatRelease: {
thiz->onRelease();
mRunning = false;
Reply(msg);
break;
}
default: {
ALOGD("Unrecognized msg: %d", msg->what());
break;
}
}
}
我们看一下AVC解码器内部是如何处理输入与输出数据的,在这个process中,处理完输入,解码,处理输出,在处理output buffer时,process的思路是这样的:从内存池申请一个GraphicBlock,对应地设置给解码器Buffer地址以供解码输出,如果解码后有帧输出,则将当前的GraphicBlock转换为C2Buffer对象,返回给上层。类似于FFMPEG,你给它一个output frame,它就将解码图片填充到frame,你取走显示。可以推断,软解码器内部应该也有申请一个队列的buffer,这个队列维护着解码所需要的参考图像。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
//省略了部分不影响理解主要流程的代码
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
// Initialize output work
work->result = C2_OK;
work->workletsProcessed = 0u;
work->worklets.front()->output.flags = work->input.flags;
size_t inOffset = 0u;
size_t inSize = 0u;
uint32_t workIndex = work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku() & 0xFFFFFFFF;
C2ReadView rView = mDummyReadView;
if (!work->input.buffers.empty()) {
//为了得到输入数据,层层访问,真正放数据的地址在rView.data()[]中
//把work这个对象用思维导图画出来,我们可以更容易的理解work,到底拥有哪些成员,如何访问
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
inSize = rView.capacity();
...
}
bool eos = ((work->input.flags & C2FrameData::FLAG_END_OF_STREAM) != 0);
bool hasPicture = false;
ALOGV("in buffer attr. size %zu timestamp %d frameindex %d, flags %x",
inSize, (int)work->input.ordinal.timestamp.peeku(),
(int)work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku(), work->input.flags);
size_t inPos = 0;
while (inPos < inSize) {
//ensureDecoderState会从内存池中fetch一个GraphicBlock
//实质上也就是调用Gralloc接口取得一个output buffer
if (C2_OK != ensureDecoderState(pool)) {
mSignalledError = true;
work->workletsProcessed = 1u;
work->result = C2_CORRUPTED;
return;
}
ivd_video_decode_ip_t s_decode_ip;
ivd_video_decode_op_t s_decode_op;
{
//mOutBlock即是上述fetch到的output buffer,通过map映射可以得到一个wView,类似于rView
//wView.data()[]指向out buffer的真正地址
//wView.data()[C2PlanarLayout::PLANE_Y]就是要存在Y变量的地址
//wView.data()[C2PlanarLayout::PLANE_U]就是要存在U变量的地址
C2GraphicView wView = mOutBlock->map().get();
...
//setDecodeArgs所作的主要工作是,告诉解码器,输入数据的地址是什么,输出地址包括Y/U/V
//分量的地址是什么,输入数据的长度是多少
if (!setDecodeArgs(&s_decode_ip, &s_decode_op, &rView, &wView,
inOffset + inPos, inSize - inPos, workIndex)) {
mSignalledError = true;
work->workletsProcessed = 1u;
work->result = C2_CORRUPTED;
return;
}
if (false == mHeaderDecoded) {
/* Decode header and get dimensions */
setParams(mStride, IVD_DECODE_HEADER);
}
//解码器库是用了第三方的,已经被谷歌收购
(void) ivdec_api_function(mDecHandle, &s_decode_ip, &s_decode_op);
}
if (s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth >= 0 && mOutputDelay != s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth) {
//目前不清楚把这个重排序长度告诉上层有什么作用,TODO
mOutputDelay = s_decode_op.i4_reorder_depth;
ALOGV("New Output delay %d ", mOutputDelay);
C2PortActualDelayTuning::output outputDelay(mOutputDelay);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<C2SettingResult>> failures;
c2_status_t err =
mIntf->config({&outputDelay}, C2_MAY_BLOCK, &failures);
if (err == OK) {
work->worklets.front()->output.configUpdate.push_back(
C2Param::Copy(outputDelay));
}
continue;
}
if (0 < s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd && 0 < s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht) {
if (mHeaderDecoded == false) {
mHeaderDecoded = true;
setParams(ALIGN64(s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd), IVD_DECODE_FRAME);
}
if (s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd != mWidth || s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht != mHeight) {
mWidth = s_decode_op.u4_pic_wd;
mHeight = s_decode_op.u4_pic_ht;
CHECK_EQ(0u, s_decode_op.u4_output_present);
C2StreamPictureSizeInfo::output size(0u, mWidth, mHeight);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<C2SettingResult>> failures;
c2_status_t err = mIntf->config({&size}, C2_MAY_BLOCK, &failures);
if (err == OK) {
work->worklets.front()->output.configUpdate.push_back(
C2Param::Copy(size));
}
continue;
}
}
(void)getVuiParams();
hasPicture |= (1 == s_decode_op.u4_frame_decoded_flag);
if (s_decode_op.u4_output_present) {
//通过createGraphicBuffer调用,将mOutBlock"转换"成C2Buffer对象
//把C2Buffer添加到work对象的输出队列中
//通过listener->onWorkDone_nb回调,可以将work返回到CCodec层
//以上是这个函数以及其内部调用的主要实现内容,内部调用的finish()函数属于SimpleC2Component
finishWork(s_decode_op.u4_ts, work);
}
inPos += s_decode_op.u4_num_bytes_consumed;
}
if (eos) {
drainInternal(DRAIN_COMPONENT_WITH_EOS, pool, work);
mSignalledOutputEos = true;
} else if (!hasPicture) {
fillEmptyWork(work);
}
work->input.buffers.clear();
}
在Component中,输入与输出对象都封装在work对象中,甚至上下层的配置交互对象也包括在work对象中,与OMX是不一样的,OMX的数据对象是BufferHeader,输入是一个Input BufferHeader,输出是一个Output BufferHeader,对象中包括buffer地址,分配的buffer大小,有效数据长度,有效数据长度的偏移量,buffer标志等。 那么,work对象也应该会包括类似的成员。
我们来看两张思维导图,全局观察work对象。
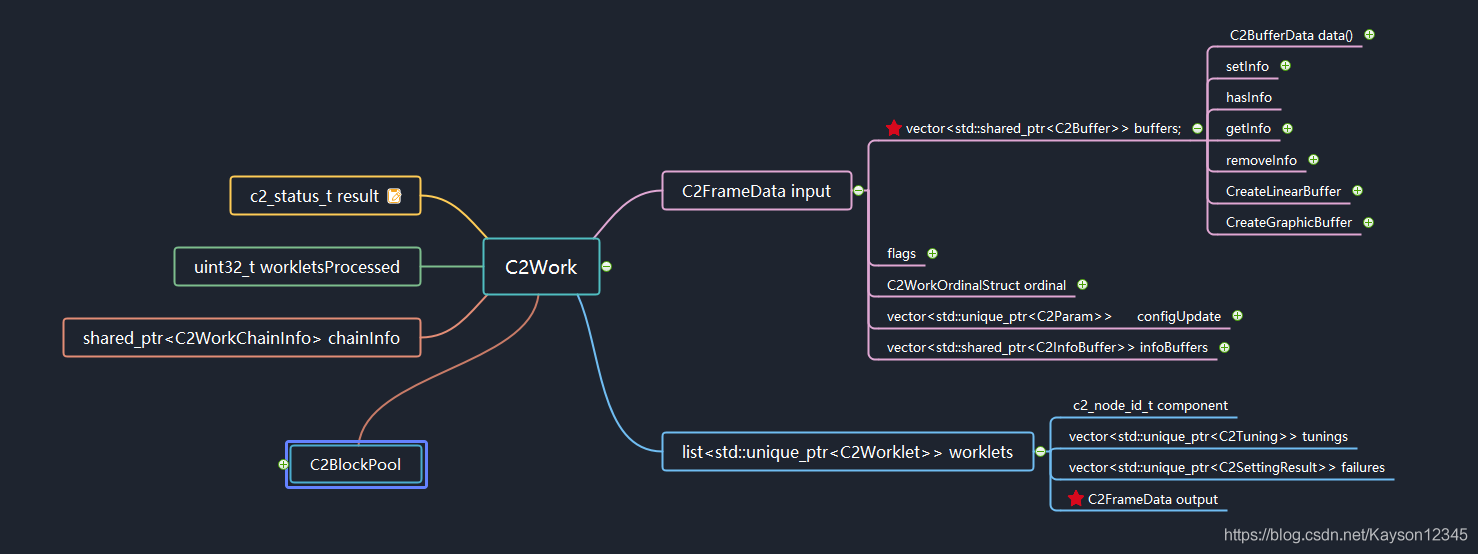
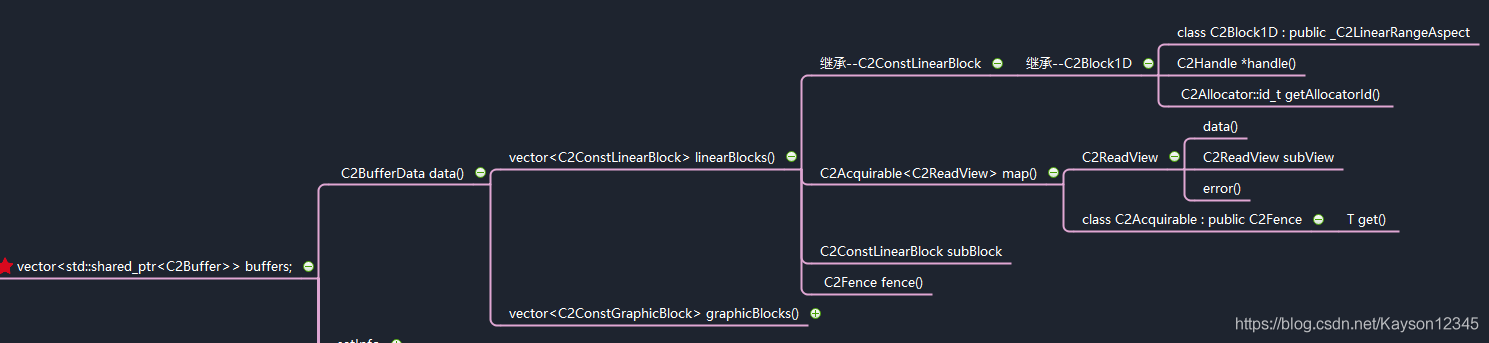
C2SoftAvcDec::process中有一句代码,从work中访问rView。
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
从上述两图中,我们可以追踪这一条访问线路,访问C2Work对象的成员C2FrameData,继续访问C2FrameData对外的成员vector linearBlocks(),C2ConstLinearBlock有一个方法C2Acquirable map(),这个映射方法返回一个C2ReadView对象,这个C2ReadView对象有一个data()[]数组,指向了Y/U/V的向量地址,也就是真正存放解码数据的内存地址。而Input与Output都是以C2FrameData来描述,Output并非像Input一样,直接作为C2Work的成员,而是作为C2Work->worklets的成员。worklet是一个list类型,C2SoftAvcDec在存放output buffer的时候,总是存放在第一个worklets的output中,参见思维导图,output是C2FrameData类型,它拥有一个C2Buffer容器,C2SoftAvcDec总是将新的output buffer丢进容器中,它可以一次丢很多个output buffer,然后一次性通过work回送到上层,上层可以一次性从work中取到多个output buffer去作渲染。C2WorkOrdinalStruct ordinal包括着buffer的pts与frameIndex信息。这里有个疑问待解决,为什么output buffer总是存放在第一个worklets的output中,worklets作为一个队列对象,有什么其他的意义?
上面我们分析了两个点,一个是模块的消息处理机制,另一个是如何送数据到解码器再取出帧数据回送到上层,接下来看第三点,CCodec每次送多少输入数据下来,component每次处理多少数据,回送输出数据给CCodec作渲染在哪些地方。
上层是调用SimpleC2Component::queue_nb接口送数据下来的。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
c2_status_t SimpleC2Component::queue_nb(std::list<std::unique_ptr<C2Work>> * const items) {
{
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
if (state->mState != RUNNING) {
return C2_BAD_STATE;
}
}
bool queueWasEmpty = false;
{
Mutexed<WorkQueue>::Locked queue(mWorkQueue);
queueWasEmpty = queue->empty();
while (!items->empty()) {
queue->push_back(std::move(items->front()));
items->pop_front();
}
}
if (queueWasEmpty) {
(new AMessage(WorkHandler::kWhatProcess, mHandler))->post();
}
return C2_OK;
}
观察上面的代码,入参是一个列表对象,也就是说,每次送多个work,一个work可以包括一个C2Buffer容器,码流都是放在容器的第一个元素,虽然一个容器可以放多个C2Buffer,但它就只放了一个C2Buffer。我们可以从下面的代码中发现,每一次的process,都只从work中取一个C2Buffer。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
...
uint32_t workIndex = work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku() & 0xFFFFFFFF;
C2ReadView rView = mDummyReadView;
if (!work->input.buffers.empty()) {
//关注buffers[0]
rView = work->input.buffers[0]->data().linearBlocks().front().map().get();
inSize = rView.capacity();
}
}
SimpleC2Component::processQueue()每次只处理一个work,处理完就把work回送上去。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
bool SimpleC2Component::processQueue() {
....
ALOGV("start processing frame #%" PRIu64, work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku());
//处理work
process(work, mOutputBlockPool);
ALOGV("processed frame #%" PRIu64, work->input.ordinal.frameIndex.peeku());
Mutexed<WorkQueue>::Locked queue(mWorkQueue);
if (work->workletsProcessed != 0u) {
queue.unlock();
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
ALOGV("returning this work");
std::shared_ptr<C2Component::Listener> listener = state->mListener;
state.unlock();
//回送work
listener->onWorkDone_nb(shared_from_this(), vec(work));
}
...
}
在没有新送下来的work需要处理的时候,processQueue()会调用drain接口作“渲染”操作,它会看解码器是否有帧数据生成,有的话,就填充到work中回送到上层。
\\av\media\codec2\components\base\SimpleC2Component.cpp
bool SimpleC2Component::processQueue() {
....
if (!work) {
c2_status_t err = drain(drainMode, mOutputBlockPool);
if (err != C2_OK) {
Mutexed<ExecState>::Locked state(mExecState);
std::shared_ptr<C2Component::Listener> listener = state->mListener;
state.unlock();
listener->onError_nb(shared_from_this(), err);
}
return hasQueuedWork;
}
...
}
另一个渲染的地方是在process()中,解码完发现有帧数据的时候,就调用finishWork()将work回送。
\\av\media\codec2\components\avc\C2SoftAvcDec.cpp
void C2SoftAvcDec::process(
const std::unique_ptr<C2Work> &work,
const std::shared_ptr<C2BlockPool> &pool) {
...
if (s_decode_op.u4_output_present) {
finishWork(s_decode_op.u4_ts, work);
}
...
}
5 小结
Component内部的逻辑还是比较好理解的,重点在于它是如何申请buffer的,如何将buffer“送”给解码器,解码完后是如何取得buffer并返回上层,难点在于work对象层层封装,当你要访问实际内存地址时,如何访问,如果要取得内存的handle,又要如何访问,这一点通过将work对象一层一层的“绘制”出来,就好懂得多。接下来问题来了,在OMX中,上下层的交互配置是通过setParamerter/getParamerter等接口进行的,那么在Codec2中是如何进行的?Codec2中到底有没有像OMX一样的BufferCountActual设计?Codec2在调用nativewindow的setMaxDequeuedBufferCount时是如何确定maxDequeueBufferCount的?GraphicBuffer的生命周期是如何控制的?
到此这篇关于一文搞懂Codec2解码组件的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Codec2解码组件内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

