Mybatis-Plus 通用CRUD的详细操作
目录
- 1、插入操作
- 1.1 方法定义
- 1.2 测试用例
- 1.3 测试
- 1.4 @TableField
- 2、更新操作
- 2.1 根据id更新
- 2.2 根据条件更新
- 3、删除操作
- 3.1 deleteById
- 3.2 deleteByMap
- 3.3 delete
- 3.4 deleteBatchIds
- 4、查询操作
- 4.1 selectById
- 4.2 selectBatchIds
- 4.3 selectOne
- 4.4 selectCount
- 4.5 selectList
- 4.6 selectPage
- 5 SQL注入的原理
通过前面的学习,我们了解到通过继承BaseMapper就可以获取到各种各样的单表操作,接下来我们将详细讲解这些
操作。
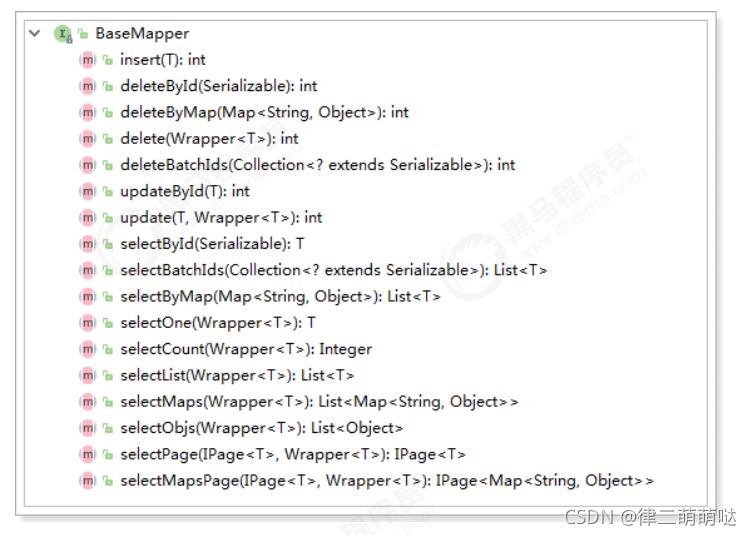
1、插入操作
1.1 方法定义
/*** 插入一条记录 * @param entity 实体对象 */ int insert(T entity);
1.2 测试用例
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class TestUserMapper {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testInsert(){
User user=new User();
user.setAge(12);
user.setName("曹操");
user.setPassword("123");
user.setMail("caocao@qq.com");
user.setUserName("曹操");
user.setAddress("北京");
//result数据库受影响的行数
int result = userMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println("result=>"+result);
//获取自增长后的id值
System.out.println(user.getId());//自增后的id会回填到对象中
}
}
1.3 测试
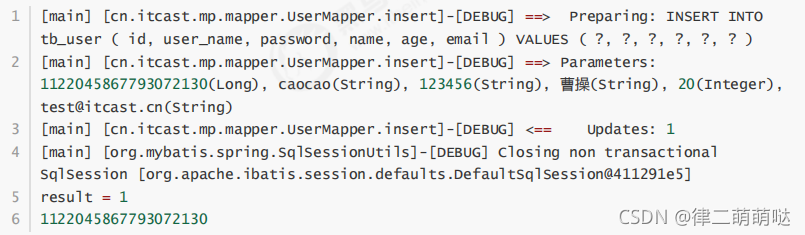
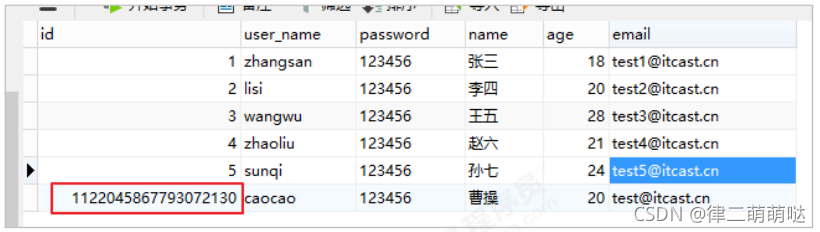
可以看到,数据已经写入到了数据库,但是,id的值不正确,我们期望的是数据库自增长,实际是MP生成了id的值
写入到了数据库。
如何设置id的生成策略呢?
MP支持的id策略
package com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation;
import lombok.Getter;
/**
* 生成ID类型枚举类
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2015-11-10
*/
@Getter
public enum IdType {
/**
* 数据库ID自增
*/
AUTO(0),
/**
* 该类型为未设置主键类型
*/
NONE(1),
/**
* 用户输入ID
* <p>该类型可以通过自己注册自动填充插件进行填充</p>
*/
INPUT(2),
/* 以下3种类型、只有当插入对象ID 为空,才自动填充。 */
/**
* 全局唯一ID (idWorker)
*/
ID_WORKER(3),
/**
* 全局唯一ID (UUID)
*/
UUID(4),
/**
* 字符串全局唯一ID (idWorker 的字符串表示)
*/
ID_WORKER_STR(5);
private final int key;
IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
修改User对象:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@TableName("tb_user")
public class User {
@TableId(value="id",type= IdType.AUTO)//设置id字段为自增长
private Long id;
private String userName;
private String password;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
数据插入成功:

1.4 @TableField
在MP中通过@TableField注解可以指定字段的一些属性,常常解决的问题有2个:
1、对象中的属性名和字段名不一致的问题(非驼峰)
2、对象中的属性字段在表中不存在的问题
使用:

其他用法,如密碼字段不加入查询字段:
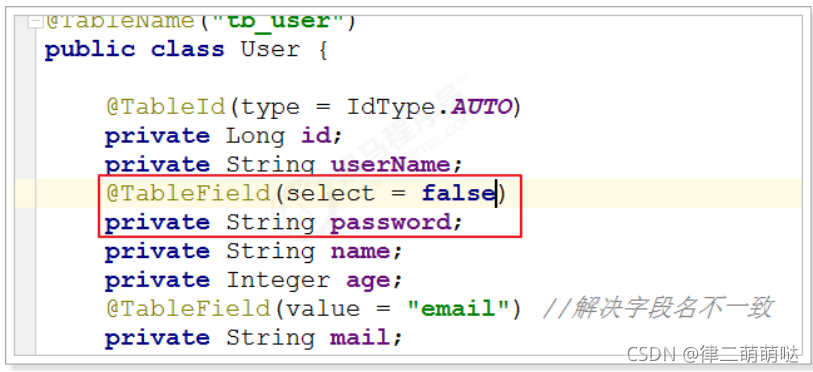
效果:
 .
.
2、更新操作
在MP中,更新操作有2种,一种是根据id更新,另一种是根据条件更新。
2.1 根据id更新
方法定义:
/*** 根据 ID 修改 ** @param entity 实体对象 */ int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testUpdateById() {
User user = new User(); user.setId(6L); //主键
user.setAge(21); //更新的字段
//根据id更新,更新不为null的字段
this.userMapper.updateById(user);
}
}
结果:
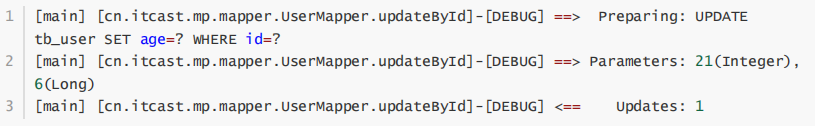

2.2 根据条件更新
方法定义:
/*** 根据 whereEntity 条件,更新记录 ** @param entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可以为 null) * @param updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句) */ int update(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);
测试用例:
@Test public void testUpdate() {
User user = new User(); user.setAge(22); //更新的字段
//更新的条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("id", 6);
//执行更新操作
int result = this.userMapper.update(user, wrapper);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
或者,通过UpdateWrapper进行更新:
@Test public void testUpdate() {
//更新的条件以及字段
UpdateWrapper<User> wrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("id", 6).set("age", 23);
//执行更新操作
int result = this.userMapper.update(null, wrapper);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
测试结果:

均可达到更新的效果。
关于wrapper更多的用法后面会详细讲解。
3、删除操作
3.1 deleteById
方法定义:
/*** 根据 ID 删除 ** @param id 主键ID */ int deleteById(Serializable id);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testDeleteById() {
//执行删除操作
int result = this.userMapper.deleteById(6L);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}

数据被删除。
3.2 deleteByMap
方法定义:
/*** 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录 ** @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象 */ int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
Map<String, Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("age",20); columnMap.put("name","张三");
//将columnMap中的元素设置为删除的条件,多个之间为and关系
int result = this.userMapper.deleteByMap(columnMap);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}

3.3 delete
方法定义:
/*** 根据 entity 条件,删除记录 ** @param wrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> wrapper);
测试用例:
@Test public void testDeleteByMap() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
user.setName("张三");
//将实体对象进行包装,包装为操作条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(user);
int result = this.userMapper.delete(wrapper);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
结果:
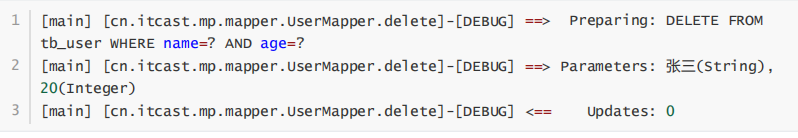
3.4 deleteBatchIds
方法定义:
/*** 删除(根据ID 批量删除) ** @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty) */ int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
//根据id集合批量删除
int result = this.userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L,10L,20L));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
结果:

4、查询操作
MP提供了多种查询操作,包括根据id查询、批量查询、查询单条数据、查询列表、分页查询等操作。
4.1 selectById
方法定义:
/*** 根据 ID 查询 ** @param id 主键ID */ T selectById(Serializable id);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
//根据id查询数据
User user = this.userMapper.selectById(2L);
System.out.println("result = " + user);
}
结果:

4.2 selectBatchIds
方法定义:
/*** 查询(根据ID 批量查询) ** @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty) */ List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testSelectBatchIds() {
//根据id集合批量查询
List<User> users = this.userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(2L, 3L, 10L));
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
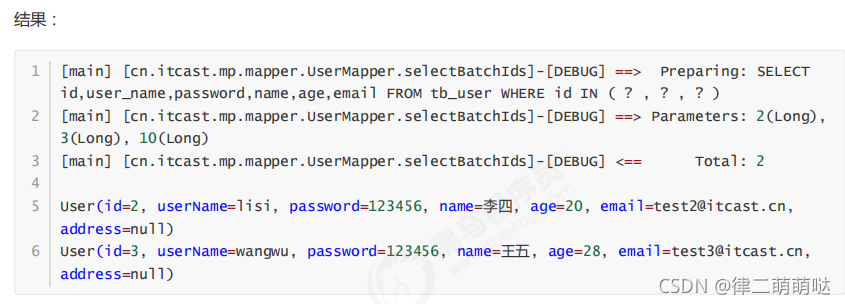
4.3 selectOne
方法定义:
/*** 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录 ** @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ T selectOne(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
测试用例:
@Test public void testSelectOne() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>();
wrapper.eq("name", "李四");
//根据条件查询一条数据,如果结果超过一条会报错
User user = this.userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
System.out.println(user);
}
结果:

4.4 selectCount
方法定义:
/*** 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询总记录数 ** @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ Integer selectCount(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testSelectCount() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>();
wrapper.gt("age", 23); //年龄大于23岁
//根据条件查询数据条数
Integer count = this.userMapper.selectCount(wrapper);
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}

4.5 selectList
方法定义:
/*** 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录 ** @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ List<T> selectList(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
测试用例:
@Test
public void testSelectList() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>();
wrapper.gt("age", 23); //年龄大于23岁
//根据条件查询数据
List<User> users = this.userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println("user = " + user);
}
}
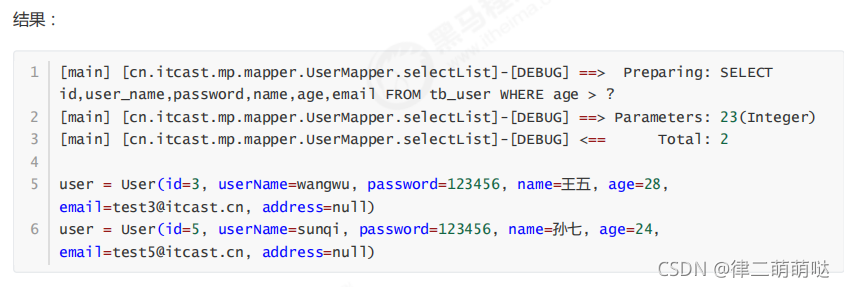
4.6 selectPage
方法定义:
/*** 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页) ** @param page 分页查询条件(可以为 RowBounds.DEFAULT) * @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null) */ IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
配置分页插件:
package cn.itcast.mp;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.PaginationInterceptor;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@MapperScan("cn.itcast.mp.mapper") //设置mapper接口的扫描包
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
/*** 分页插件 */
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
}
测试用例:
@Test
public void testSelectPage() {
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>();
wrapper.gt("age", 20); //年龄大于20岁
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1,1);
//根据条件查询数据
IPage<User> iPage = this.userMapper.selectPage(page, wrapper);
System.out.println("数据总条数:" + iPage.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页数:" + iPage.getPages());
List<User> users = iPage.getRecords();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println("user = " + user);
}
}
结果:

5 SQL注入的原理
前面我们已经知道,MP在启动后会将BaseMapper中的一系列的方法注册到mappedStatements中,那么究竟是如
何注入的呢?流程又是怎么样的?下面我们将一起来分析下。
在MP中,ISqlInjector负责SQL的注入工作,它是一个接口,AbstractSqlInjector是它的实现类,实现关系如下:

在AbstractSqlInjector中,主要是由inspectInject()方法进行注入的,如下:
@Override
public void inspectInject(MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant, Class<?> mapperClass) {
Class<?> modelClass = extractModelClass(mapperClass);
if (modelClass != null) {
String className = mapperClass.toString();
Set<String> mapperRegistryCache = GlobalConfigUtils.getMapperRegistryCache(builderAssistant.getConfiguration());
if (!mapperRegistryCache.contains(className)) {
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = this.getMethodList();
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(methodList)) {
TableInfo tableInfo = TableInfoHelper.initTableInfo(builderAssistant, modelClass);
// 循环注入自定义方法
methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo));
} else {
logger.debug(mapperClass.toString() + ", No effective injection method was found.");
}
mapperRegistryCache.add(className);
}
}
}
在实现方法中, methodList.forEach(m -> m.inject(builderAssistant, mapperClass, modelClass, tableInfo)); 是关键,循环遍历方法,进行注入。
最终调用抽象方法injectMappedStatement进行真正的注入:
/**
* 注入自定义 MappedStatement
*
* @param mapperClass mapper 接口
* @param modelClass mapper 泛型
* @param tableInfo 数据库表反射信息
* @return MappedStatement
*/
public abstract MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo);
查看该方法的实现:
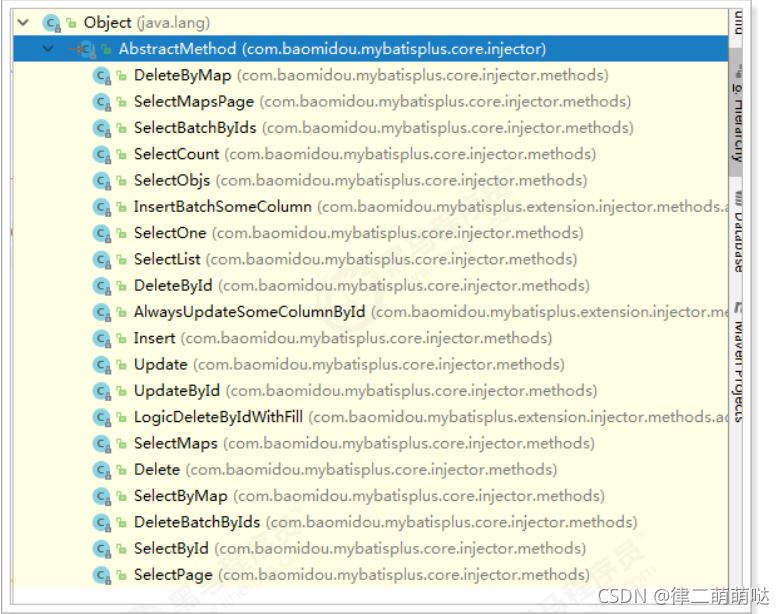
以SelectById为例查看:

可以看到,生成了SqlSource对象,再将SQL通过addSelectMappedStatement方法添加到mappedStatements中。

到此这篇关于Mybatis-Plus 通用CRUD的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Mybatis-Plus 通用CRUD内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!

