SpringBoot应用启动过程分析
SpringBoot项目通过SpringApplication.run(App.class, args)来启动:
@Configuration
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
接下来,通过源码来看看SpringApplication.run()方法的执行过程。如果对源码不感兴趣,直接下拉到文章末尾,看启动框图。
1、调用SpringApplication类的静态方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, String... args) {
return run(new Object[] { source }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}
2、SpringApplication对象初始化
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
initialize(sources);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
// 判断是否为WEB环境
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
// 找到META-INF/spring.factories中ApplicationContextInitializer所有实现类,并将其实例化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 找到META-INF/spring.factories中ApplicationListener所有实现类,并将其实例化
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 获取当前main方法类对象,即测试类中的App实例
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
对象初始化过程中,使用到了getSpringFactoriesInstances方法:
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 读取META-INF/spring.factories指定接口的实现类
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<T>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) constructor.newInstance(args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
// 读取META-INF/spring.factories文件
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories文件内容,spring boot版本1.3.6.RELEASE # PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\ org.springframework.boot.context.web.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\ org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
ApplicationListener接口是Spring框架的事件监听器,其作用可理解为SpringApplicationRunListener发布通知事件时,由ApplicationListener负责接收。SpringApplicationRunListener接口的实现类就是EventPublishingRunListener,其在SpringBoot启动过程中,负责注册ApplicationListener监听器,在不同时间节点发布不同事件类型,如果有ApplicationListener实现类监听了该事件,则接收处理。
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* 通知监听器,SpringBoot开始启动
*/
void started();
/**
* 通知监听器,环境配置完成
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);
/**
* 通知监听器,ApplicationContext已创建并初始化完成
*/
void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* 通知监听器,ApplicationContext已完成IOC配置
*/
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context);
/**
* 通知监听器,SpringBoot开始完毕
*/
void finished(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception);
}
附图为ApplicationListener监听接口实现类,每个类对应了一种事件。

3、SpringApplication核心run方法
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 任务执行时间监听,记录起止时间差
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 启动SpringApplicationRunListener监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.started();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
// 创建并刷新ApplicationContext
context = createAndRefreshContext(listeners, applicationArguments);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 通知监听器,应用启动完毕
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
这里,需要看看createAndRefreshContext()方法是如何创建并刷新ApplicationContext。
private ConfigurableApplicationContext createAndRefreshContext(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
// Create and configure the environment
// 创建并配置运行环境,WebEnvironment与StandardEnvironment选其一
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
if (isWebEnvironment(environment) && !this.webEnvironment) {
environment = convertToStandardEnvironment(environment);
}
// 是否打印Banner,就是启动程序时出现的图形
if (this.bannerMode != Banner.Mode.OFF) {
printBanner(environment);
}
// Create, load, refresh and run the ApplicationContext
// 创建、装置、刷新、运行ApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
// 通知监听器,ApplicationContext创建完毕
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
// Load the sources
// 将beans载入到ApplicationContext容器中
Set<Object> sources = getSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[sources.size()]));
// 通知监听器,beans载入ApplicationContext完毕
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
// Refresh the context
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
return context;
}
其中利用createApplicationContext()来实例化ApplicationContext对象,即DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS 、DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS两个对象其中一个。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment
? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}
postProcessApplicationContext(context)、applyInitializers(context)均为初始化ApplicationContext工作。
SpringBoot启动过程分析就先到这里,过程中关注几个对象:
ApplicationContext:Spring高级容器,与BeanFactory类似。
SpringApplicationRunListener:SprintBoot启动监听器,负责向ApplicationListener注册各类事件。
Environment:运行环境。
4、启动过程框图
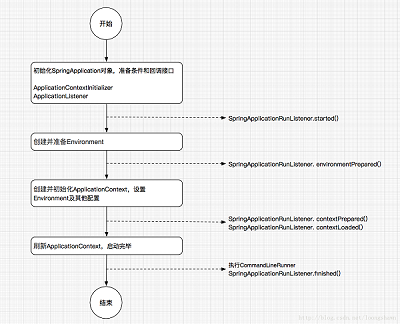
5、接口文档
http://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/javadoc-api/
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的SpringBoot应用启动过程分析,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对我们网站的支持!

