新手了解java IO基础知识
目录
- 一、File类
- 1、简介
- 2、创建方式
- 3、常用方法
- 二、IO概念
- 1.什么是输入
- 2.什么输出(Output)
- 三、流的分类
- 1、InputStream(字节流)
- 2、OutputStream(字节流)
- 3、Reader(字符流)
- 4、Writer(字符流)
- 四、总结(1+2)
- 1. File类及方法的使用
- 2.IO流的分类
- 3.IO流的四个基本类
- 总结
一、File类
1、简介
java.io.File类:文件和文件目录路径的抽象表示形式,与平台无关 File 能新建、删除、重命名文件和目录,但 File 不能访问文件内容本 身。如果需要访问文件内容本身,则需要使用输入/输出流。 想要在Java程序中表示一个真实存在的文件或目录,那么必须有一个 File对象。
2、创建方式
public File(String pathname);//以pathname为路径创建File对象,可以是绝对路径或者相对路径。
- 绝对路径:是一个固定的路径,从盘符开始
- 相对路径:是相对于某个位置开始
public File(String parent,String child);//以parent为父路径,child为子路径创建File对象。
public File(File parent,String child);//根据一个父File对象和子文件路径创建File对象。
3、常用方法
public String getAbsolutePath()//获取绝对路径 public String getPath() //获取路径 public String getName() //获取名称 public String getParent()//获取上层文件目录路径。若无,返回null public long length() //获取文件长度(即:字节数) public long lastModified() //获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值 public String[] list() //获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的名称数组 public File[] listFiles()//获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的File数组 public boolean createNewFile()//当且仅当不存在具有此抽象路径名指定名称的文件时,不可分地创建一个新的空文件。 public boolean delete() //删除此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录。 public boolean exists()//测试此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在。 public String[] list()//返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录。 public boolean mkdirs()//创建此抽象路径名指定的目录,包括所有必需但不存在的父目录。 public boolean isDirectory()//判断是否是文件目录 public boolean isFile()//判断是否是文件
示例:
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//File(String pathname);//以pathname为路径创建File对象
File file = new File("E:\\aaa");
//File(File parent,String child);//根据一个父File对象和子文件路径创建File对象。
File file1 = new File(file,"test.txt");
//boolean exists()判断文件或目录是否存在。
if (!(file.exists())){
// boolean mkdirs()创建此路径名指定的目录,包括所有必需但不存在的父目录。
file.mkdirs();
}else {
try {
//boolean createNewFile()当且仅当不存在具有此路径名指定名称的文件时,创建一个新的空文件。
file1.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//String getPath()获取路径
System.out.println(file.getPath());
//long length()获取文件长度(即:字节数)
System.out.println(file.length());
//String getName()获取文件名称
System.out.println(file.getName());
//long lastModified()获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值
System.out.println(file.getName());
// public boolean isFile() :判断是否是文件
System.out.println(file.isFile());
// delete(file);
}
//递归的方式删除文件或者文件夹
public static void delete(File file){
//File[] listFiles() 获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的名称数组
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//boolean isDirectory()判断是否是文件目录
if (f.isDirectory()){
delete(f);
}
//boolean delete()删除此路径名表示的文件或目录。
f.delete();
}
file.delete();
}
说明:Java中的删除不到回收站,要删除一个文件目录,注意该文件目录内不能包含文件或者文件目录。
二、IO概念
- I/O 即输入Input/ 输出Output的缩写,其实就是计算机调度把各个存储中(包括内存和外部存储)的数据写入写出
- java中用“流(stream)”来抽象表示这么一个写入写出的功能,封装成一个“类”,都放在java.io这个包里面。
- java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并 通过标准的方法输入或输出数据
1.什么是输入
程序从内存中读取数据叫输入Input。
2.什么输出(Output)
程序把数据写入到内存中叫输出Output。
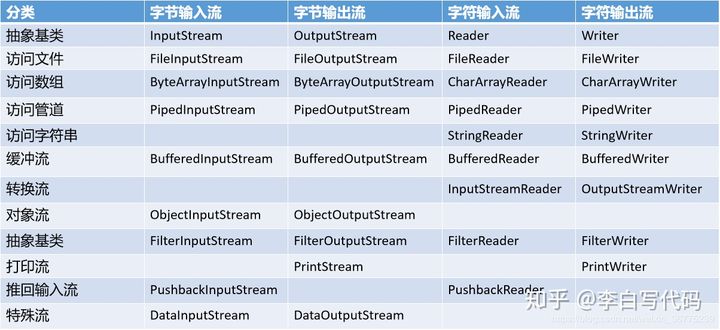
三、流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
IO流体系
1、InputStream(字节流)
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
iprt();
}
public static void ipst(){
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\\1.txt");
int i;
while ( (i = inputStream.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (inputStream != null){
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
说明:使用InputStream向内存中读如文件数据。
2、OutputStream(字节流)
示例:
public class ImageCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\KDA.jpg");
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:\\aaa\\KDA.jpg")
){
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int i;
while ((i = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1){
outputStream.write(bytes,0,i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
说明:使用输入流与输出流结合实现图片复制的功能。
3、Reader(字符流)
示例:
public static void iprt(){
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("C:\\1.txt");
int i ;
while ((i = reader.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
说明:使用Reader(字符流)从文件中读入数据。
4、Writer(字符流)
public static void iprt(){
Reader reader = null;
Writer writer = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\52425\\Desktop\\1.txt");
writer = new FileWriter("C:\\2.txt");
int i ;
while ((i = reader.read()) != -1){
writer.write(i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
writer.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
说明:使用字符流实现文件复制功能。
四、总结(1+2)
1. File类及方法的使用
File是操作文件/目录的类,可以对文件/目录进行创建,重命名, 删除等操作。
2.IO流的分类
- 根据数据大小可分为:字节流和字符流
- 根据流向可分为:输入流和输出流
- 根据功能可分为:节点流和处理流
3.IO流的四个基本类
- 字节输入流:InputStream,它的常用子类是FileInputStream
- 字节输出流:OutputStream,它的常用子类是OutputStream
- 字符输入流:Reader,它的常用子类是FileReader
- 字符输出流:Writer,它的常用子类是FileWriter
总结
本篇关于java IO的文章就到这里了,希望能帮到你,也希望你能够多多关注我们的更多内容!
赞 (0)

