详解Java中CountDownLatch异步转同步工具类
使用场景
由于公司业务需求,需要对接socket、MQTT等消息队列。
众所周知 socket 是双向通信,socket的回复是人为定义的,客户端推送消息给服务端,服务端的回复是两条线。无法像http请求有回复。
下发指令给硬件时,需要校验此次数据下发是否成功。
用户体验而言,点击按钮就要知道此次的下发成功或失败。
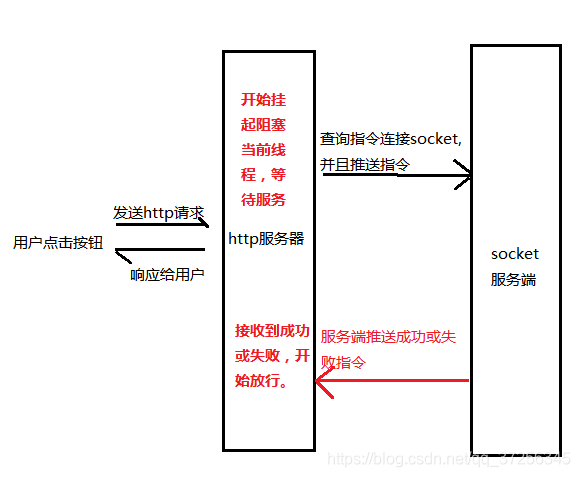
如上图模型,
第一种方案使用Tread.sleep
优点:占用资源小,放弃当前cpu资源
缺点: 回复速度快,休眠时间过长,仍然需要等待休眠结束才能返回,响应速度是固定的,无法及时响应第二种方案使用CountDownLatch
package com.lzy.demo.delay;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class CountDownLatchPool {
//countDonw池
private final static Map<Integer, CountDownLatch> countDownLatchMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//延迟队列
private final static DelayQueue<MessageDelayQueueUtil> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
private volatile static boolean flag =false;
//单线程池
private final static ExecutorService t = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1));
public static void addCountDownLatch(Integer messageId) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.putIfAbsent(messageId,new CountDownLatch(1) );
if(countDownLatch == null){
countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.get(messageId);
}
try {
addDelayQueue(messageId);
countDownLatch.await(3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("阻塞等待结束~~~~~~");
}
public static void removeCountDownLatch(Integer messageId){
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.get(messageId);
if(countDownLatch == null)
return;
countDownLatch.countDown();
countDownLatchMap.remove(messageId);
System.out.println("清除Map数据"+countDownLatchMap);
}
private static void addDelayQueue(Integer messageId){
delayQueue.add(new MessageDelayQueueUtil(messageId));
clearMessageId();
}
private static void clearMessageId(){
synchronized (CountDownLatchPool.class){
if(flag){
return;
}
flag = true;
}
t.execute(()->{
while (delayQueue.size() > 0){
System.out.println("进入线程并开始执行");
try {
MessageDelayQueueUtil take = delayQueue.take();
Integer messageId1 = take.getMessageId();
removeCountDownLatch(messageId1);
System.out.println("清除队列数据"+messageId1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
flag = false;
System.out.println("结束end----");
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/*
测试超时清空map
new Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(1)).start();
new Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(2)).start();
new Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(3)).start();
*/
//提前创建线程,清空countdown
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(500L);
removeCountDownLatch(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
//开始阻塞
addCountDownLatch(1);
//通过调整上面的sleep我们发现阻塞市场取决于countDownLatch.countDown()执行时间
System.out.println("阻塞结束----");
}
}
class MessageDelayQueueUtil implements Delayed {
private Integer messageId;
private long avaibleTime;
public Integer getMessageId() {
return messageId;
}
public void setMessageId(Integer messageId) {
this.messageId = messageId;
}
public long getAvaibleTime() {
return avaibleTime;
}
public void setAvaibleTime(long avaibleTime) {
this.avaibleTime = avaibleTime;
}
public MessageDelayQueueUtil(Integer messageId){
this.messageId = messageId;
//avaibleTime = 当前时间+ delayTime
//重试3次,每次3秒+1秒的延迟
this.avaibleTime=3000*3+1000 + System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
long diffTime= avaibleTime- System.currentTimeMillis();
return unit.convert(diffTime,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
//compareTo用在DelayedUser的排序
return (int)(this.avaibleTime - ((MessageDelayQueueUtil) o).getAvaibleTime());
}
}
由于socket并不确定每次都会有数据返回,所以map的数据会越来越大,最终导致内存溢出
需定时清除map内的无效数据。
可以使用DelayedQuene延迟队列来处理,相当于给对象添加一个过期时间
使用方法 addCountDownLatch 等待消息,异步回调消息清空removeCountDownLatch
到此这篇关于详解Java中CountDownLatch异步转同步工具类的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关CountDownLatch异步转同步工具类内容请搜索我们以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持我们!
赞 (0)

