.NET 6线程池ThreadPool实现概述
目录
- 前言
- 任务的调度
- 基本调度单元
- IThreadPoolWorkItem 实现类的实例。
- Task
- 全局队列
- 本地队列
- 偷窃机制
- Worker Thread 的生命周期管理
- 线程注入实验
- .NET 5 实验一 默认线程池配置
- .NET 5 实验二 调整 ThreadPool 设置
- .NET 5 实验三 tcs.Task.Wait() 改为 Thread.Sleep
- .NET 6 实验一 默认 ThreadPool 设置
- .NET 6 实验二 调整 ThreadPool 设置
- .NET 6 实验三 tcs.Task.Wait() 改为 Thread.Sleep
- 线程注入
- 1. 第一个线程的出现
- 2. 达到 min threads 之前的线程数增长
- 3. 避免饥饿机制(Starvation Avoidance)
- 线程注入在 .NET 6 中的改进
- 爬山算法(Hill Climbing)
- 不必要线程的销毁
- 参考资料
前言
在即将发布的 .NET 6 runtime 中,默认的线程池实现从 C++ 代码改为了 C#,更方便我们学习线程池的设计了。
https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/tree/release/6.0/src/libraries/System.Threading.ThreadPool
新的线程池实现位于 PortableThreadPool 中,原 ThreadPool 中的对外公开的接口会直接调用 PortableThreadPool 中的实现。
通过设置环境变量 ThreadPool_UsePortableThreadPool 为 0 可以设置成使用老的线程池实现。
https://github.com/dotnet/runtime/pull/43841/commits/b0d47b84a6845a70f011d1b0d3ce5adde9a4d7b7
本文以 .NET 6 runtime 源码作为学习材料,对线程池的设计进行介绍。从目前的理解上来看,其整体的设计与原来 C++ 的实现并没有特别大的出入。
注意:
- 本文不涉及细节的代码实现,主要为大家介绍其整体设计。所展示的代码并非原封不动的源码,而是为了方便理解的简化版。
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(int workerThreads, int completionPortThreads)中的completionPortThreads所相关的IOCP线程池是 .NET Framework 时代的遗留产物,用于管理 Windows 平台专有的 IOCP 的回调线程池。目前没看到有什么地方在用它了,completionPortThreads 这个参数也已经没有意义,底层IO库是自己维护的IO等待线程池。本文只涉及 worker thread 池的介绍。- 本文理解并不完整也不一定完全正确,有异议的地方欢迎留言讨论。
- 为了解释问题,一部分代码会运行在 .NET 6 之前的环境中。
任务的调度
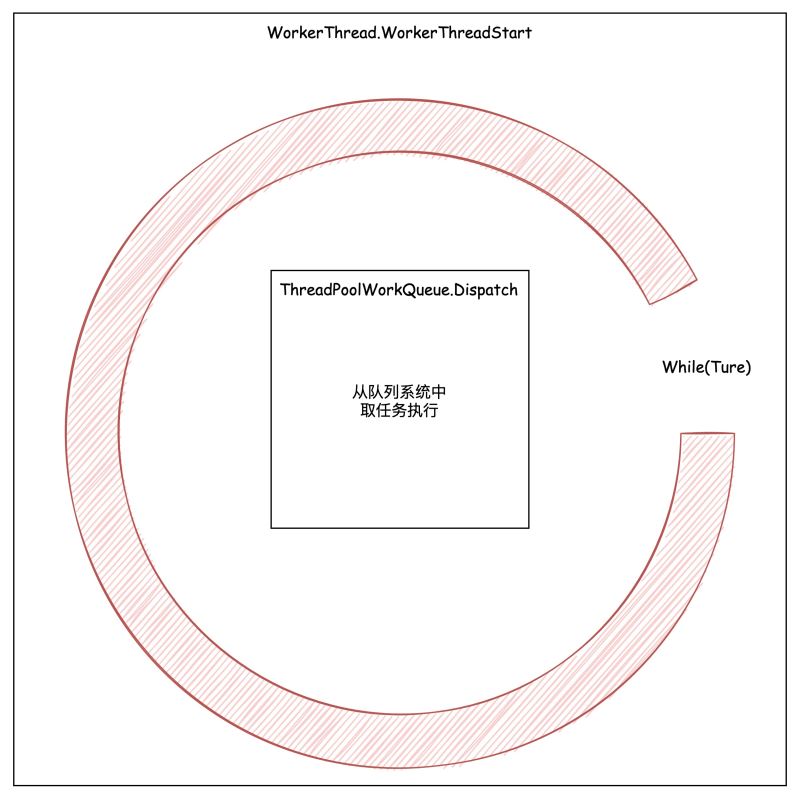
线程池的待执行任务被存放在一个队列系统中。这个系统包括一个 全局队列,以及绑定在每一个 Worker Thread 上 的 本地队列 。而线程池中的每一个线程都在执行 while(true) 的循环,从这个队列系统中领取并执行任务。
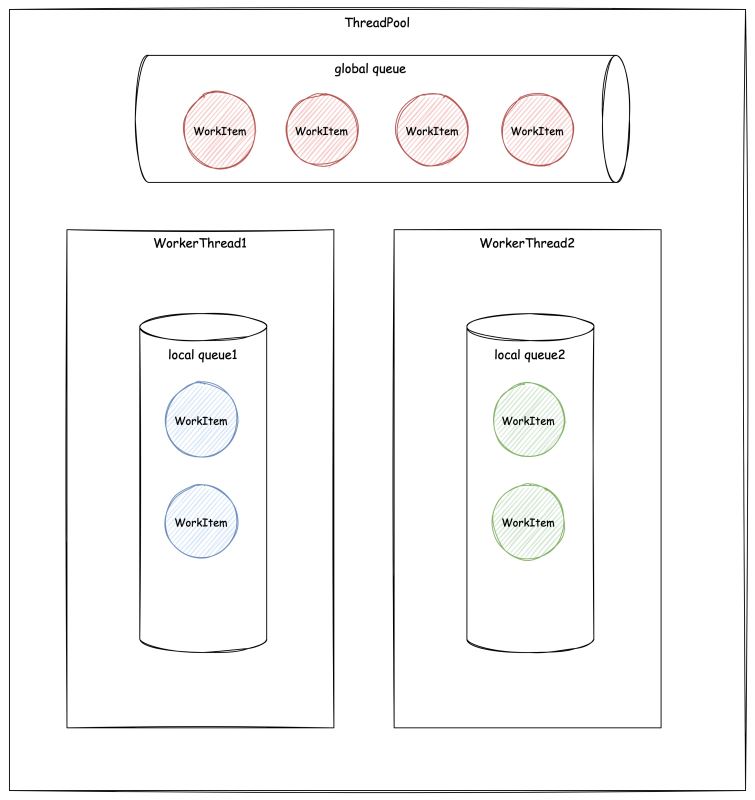
在 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem 的重载方法 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem<TState>(Action<TState> callBack, TState state, bool preferLocal) 里有一个 preferLocal 参数。
调用不带 preferLocal 参数的 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem 方法重载,任务会被放到全局队列。
当 preferLocal 为 true 的时候,如果调用 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem 代码的线程正好是个线程池里的某个线程,则该任务就会进入该线程的本地队列中。除此之外的情况则会被放到全局队列中等待未来被某个 Worker Thread 捡走。
在线程池外的线程中调用,不管 preferLocal 传的是什么,任务都会被放到全局队列。

基本调度单元
本地队列和全局队列的元素类型被定义为 object,实际的任务类型分为两类,在从队列系统取到任务之后会判断类型并执行对应的方法。
IThreadPoolWorkItem 实现类的实例。
/// <summary>Represents a work item that can be executed by the ThreadPool.</summary>
public interface IThreadPoolWorkItem
{
void Execute();
}
执行 Execute 方法也就代表着任务的执行。
IThreadPoolWorkItem 的具体实现有很多,例如通过 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack) 传入的 callBack 委托实例会被包装到一个 QueueUserWorkItemCallback 实例里。QueueUserWorkItemCallback 是 IThreadPoolWorkItem 的实现类。
Task
class Task
{
internal void InnerInvoke();
}
执行 InnerInvoke 会执行 Task 所包含的委托。
全局队列
全局队列 是由 ThreadPoolWorkQueue 维护的,同时它也是整个队列系统的入口,直接被 ThreadPool 所引用。
public static class ThreadPool
{
internal static readonly ThreadPoolWorkQueue s_workQueue = new ThreadPoolWorkQueue();
public static bool QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack, object state)
{
object tpcallBack = new QueueUserWorkItemCallback(callBack!, state);
s_workQueue.Enqueue(tpcallBack, forceGlobal: true);
return true;
}
}
internal sealed class ThreadPoolWorkQueue
{
// 全局队列
internal readonly ConcurrentQueue<object> workItems = new ConcurrentQueue<object>();
// forceGlobal 为 true 时,push 到全局队列,否则就放到本地队列
public void Enqueue(object callback, bool forceGlobal);
}
本地队列
线程池中的每一个线程都会绑定一个 ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals 实例,在 workStealingQueue 这个字段上保存着本地队列。
internal sealed class ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals
{
// 绑定在线程池线程上
[ThreadStatic]
public static ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals threadLocals;
// 持有全局队列的引用,以便能在需要的时候将任务转移到全局队列上
public readonly ThreadPoolWorkQueue workQueue;
// 本地队列的直接维护者
public readonly ThreadPoolWorkQueue.WorkStealingQueue workStealingQueue;
public readonly Thread currentThread;
public ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals(ThreadPoolWorkQueue tpq)
{
workQueue = tpq;
workStealingQueue = new ThreadPoolWorkQueue.WorkStealingQueue();
// WorkStealingQueueList 会集中管理 workStealingQueue
ThreadPoolWorkQueue.WorkStealingQueueList.Add(workStealingQueue);
currentThread = Thread.CurrentThread;
}
// 提供将本地队列中的任务转移到全局队列中去的功能,
// 当 ThreadPool 通过后文将会介绍的 HillClimbing 算法判断得出当前线程是多余的线程后,
// 会调用此方法对任务进行转移
public void TransferLocalWork()
{
while (workStealingQueue.LocalPop() is object cb)
{
workQueue.Enqueue(cb, forceGlobal: true);
}
}
~ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals()
{
if (null != workStealingQueue)
{
// TransferLocalWork 真正的目的并非是为了在这里被调用,这边只是确保任务不会丢的 fallback 逻辑
TransferLocalWork();
ThreadPoolWorkQueue.WorkStealingQueueList.Remove(workStealingQueue);
}
}
}
偷窃机制
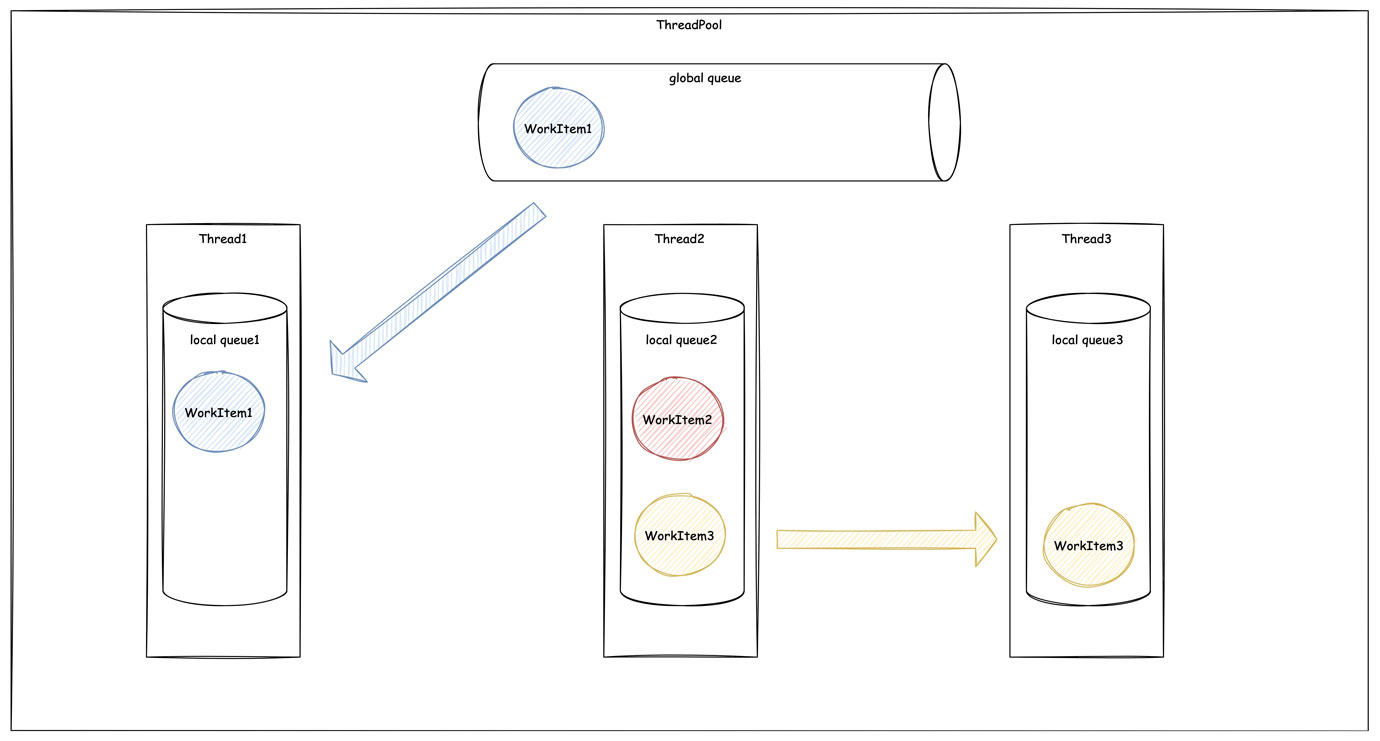
这里思考一个问题,为什么本地队列的名字会被叫做 WorkStealingQueue 呢?
所有 Worker Thread 的 WorkStealingQueue 都被集中在 WorkStealingQueueList 中。对线程池中其他所有线程可见。
Worker Thread 的 while(true) 中优先会从自身的 WorkStealingQueue 中取任务。如果本地队列已经被清空,就会从全局队列中取任务。例如下图的 Thread1 取全局队列中领取了一个任务。
同时 Thread3 也没活干了,但是全局队列中的任务被 Thread1 抢走了。这时候就会去 从 Thread2 的本地队列中抢 Thread2 的活。
Worker Thread 的生命周期管理
接下来我们把格局放大,关注点从 Worker Thread 的打工日常转移到对它们的生命周期管理上来。
为了更方便的解释线程管理的机制,这边使用下面使用一些代码做演示。
代码参考自 https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet/performance-improvements-in-net-6/。
线程注入实验
Task.Run 会将 Task 调度到线程池中执行,下面的示例代码中等效于 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack),会把 Task 放到队列系统的全局队列中(顺便一提,如果在一个线程池线程中执行 Task.Run 会将 Task 调度到此线程池线程的本地队列中)。
.NET 5 实验一 默认线程池配置
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var tcs = new TaskCompletionSource();
var tasks = new List<Task>();
for (int i = 1; i <= Environment.ProcessorCount * 2; i++)
{
int id = i;
Console.WriteLine($"Loop Id: {id:00} | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000} | Busy Threads: {GetBusyThreads()}");
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Task Id: {id:00} | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000} | Busy Threads: {GetBusyThreads()}");
tcs.Task.Wait();
}));
}
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Task SetResult | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000} | Busy Threads: {GetBusyThreads()}");
tcs.SetResult();
}));
Task.WaitAll(tasks.ToArray());
Console.WriteLine($"Done: | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000}");
}
static int GetBusyThreads()
{
ThreadPool.GetAvailableThreads(out var available, out _);
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out var max, out _);
return max - available;
}
首先在代码在 .NET 5 环境中运行以下代码,CPU 逻辑核心数 12。
Loop Id: 01 | 0.000 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.112 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.112 | Busy Threads: 2 Loop Id: 04 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 4 Loop Id: 05 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 7 Loop Id: 06 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 07 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 01 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 02 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 03 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 07 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 04 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 05 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 08 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 08 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 09 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 11 Loop Id: 10 | 0.113 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 11 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 12 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 13 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 14 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 15 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 16 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 17 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 18 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 19 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 20 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 21 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 22 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 23 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 24 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 09 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 06 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 10 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 11 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 12 | 0.114 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 13 | 1.091 | Busy Threads: 13 Task Id: 14 | 1.594 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 15 | 2.099 | Busy Threads: 15 Task Id: 16 | 3.102 | Busy Threads: 16 Task Id: 17 | 3.603 | Busy Threads: 17 Task Id: 18 | 4.107 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 19 | 4.611 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 20 | 5.113 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 21 | 5.617 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 22 | 6.122 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 23 | 7.128 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 24 | 7.632 | Busy Threads: 24 Task SetResult | 8.135 | Busy Threads: 25 Done: | 8.136
Task.Run 会把 Task 调度到线程池上执行,前 24 个 task 都会被阻塞住,直到第 25 个被执行。每次都会打印出当前线程池中正在执行任务的线程数(也就是创建完成的线程数)。
可以观察到以下结果:
- 前几次循环,线程随着 Task 数量递增,后面几次循环直到循环结束为止,线程数一直维持在 12 没有发生变化。
- 线程数在达到 12 之前,零间隔时间增加。第 12 到 第 13 线程间隔 1s 不到,往后约 500ms 增加一个线程。
.NET 5 实验二 调整 ThreadPool 设置
在上面的代码最前面加入以下两行代码,继续在 .NET 5 环境运行一次。
ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out int defaultMinThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"DefaultMinThreads: {defaultMinThreads}");
ThreadPool.SetMinThreads(14, completionPortThreads);
运行结果如下
DefaultMinThreads: 12 Loop Id: 01 | 0.000 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.003 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.003 | Busy Threads: 2 Loop Id: 04 | 0.003 | Busy Threads: 5 Loop Id: 05 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 8 Task Id: 01 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 03 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 06 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 02 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 04 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Task Id: 05 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 07 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 08 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 09 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 11 Loop Id: 10 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 08 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 06 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 09 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 10 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 11 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 12 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 13 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 14 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 15 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 16 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 17 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 18 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 19 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 20 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 21 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 22 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 11 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 23 | 0.004 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 24 | 0.005 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 07 | 0.005 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 12 | 0.005 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 13 | 0.005 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 14 | 0.005 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 15 | 0.982 | Busy Threads: 15 Task Id: 16 | 1.486 | Busy Threads: 16 Task Id: 17 | 1.991 | Busy Threads: 17 Task Id: 18 | 2.997 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 19 | 3.501 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 20 | 4.004 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 21 | 4.509 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 22 | 5.014 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 23 | 5.517 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 24 | 6.021 | Busy Threads: 24 Task SetResult | 6.522 | Busy Threads: 25 Done: | 6.523
在调整完线程池的最小线程数量之后,线程注入速度发生转折的时间点从第 12(默认min threads) 个线程换到了第 14(修改后的min threads)个线程。
整体时间也从 8s 缩到 6s。
.NET 5 实验三 tcs.Task.Wait() 改为 Thread.Sleep
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
var tasks = new List<Task>();
for (int i = 1; i <= Environment.ProcessorCount * 2; i++)
{
int id = i;
Console.WriteLine(
$"Loop Id: {id:00} | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000} | Busy Threads: {GetBusyThreads()}");
tasks.Add(Task.Run(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine(
$"Task Id: {id:00} | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000} | Busy Threads: {GetBusyThreads()}");
Thread.Sleep(Environment.ProcessorCount * 1000);
}));
}
Task.WhenAll(tasks.ToArray()).ContinueWith(_ =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"Done: | {sw.Elapsed.TotalSeconds:0.000}");
});
Console.ReadLine();
}
Loop Id: 01 | 0.000 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.027 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.027 | Busy Threads: 2 Loop Id: 04 | 0.027 | Busy Threads: 3 Loop Id: 05 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 4 Loop Id: 06 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 07 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 08 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 09 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 10 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 11 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 12 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 13 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 14 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 15 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 16 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 17 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 18 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 19 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 20 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 21 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 22 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 23 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 24 | 0.028 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 01 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 05 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 03 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 08 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 09 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 10 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 06 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 11 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 12 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 04 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 02 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 07 | 0.029 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 13 | 1.018 | Busy Threads: 13 Task Id: 14 | 1.522 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 15 | 2.025 | Busy Threads: 15 Task Id: 16 | 2.530 | Busy Threads: 16 Task Id: 17 | 3.530 | Busy Threads: 17 Task Id: 18 | 4.035 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 19 | 4.537 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 20 | 5.040 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 21 | 5.545 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 22 | 6.048 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 23 | 7.049 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 24 | 8.056 | Busy Threads: 24 Done: | 20.060
达到 min threads (默认12)之后,线程注入速度明显变慢,最快间隔 500ms。
.NET 6 实验一 默认 ThreadPool 设置
将 .NET 5 实验一的代码在 .NET 6 执行一次
Loop Id: 01 | 0.001 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 3 Loop Id: 04 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 6 Loop Id: 05 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 4 Loop Id: 06 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 5 Loop Id: 07 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 6 Loop Id: 08 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 8 Task Id: 01 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 04 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 03 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 02 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 05 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 11 Loop Id: 09 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 10 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 11 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 12 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 13 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 09 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 14 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 15 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 16 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 17 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 06 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 18 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 19 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 20 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 21 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 22 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 23 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 24 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 10 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 07 | 0.019 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 11 | 0.019 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 08 | 0.019 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 12 | 0.019 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 13 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 16 Task Id: 14 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 17 Task Id: 15 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 16 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 17 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 18 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 19 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 20 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 21 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 24 Task Id: 23 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 24 Task Id: 22 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 24 Task Id: 24 | 0.020 | Busy Threads: 24 Task SetResult | 0.045 | Busy Threads: 25 Done: | 0.046
与实验一相比,虽然线程数仍然停留在 12 了一段时间,但随后线程就立即增长了,后文会介绍 .NET 6 在这方面做出的改进。
.NET 6 实验二 调整 ThreadPool 设置
将 .NET 5 实验二的代码在 .NET 6 中执行一次
DefaultMinThreads: 12 Loop Id: 01 | 0.001 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.014 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.014 | Busy Threads: 2 Loop Id: 04 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 5 Loop Id: 05 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 4 Loop Id: 06 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 5 Loop Id: 07 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 7 Loop Id: 08 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 8 Loop Id: 09 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 11 Task Id: 06 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 01 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 02 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 05 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 03 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 04 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 07 | 0.015 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 08 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 9 Task Id: 09 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 10 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 11 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 12 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 11 Loop Id: 13 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 13 Task Id: 10 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 14 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 15 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 16 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 11 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 17 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 18 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 19 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 20 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 21 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 22 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 23 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Loop Id: 24 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 12 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 13 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 14 | 0.016 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 15 | 0.017 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 16 | 0.017 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 17 | 0.017 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 18 | 0.017 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 19 | 0.017 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 20 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 21 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 24 Task Id: 22 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 25 Task Id: 23 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 26 Task Id: 24 | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 26 Task SetResult | 0.018 | Busy Threads: 25 Done: | 0.019
前半部分有部分日志乱序,可以看到,与实验三一样,维持在最大线程数一小段时间之后,立即就开始了线程增长。
.NET 6 实验三 tcs.Task.Wait() 改为 Thread.Sleep
将 .NET 5 实验三的代码在 .NET 6 中执行一次
Loop Id: 01 | 0.003 | Busy Threads: 0 Loop Id: 02 | 0.024 | Busy Threads: 1 Loop Id: 03 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 2 Loop Id: 04 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 3 Loop Id: 05 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 7 Loop Id: 06 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 5 Loop Id: 07 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 6 Loop Id: 08 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 7 Loop Id: 09 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 9 Loop Id: 10 | 0.025 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 11 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 10 Loop Id: 12 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 11 Loop Id: 13 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 14 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 15 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 16 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 17 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 18 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 19 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 20 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 21 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 22 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 23 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Loop Id: 24 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 01 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 02 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 05 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 04 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 06 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 08 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 09 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 03 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 11 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 10 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 07 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 12 | 0.026 | Busy Threads: 12 Task Id: 13 | 1.026 | Busy Threads: 13 Task Id: 14 | 2.027 | Busy Threads: 14 Task Id: 15 | 3.028 | Busy Threads: 15 Task Id: 16 | 4.030 | Busy Threads: 16 Task Id: 17 | 5.031 | Busy Threads: 17 Task Id: 18 | 6.032 | Busy Threads: 18 Task Id: 19 | 6.533 | Busy Threads: 19 Task Id: 20 | 7.035 | Busy Threads: 20 Task Id: 21 | 8.036 | Busy Threads: 21 Task Id: 22 | 8.537 | Busy Threads: 22 Task Id: 23 | 9.538 | Busy Threads: 23 Task Id: 24 | 10.039 | Busy Threads: 24 Done: | 22.041
结果与 .NET 5 的实验三相差不大。
线程注入
对照上述的几组实验结果,接下来以 .NET 6 中 C# 实现的 ThreadPool 作为资料来理解一下线程注入的几个阶段(按个人理解进行的划分,仅供参考)。
1. 第一个线程的出现
随着任务被调度到队列上,第一个线程被创建出来。
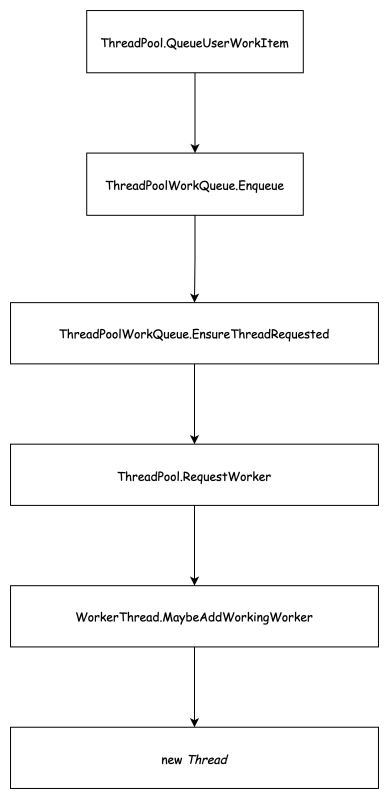
下面是线程池在执行第一个任务的时候的代码摘要,涉及到计数的并执行相关处理的地方,代码都使用了 while(xxx) + Interlocked 的方式来进行并发控制,可以理解成乐观锁。这一阶段,实际上我们只需要关注到 ThreadPoolWorkQueue.EnsureThreadRequested 方法就行了。
可利用 Rider 的反编译 Debug 功能帮助我们学习。
下面是第一个 Task.Run 的代码执行路径
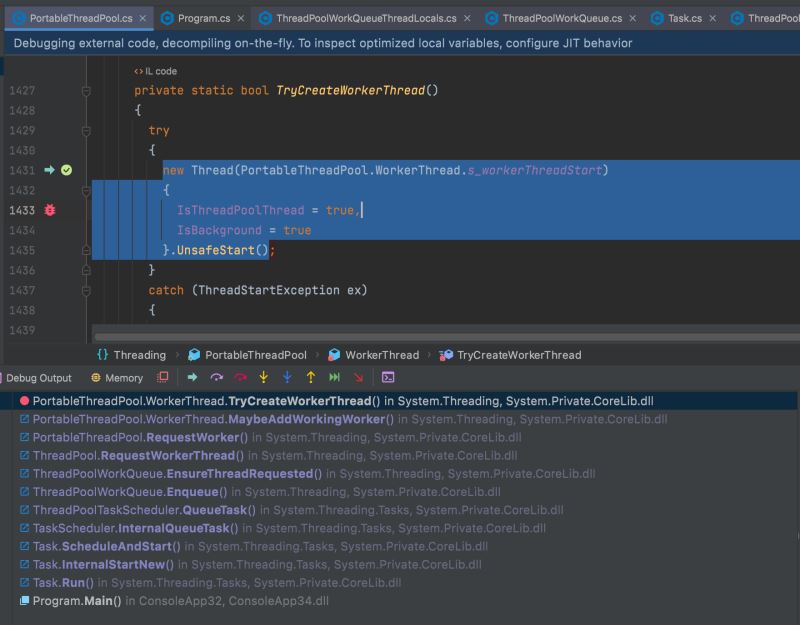
注意:执行环节是 Main Thread
public static class ThreadPool
{
internal static readonly ThreadPoolWorkQueue s_workQueue = new ThreadPoolWorkQueue();
public static bool QueueUserWorkItem(WaitCallback callBack, object state)
{
object tpcallBack = new QueueUserWorkItemCallback(callBack!, state);
s_workQueue.Enqueue(tpcallBack, forceGlobal: true);
return true;
}
}
internal sealed class ThreadPoolWorkQueue
{
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
private struct CacheLineSeparated
{
private readonly Internal.PaddingFor32 pad1;
public volatile int numOutstandingThreadRequests;
private readonly Internal.PaddingFor32 pad2;
}
private CacheLineSeparated _separated;
public void Enqueue(object callback, bool forceGlobal)
{
// 线程池中执行的任务有两种:IThreadPoolWorkItem、Task
Debug.Assert((callback is IThreadPoolWorkItem) ^ (callback is Task));
if (loggingEnabled && FrameworkEventSource.Log.IsEnabled())
FrameworkEventSource.Log.ThreadPoolEnqueueWorkObject(callback);
ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals? tl = null;
if (!forceGlobal)
// 获取本地队列,如果执行改代码的线程不是线程池线程,
// 那这边是获取不到的,就算 forceGlobal 是 false,
// 也会把任务放到全局队列
tl = ThreadPoolWorkQueueThreadLocals.threadLocals;
if (null != tl)
{
// 放到本地队列
tl.workStealingQueue.LocalPush(callback);
}
else
{
// 当道全局队列
workItems.Enqueue(callback);
}
EnsureThreadRequested();
}
internal void EnsureThreadRequested()
{
//
// If we have not yet requested #procs threads, then request a new thread.
//
// CoreCLR: Note that there is a separate count in the VM which has already been incremented
// by the VM by the time we reach this point.
//
int count = _separated.numOutstandingThreadRequests;
while (count < Environment.ProcessorCount)
{
int prev = Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _separated.numOutstandingThreadRequests, count + 1, count);
if (prev == count)
{
ThreadPool.RequestWorkerThread();
break;
}
count = prev;
}
}
public static class ThreadPool
{
/// <summary>
/// This method is called to request a new thread pool worker to handle pending work.
/// </summary>
internal static void RequestWorkerThread() => PortableThreadPool.ThreadPoolInstance.RequestWorker();
}
internal sealed class PortableThreadPool
{
public static readonly PortableThreadPool ThreadPoolInstance = new PortableThreadPool();
internal void RequestWorker()
{
// The order of operations here is important. MaybeAddWorkingWorker() and EnsureRunning() use speculative checks to
// do their work and the memory barrier from the interlocked operation is necessary in this case for correctness.
Interlocked.Increment(ref _separated.numRequestedWorkers);
WorkerThread.MaybeAddWorkingWorker(this);
// 初始化 GateThread
GateThread.EnsureRunning(this);
}
/// <summary>
/// The worker thread infastructure for the CLR thread pool.
/// </summary>
private static class WorkerThread
{
internal static void MaybeAddWorkingWorker(PortableThreadPool threadPoolInstance)
{
ThreadCounts counts = threadPoolInstance._separated.counts;
short numExistingThreads, numProcessingWork, newNumExistingThreads, newNumProcessingWork;
// 这个 while (true) 是确保计算出正确的待创建线程数
while (true)
{
numProcessingWork = counts.NumProcessingWork;
if (numProcessingWork >= counts.NumThreadsGoal)
{
return;
}
newNumProcessingWork = (short)(numProcessingWork + 1);
numExistingThreads = counts.NumExistingThreads;
newNumExistingThreads = Math.Max(numExistingThreads, newNumProcessingWork);
ThreadCounts newCounts = counts;
newCounts.NumProcessingWork = newNumProcessingWork;
newCounts.NumExistingThreads = newNumExistingThreads;
ThreadCounts oldCounts = threadPoolInstance._separated.counts.InterlockedCompareExchange(newCounts, counts);
if (oldCounts == counts)
{
break;
}
counts = oldCounts;
}
int toCreate = newNumExistingThreads - numExistingThreads;
int toRelease = newNumProcessingWork - numProcessingWork;
if (toRelease > 0)
{
s_semaphore.Release(toRelease);
}
while (toCreate > 0)
{
if (TryCreateWorkerThread())
{
toCreate--;
continue;
}
counts = threadPoolInstance._separated.counts;
while (true)
{
ThreadCounts newCounts = counts;
newCounts.SubtractNumProcessingWork((short)toCreate);
newCounts.SubtractNumExistingThreads((short)toCreate);
ThreadCounts oldCounts = threadPoolInstance._separated.counts.InterlockedCompareExchange(newCounts, counts);
if (oldCounts == counts)
{
break;
}
counts = oldCounts;
}
break;
}
}
private static bool TryCreateWorkerThread()
{
try
{
// Thread pool threads must start in the default execution context without transferring the context, so
// using UnsafeStart() instead of Start()
Thread workerThread = new Thread(s_workerThreadStart);
workerThread.IsThreadPoolThread = true;
workerThread.IsBackground = true;
// thread name will be set in thread proc
workerThread.UnsafeStart();
}
catch (ThreadStartException)
{
return false;
}
catch (OutOfMemoryException)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
}
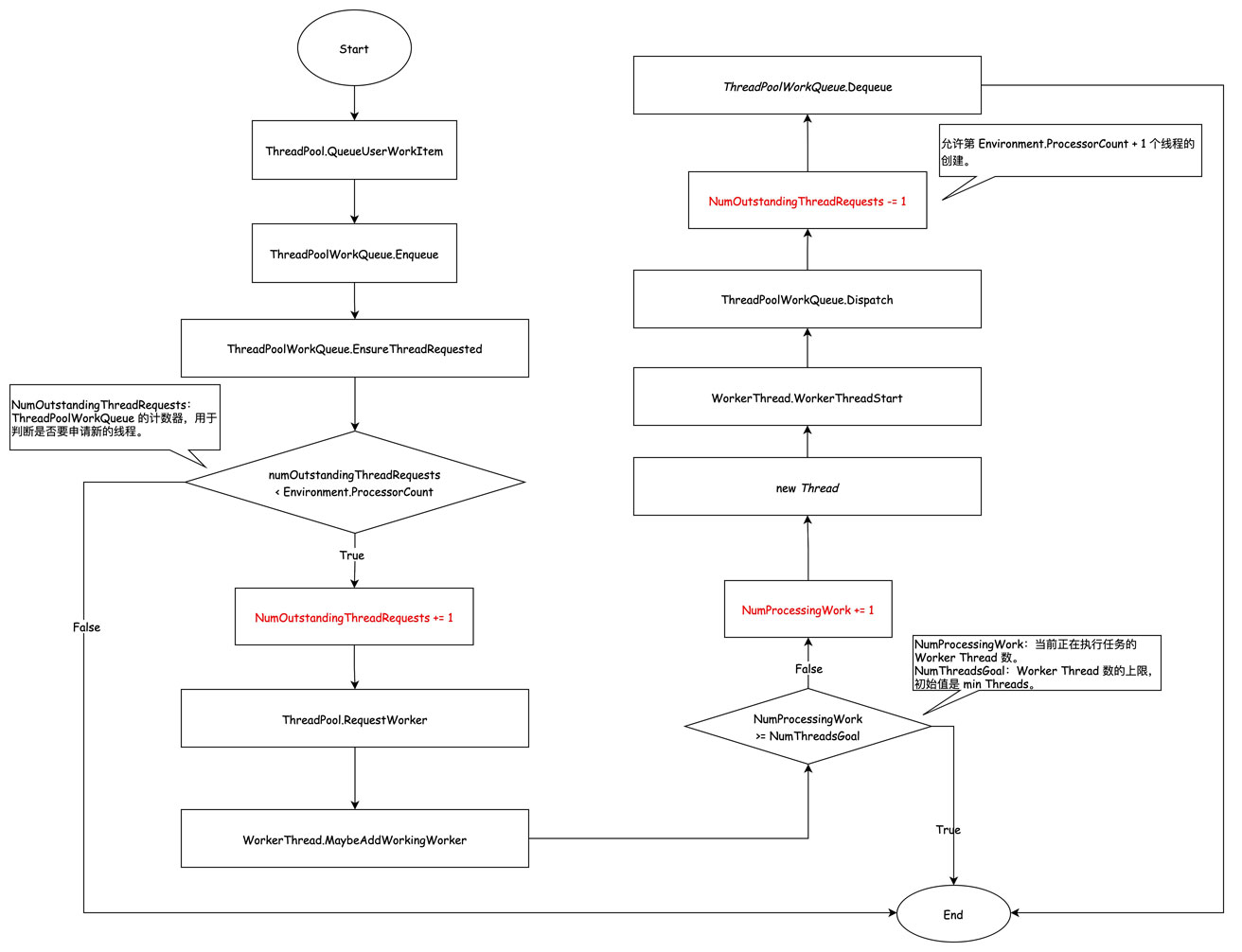
2. 达到 min threads 之前的线程数增长
细心的朋友会发现上面代码里 EnsureThreadRequested 方法有一个终止条件,_separated.numOutstandingThreadRequests == Environment.ProcessorCount,每次新增一个 ThreadRequested,这个数就会 +1,似乎允许创建的最大 Worker Thread 是 Environment.ProcessorCount?
其实 ThreadPoolWorkQueue 维护的 NumOutstandingThreadRequests 这个值会在线程池线程真正跑起来之后,会在 ThreadPoolWorkQueue.Dispatch方法中 -1。也就是说,只要有一个线程真正运行起来了,就能创建第 Environment.ProcessorCount + 1 个Thread。当然,在向 ThreadPoolWorkQueue 加入第13个任务的时候,第13个 Worker Thread 就算不允许创建也没关系,因为任务已经入队了,会被运行起来的 Worker Thread 取走。
min threads 初始值为 运行环境 CPU 核心数,可通过 ThreadPool.SetMinThreads 进行设置,参数有效范围是 [1, max threads]。
PortableThreadPool里维护了一个计数器 PortableThreadPool.ThreadPoolInstance._separated.counts,记录了 Worker Thread 相关的三个数值:
- NumProcessingWork:当前正在执行任务的 Worker Thread。
- NumExistingThreads:当前线程池中实际有的 Worker Thread。
- NumThreadsGoal:当前允许创建的最大 Worker Thread,初始值为 min threads。
internal class PortableThreadPool
{
public static readonly PortableThreadPool ThreadPoolInstance = new PortableThreadPool();
private CacheLineSeparated _separated;
private struct CacheLineSeparated
{
public ThreadCounts counts;
}
/// <summary>
/// Tracks information on the number of threads we want/have in different states in our thread pool.
/// </summary>
private struct ThreadCounts
{
/// <summary>
/// Number of threads processing work items.
/// </summary>
public short NumProcessingWork { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Number of thread pool threads that currently exist.
/// </summary>
public short NumExistingThreads { get; set; }
// <summary>
/// Max possible thread pool threads we want to have.
/// </summary>
public short NumThreadsGoal { get; set; }
}
}
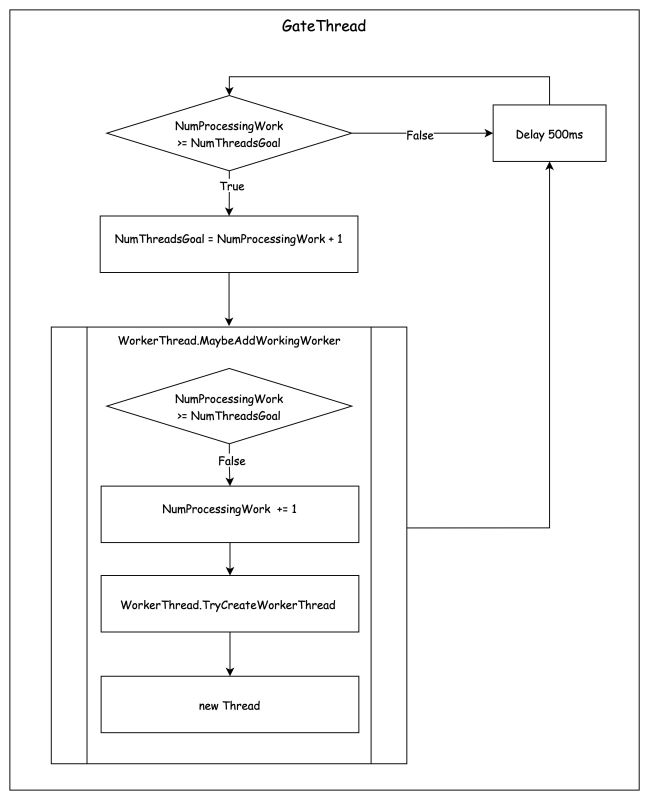
3. 避免饥饿机制(Starvation Avoidance)
上面讲到,随着任务进入队列系统,Worker Thread 将随之增长,直到达到 NumThreadsGoal。
NumThreadsGoal 是12,前 12 个线程都被堵住了,加入到队列系统的第 13 个任务没办法被这前 12 个线程领走执行。
在这种情况下,线程池的 Starvation Avoidance 机制就起到作用了。
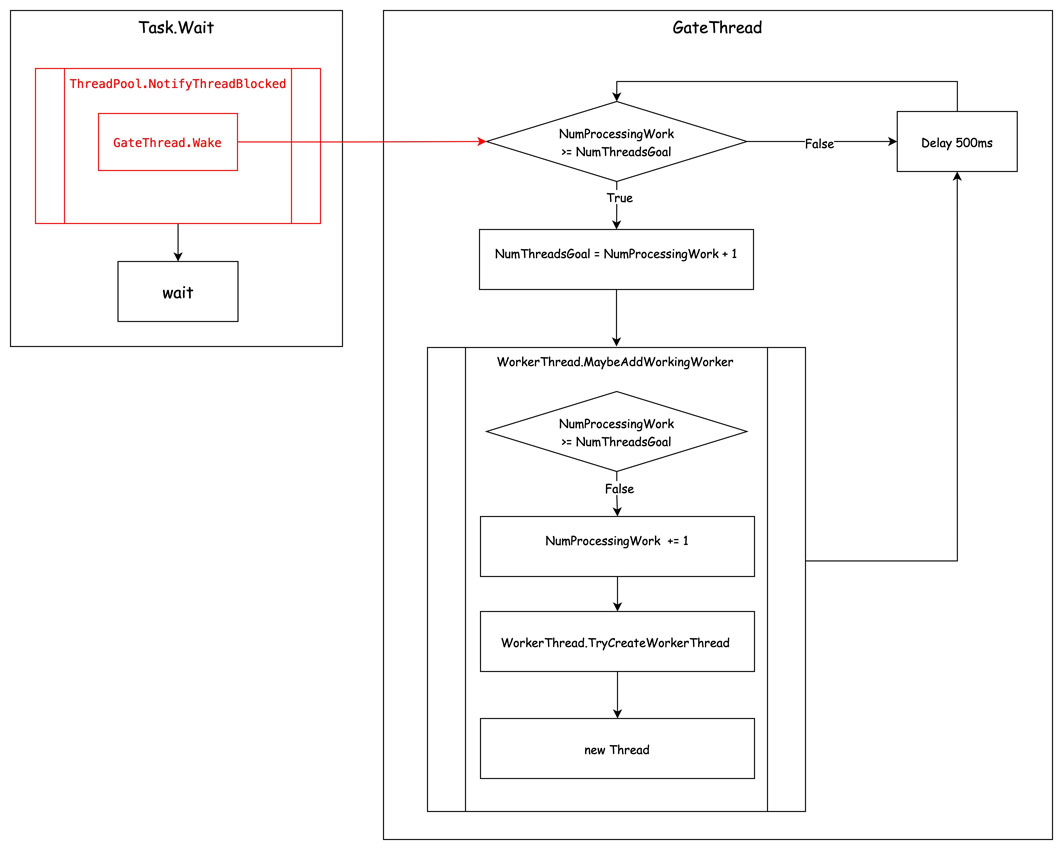
在上述所说的第一个阶段,除了线程池中的第一个线程会被创建之外,GateThread 也会随之被初始化。在第一阶段的代码摘录中,可以看到 GateThread 的初始化。
internal sealed class PortableThreadPool
{
public static readonly PortableThreadPool ThreadPoolInstance = new PortableThreadPool();
internal void RequestWorker()
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref _separated.numRequestedWorkers);
WorkerThread.MaybeAddWorkingWorker(this);
// 初始化 GateThread
GateThread.EnsureRunning(this);
}
}
在 GateThread 是一个独立的线程,每隔 500ms 进行检查一下,如果 NumProcessingWork >= NumThreadsGoal(WorkerThread.MaybeAddWorkingWorker 不添加 Worker Thread 的判断条件),就设置新的 NumThreadsGoal = NumProcessingWork + 1,并调用 WorkerThread.MaybeAddWorkingWorker,这样新的 Worker Thread 就可以被 WorkerThread.MaybeAddWorkingWorker 创建。
这就解释了,为什么 .NET 5 实验一、二在线程数达到min threads(NumThreadsGoal 的默认值)之后,后面 Worker Thread 的增长是每 500ms 一个。
由于在第三阶段中,线程的增长会比较缓慢,有经验的开发会在应用启动的时候设置一个较大的 min threads,使其较晚或不进入第三阶段。
线程注入在 .NET 6 中的改进
.NET 6 与 .NET 5 的实验二相比,达到 min threads 之后,线程的增长速度有明显的差异,而两者的实验三却相差不大。
.NET 6 对于 Task.Wait 导致线程池线程阻塞的场景进行了优化,但如果并非此原因导致的线程数不够用,依旧是 Starvation Avoidance 的策略。
新的 ThreadPool 提供了一个 ThreadPool.NotifyThreadBlocked 的内部接口,里面会调用 GateThread.Wake 去唤醒 GateThread 本来 500ms 执行一次的逻辑,这 500ms 的间隔时间是通过 AutoResetEvent 实现的,所以 GateThread.Wake 也很简单。
关键代码示意,非真实代码:
internal class PortableThreadPool
{
public bool NotifyThreadBlocked()
{
// ...
GateThread.Wake(this);
return true;
}
private static class GateThread
{
private static readonly AutoResetEvent DelayEvent = new AutoResetEvent(initialState: false);
// GateThread 入口方法
private static void GateThreadStart()
{
while(true)
{
DelayEvent.WaitOne(500);
// ...
}
}
public static void Wake(PortableThreadPool threadPoolInstance)
{
DelayEvent.Set();
EnsureRunning(threadPoolInstance);
}
}
爬山算法(Hill Climbing)
除了上述介绍的线程注入机制外,从CLR 4.0开始,线程池内实现了一个根据采集到线程池吞吐率数据(每次任务完成时记录数据),推导出该算法认为最优的线程池线程数量。
算法实现位于 HillClimbing.ThreadPoolHillClimber.Update,有兴趣的朋友可以去看一下。
public (int newThreadCount, int newSampleMs) Update(int currentThreadCount, double sampleDurationSeconds, int numCompletions)
- currentThreadCount:当前线程数
- sampleDurationSeconds:采样间隔
- numCompletions:这段采样时间间隔内完成的任务数
- newThreadCount:新的线程数
- newSample:新的采样间隔时间
不必要线程的销毁
如果线程需要被移除的时候,本地队列还存在待执行任务,则会将这些任务转移到全局队列中。
在以下几个场景中,线程池将会销毁掉不需要的线程,并不一定全面,只限于笔者当前认知。
- 在无法从队列系统领取到任务时。
- 通过爬山算法认定当前线程属于多余线程时。
参考资料
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/3813/NET-s-ThreadPool-Class-Behind-The-Scenes
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/dotnet/performance-improvements-in-net-6/
https://mattwarren.org/2017/04/13/The-CLR-Thread-Pool-Thread-Injection-Algorithm/
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-CN/previous-versions/msp-n-p/ff963549(v=pandp.10)?redirectedfrom=MSDN
到此这篇关于.NET 6线程池ThreadPool实现方法的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

