TensorFlow实现简单的CNN的方法
这里,我们将采用Tensor Flow内建函数实现简单的CNN,并用MNIST数据集进行测试
第1步:加载相应的库并创建计算图会话
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist import read_data_sets import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #创建计算图会话 sess = tf.Session()
第2步:加载MNIST数据集,这里采用TensorFlow自带数据集,MNIST数据为28×28的图像,因此将其转化为相应二维矩阵
#数据集 data_dir = 'MNIST_data' mnist = read_data_sets(data_dir) train_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x,[28,28]) for x in mnist.train.images] ) test_xdata = np.array([np.reshape(x,[28,28]) for x in mnist.test.images] ) train_labels = mnist.train.labels test_labels = mnist.test.labels
第3步:设置模型参数
这里采用随机批量训练的方法,每训练10次对测试集进行测试,共迭代1500次,学习率采用指数下降的方式,初始学习率为0.1,每训练10次,学习率乘0.9,为了进行对比,后面会给出固定学习率为0.01的损失曲线图和准确率图
#设置模型参数
batch_size = 100 #批量训练图像张数
initial_learning_rate = 0.1 #学习率
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False) ;
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(initial_learning_rate,
global_step=global_step,
decay_steps=10,decay_rate=0.9)
evaluation_size = 500 #测试图像张数
image_width = 28 #图像的宽和高
image_height = 28
target_size = 10 #图像的目标为0~9共10个目标
num_channels = 1 #灰度图,颜色通道为1
generations = 1500 #迭代500次
evaluation_step = 10 #每训练十次进行一次测试
conv1_features = 25 #卷积层的特征个数
conv2_features = 50
max_pool_size1 = 2 #池化层大小
max_pool_size2 = 2
fully_connected_size = 100 #全连接层的神经元个数
第4步:声明占位符,注意这里的目标y_target类型为int32整型
#声明占位符 x_input_shape = [batch_size,image_width,image_height,num_channels] x_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=x_input_shape) y_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[batch_size]) evaluation_input_shape = [evaluation_size,image_width,image_height,num_channels] evaluation_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=evaluation_input_shape) evaluation_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[evaluation_size])
第5步:声明卷积层和全连接层的权重和偏置,这里采用2层卷积层和1层隐含全连接层
#声明卷积层的权重和偏置 #卷积层1 #采用滤波器为4X4滤波器,输入通道为1,输出通道为25 conv1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4,4,num_channels,conv1_features],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([conv1_features],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) #卷积层2 #采用滤波器为4X4滤波器,输入通道为25,输出通道为50 conv2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([4,4,conv1_features,conv2_features],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) conv2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([conv2_features],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) #声明全连接层权重和偏置 #卷积层过后图像的宽和高 conv_output_width = image_width // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2) #//表示整除 conv_output_height = image_height // (max_pool_size1 * max_pool_size2) #全连接层的输入大小 full1_input_size = conv_output_width * conv_output_height *conv2_features full1_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([full1_input_size,fully_connected_size],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) full1_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) full2_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([fully_connected_size,target_size],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32)) full2_bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([target_size],stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32))
第6步:声明CNN模型,这里的两层卷积层均采用Conv-ReLU-MaxPool的结构,步长为[1,1,1,1],padding为SAME
全连接层隐层神经元为100个,输出层为目标个数10
def my_conv_net(input_data):
#第一层:Conv-ReLU-MaxPool
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_data,conv1_weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1,conv1_bias))
max_pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1,ksize=[1,max_pool_size1,max_pool_size1,1],strides=[1,max_pool_size1,max_pool_size1,1],padding='SAME')
#第二层:Conv-ReLU-MaxPool
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(max_pool1, conv2_weight, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv2_bias))
max_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, max_pool_size2, max_pool_size2, 1],
strides=[1, max_pool_size2, max_pool_size2, 1], padding='SAME')
#全连接层
#先将数据转化为1*N的形式
#获取数据大小
conv_output_shape = max_pool2.get_shape().as_list()
#全连接层输入数据大小
fully_input_size = conv_output_shape[1]*conv_output_shape[2]*conv_output_shape[3] #这三个shape就是图像的宽高和通道数
full1_input_data = tf.reshape(max_pool2,[conv_output_shape[0],fully_input_size]) #转化为batch_size*fully_input_size二维矩阵
#第一层全连接
fully_connected1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(full1_input_data,full1_weight),full1_bias))
#第二层全连接输出
model_output = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(fully_connected1,full2_weight),full2_bias))#shape = [batch_size,target_size]
return model_output
model_output = my_conv_net(x_input)
test_model_output = my_conv_net(evaluation_input)
第7步:定义损失函数,这里采用softmax函数作为损失函数
#损失函数 loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output,labels=y_target))
第8步:建立测评与评估函数,这里对输出层进行softmax,再通过np.argmax找出每行最大的数所在位置,再与目标值进行比对,统计准确率
#预测与评估 prediction = tf.nn.softmax(model_output) test_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(test_model_output) def get_accuracy(logits,targets): batch_predictions = np.argmax(logits,axis=1)#返回每行最大的数所在位置 num_correct = np.sum(np.equal(batch_predictions,targets)) return 100*num_correct/batch_predictions.shape[0]
第9步:初始化模型变量并创建优化器
#创建优化器 opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate) train_step = opt.minimize(loss) #初始化变量 init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess.run(init)
第10步:随机批量训练并进行绘图
#开始训练
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
Learning_rate_vec = []
for i in range(generations):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(train_xdata),size=batch_size)
rand_x = train_xdata[rand_index]
rand_x = np.expand_dims(rand_x,3)
rand_y = train_labels[rand_index]
Learning_rate_vec.append(sess.run(learning_rate, feed_dict={global_step: i}))
train_dict = {x_input:rand_x,y_target:rand_y}
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x_input:rand_x,y_target:rand_y,global_step:i})
temp_train_loss = sess.run(loss,feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_prediction = sess.run(prediction,feed_dict=train_dict)
temp_train_acc = get_accuracy(temp_train_prediction,rand_y)
#测试集
if (i+1)%evaluation_step ==0:
eval_index = np.random.choice(len(test_xdata),size=evaluation_size)
eval_x = test_xdata[eval_index]
eval_x = np.expand_dims(eval_x,3)
eval_y = test_labels[eval_index]
test_dict = {evaluation_input:eval_x,evaluation_target:eval_y}
temp_test_preds = sess.run(test_prediction,feed_dict=test_dict)
temp_test_acc = get_accuracy(temp_test_preds,eval_y)
test_acc.append(temp_test_acc)
train_acc.append(temp_train_acc)
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
#画损失曲线
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(train_loss,'k-')
ax.set_xlabel('Generation')
ax.set_ylabel('Softmax Loss')
fig.suptitle('Softmax Loss per Generation')
#画准确度曲线
index = np.arange(start=1,stop=generations+1,step=evaluation_step)
fig2 = plt.figure()
ax2 = fig2.add_subplot(111)
ax2.plot(train_acc,'k-',label='Train Set Accuracy')
ax2.plot(index,test_acc,'r--',label='Test Set Accuracy')
ax2.set_xlabel('Generation')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy')
fig2.suptitle('Train and Test Set Accuracy')
#画图
fig3 = plt.figure()
actuals = rand_y[0:6]
train_predictions = np.argmax(temp_train_prediction,axis=1)[0:6]
images = np.squeeze(rand_x[0:6])
Nrows = 2
Ncols =3
for i in range(6):
ax3 = fig3.add_subplot(Nrows,Ncols,i+1)
ax3.imshow(np.reshape(images[i],[28,28]),cmap='Greys_r')
ax3.set_title('Actual: '+str(actuals[i]) +' pred: '+str(train_predictions[i]))
#画学习率
fig4 = plt.figure()
ax4 = fig4.add_subplot(111)
ax4.plot(Learning_rate_vec,'k-')
ax4.set_xlabel('step')
ax4.set_ylabel('Learning_rate')
fig4.suptitle('Learning_rate')
plt.show()
下面给出固定学习率图像和学习率随迭代次数下降的图像:
首先给出固定学习率图像:
下面是损失曲线
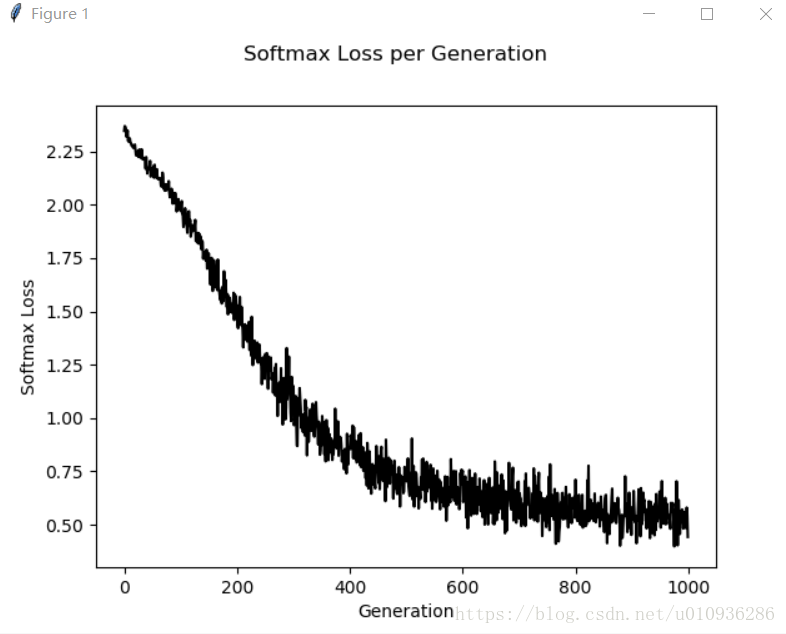
下面是准确率
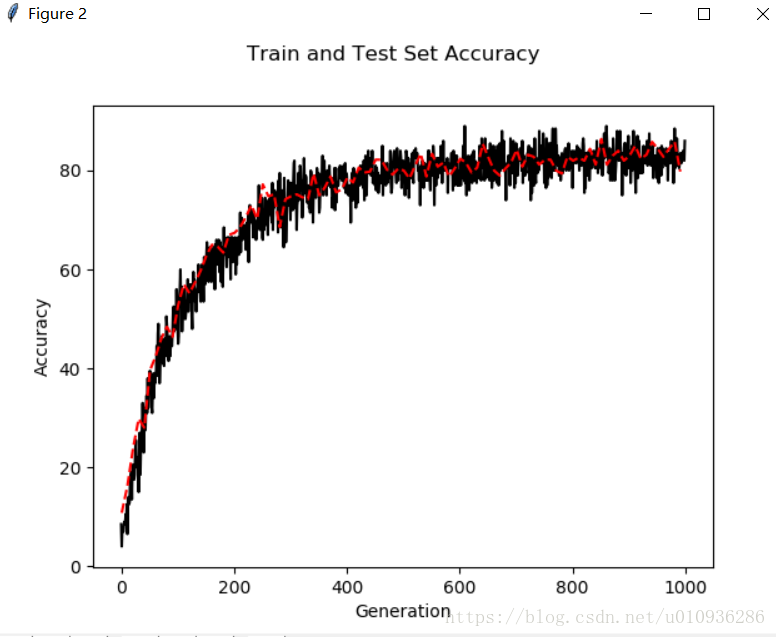
我们可以看出,固定学习率损失函数下降速度较缓,同时其最终准确率为80%~90%之间就不再提高了
下面给出学习率随迭代次数降低的曲线:
首先给出学习率随迭代次数降低的损失曲线
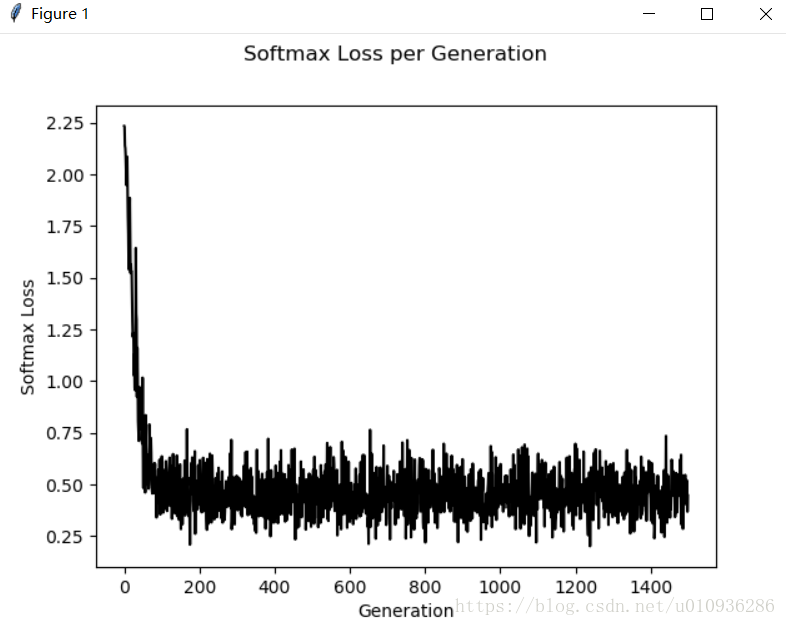
然后给出相应的准确率曲线
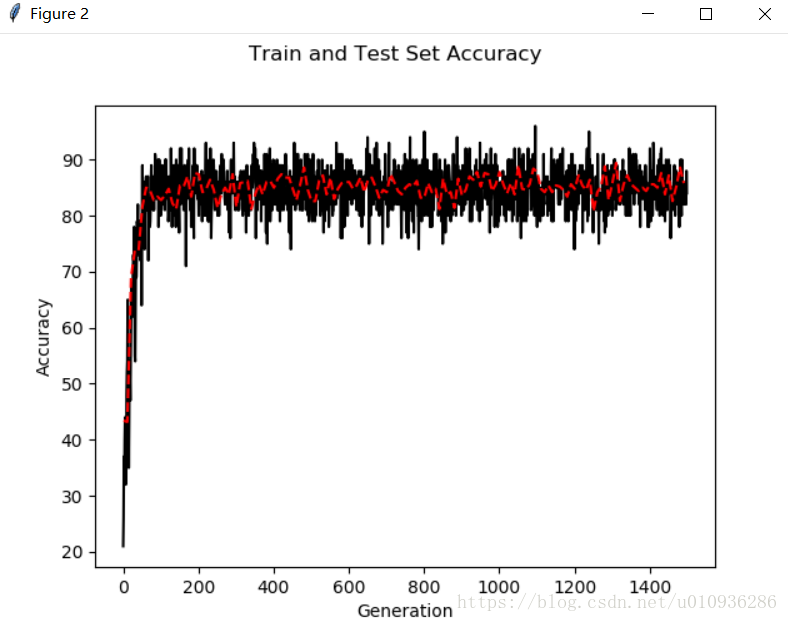
我们可以看出其损失函数下降很快,同时准确率也可以达到90%以上
下面给出随机抓取的图像相应的识别情况:

至此我们实现了简单的CNN来实现MNIST手写图数据集的识别,如果想进一步提高其准确率,可以通过改变CNN网络参数,如通道数、全连接层神经元个数,过滤器大小,学习率,训练次数,加入dropout层等等,也可以通过增加CNN网络深度来进一步提高其准确率
下面给出一组参数:
初始学习率:initial_learning_rate=0.05
迭代步长:decay_steps=50,每50步改变一次学习率
下面是仿真结果:
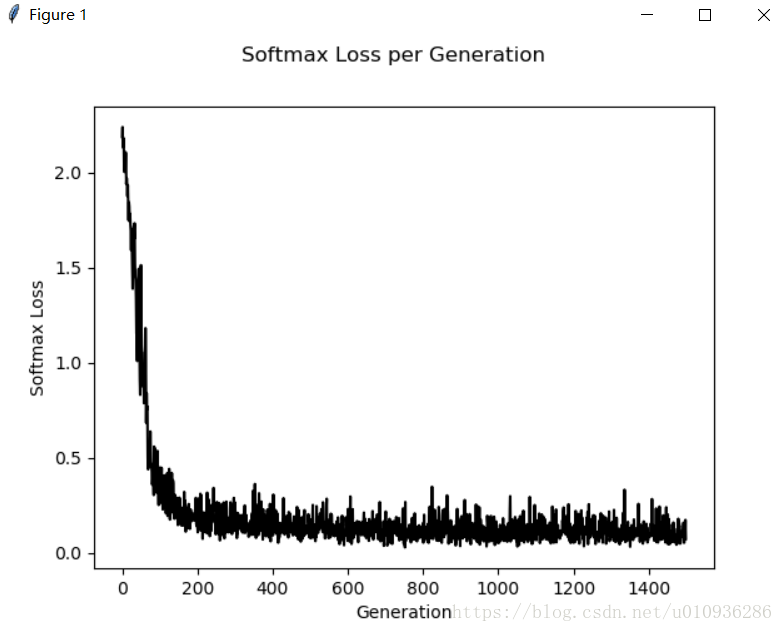
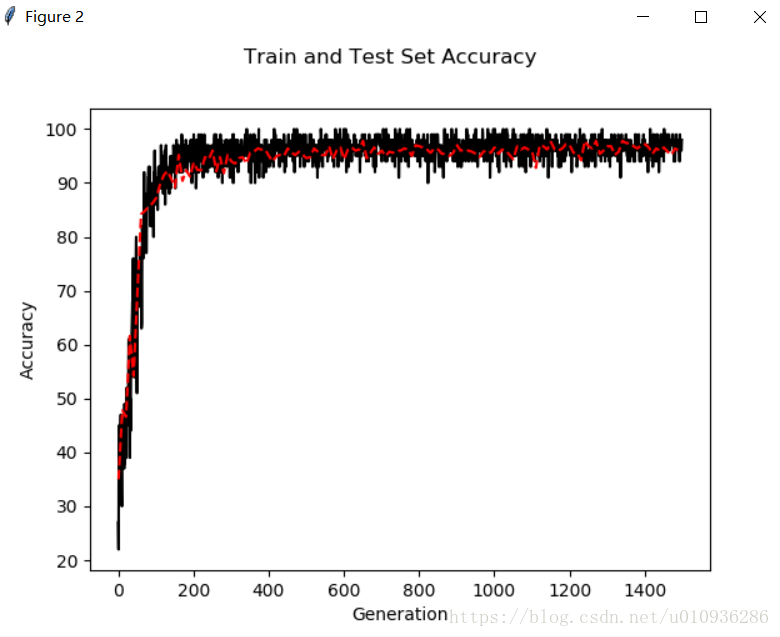

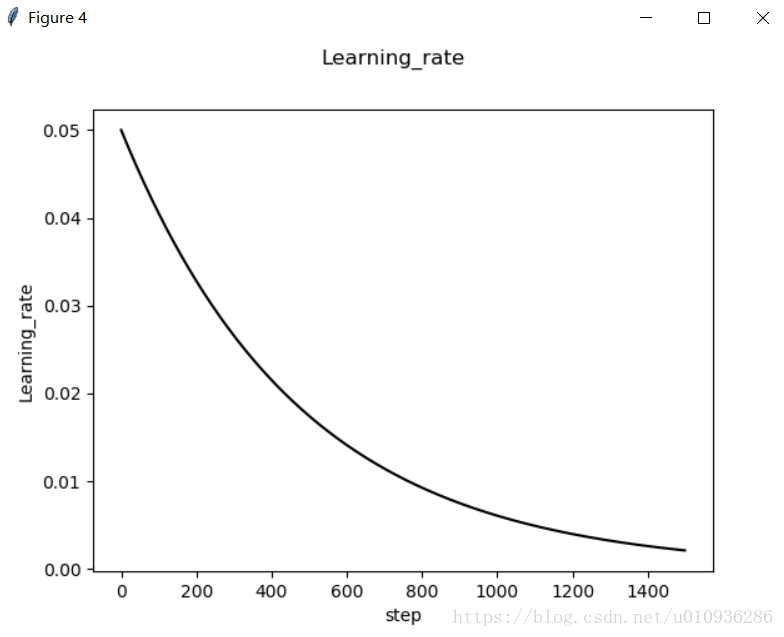
我们可以看出,通过调整超参数,其既保证了损失函数能够快速下降,又进一步提高了其模型准确率,我们在训练次数为1500次的基础上,准确率已经达到97%以上。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

