详解vue-cli脚手架中webpack配置方法
什么是webpack
webpack是一个module bundler(模块打包工具),所谓的模块就是在平时的前端开发中,用到一些静态资源,如JavaScript、CSS、图片等文件,webpack就将这些静态资源文件称之为模块
webpack支持AMD和CommonJS,以及其他的一些模块系统,并且兼容多种JS书写规范,可以处理模块间的以来关系,所以具有更强大的JS模块化的功能,它能对静态资源进行统一的管理以及打包发布,在官网中用这张图片介绍:
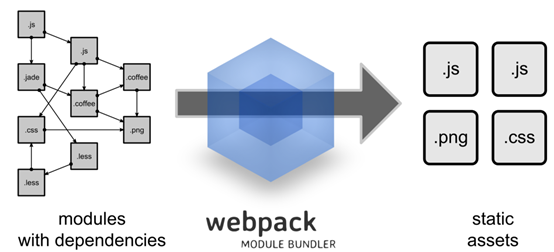
它在很多地方都能替代Grunt和Gulp,因为它能够编译打包CSS,做CSS预处理,对JS的方言进行编译,打包图片,代码压缩等等。所以在我接触了webpack之后,就不太想用gulp了
为什么使用webpack
总结如下:
- 对 CommonJS 、AMD 、ES6的语法做了兼容;
- 对js、css、图片等资源文件都支持打包;
- 串联式模块加载器以及插件机制,让其具有更好的灵活性和扩展性,例如提供对CoffeeScript、ES6的支持;
- 有独立的配置文件webpack.config.js;
- 可以将代码切割成不同的chunk,实现按需加载,降低了初始化时间;
- 支持 SourceUrls 和 SourceMaps,易于调试;
- 具有强大的Plugin接口,大多是内部插件,使用起来比较灵活;
- webpack 使用异步 IO 并具有多级缓存。这使得 webpack 很快且在增量编译上更加快;
webpack主要是用于vue和React较多,其实它就非常像Browserify,但是将应用打包为多个文件。如果单页面应用有多个页面,那么用户只从下载对应页面的代码. 当他么访问到另一个页面, 他们不需要重新下载通用的代码。
基于本人项目使用
vue webpack的配置文件的基本目录结构如下:
config ├── dev.env.js //dev环境变量配置 ├── index.js // dev和prod环境的一些基本配置 └── prod.env.js // prod环境变量配置 build ├── build.js // npm run build所执行的脚本 ├── check-versions.js // 检查npm和node的版本 ├── logo.png ├── utils.js // 一些工具方法,主要用于生成cssLoader和styleLoader配置 ├── vue-loader.conf.js // vueloader的配置信息 ├── webpack.base.conf.js // dev和prod的公共配置 ├── webpack.dev.conf.js // dev环境的配置 └── webpack.prod.conf.js // prod环境的配置
Config文件夹下文件详解
dev.env.js
config内的文件其实是服务于build的,大部分是定义一个变量export出去
use strict //[采用严格模式]
/**
* [webpack-merge提供了一个合并函数,它将数组和合并对象创建一个新对象
]
*/
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const prodEnv = require('./prod.env')
module.exports = merge(prodEnv, {
NODE_ENV: '"development"'
})
prod.env.js
当开发时调取dev.env.js的开发环境配置,发布时调用prod.env.js的生产环境配置
use strict
module.exports = {
NODE_ENV: '"production"'
}
index.js
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
/**
* [开发环境配置]
*/
dev: {
assetsSubDirectory: 'static', // [子目录,一般存放css,js,image等文件]
assetsPublicPath: '/', // [根目录]
/**
* [配置服务代理]
*/
proxyTable: {
'/hcm': {
target: 'https://127.0.0.1:8448',
changeOrigin: true,
secure: false
},
headers: {
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS",
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "X-Requested-With, content-type, Authorization"
}
},
host: '127.0.0.1', // [浏览器访问地址]
port: 8083, // [端口号设置,端口号占用出现问题可在此处修改]
autoOpenBrowser: true, // [是否在编译(输入命令行npm run dev)后打开http://127.0.0.1:8083/页面]
errorOverlay: true, // [浏览器错误提示]
notifyOnErrors: true, // [跨平台错误提示]
poll:false, // [使用文件系统(file system)获取文件改动的通知devServer.watchOptions]
useEslint: true, // [是否启用代码规范检查]
showEslintErrorsInOverlay: false, // [是否展示eslint的错误提示]
devtool: 'eval-source-map', // [增加调试,该属性为原始源代码]
cacheBusting: true, // [使缓存失效]
cssSourceMap: false // [代码压缩后进行调bug定位将非常困难,于是引入sourcemap记录压缩前后的位置信息记录,当产生错误时直接定位到未压缩前的位置,将大大的方便我们调试]
},
/**
* [生产环境配置]
*/
build: {
/**
* [index、login、license、forbidden、notfound、Internal.licenses编译后生成的位置和名字,根据需要改变后缀]
*/
index: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/index.html'),
login: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/login.html'),
license: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/license.html'),
forbidden: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/error/403.html'),
notfound: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/error/404.html'),
internal: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/error/500.html'),
licenses: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/docs/licenses.html'),
/**
* [编译后存放生成环境代码的位置]
*/
assetsRoot: path.resolve(__dirname, '../../hcm-modules/hcm-web/src/main/resources/META-INF/resources'),
assetsSubDirectory: 'static', //js、css、images存放文件夹名
assetsPublicPath: './', //发布的根目录,通常本地打包dist后打开文件会报错,此处修改为./。如果是上线的文件,可根据文件存放位置进行更改路径
productionSourceMap: true,
devtool: '#source-map',
productionGzip: false, //unit的gzip命令用来压缩文件,gzip模式下需要压缩的文件的扩展名有js和css
productionGzipExtensions: ['js', 'css'],
bundleAnalyzerReport: process.env.npm_config_report //打包分析
}
}
build文件夹下文件详解
build.js
该文件作用,即构建生产版本。package.json中的scripts的build就是node build/build.js,输入命令行npm run build对该文件进行编译生成生产环境的代码。
require('./check-versions')() //check-versions:调用检查版本的文件。加()代表直接调用该函数
process.env.NODE_ENV = 'production' //设置当前是生产环境
/**
*下面定义常量引入插件
*/
const ora = require('ora') //加载动画
const rm = require('rimraf') //删除文件
const path = require('path')
const chalk = require('chalk') //对文案输出的一个彩色设置
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config') //默认读取下面的index.js文件
const webpackConfig = require('./webpack.prod.conf')
const spinner = ora('building for production...') //调用start的方法实现加载动画,优化用户体验
spinner.start()
//先删除dist文件再生成新文件,因为有时候会使用hash来命名,删除整个文件可避免冗余
rm(path.join(config.build.assetsRoot, config.build.assetsSubDirectory), err => {
if (err) throw err
webpack(webpackConfig, (err, stats) => {
spinner.stop()
if (err) throw err
process.stdout.write(stats.toString({
colors: true,
modules: false,
children: false,
chunks: false,
chunkModules: false
}) + '\n\n')
if (stats.hasErrors()) {
console.log(chalk.red(' Build failed with errors.\n'))
process.exit(1)
}
console.log(chalk.cyan(' Build complete.\n'))
console.log(chalk.yellow(
' Tip: built files are meant to be served over an HTTP server.\n' +
' Opening index.html over file:// won\'t work.\n'
))
})
})
check-versions.js
该文件用于检测node和npm的版本,实现版本依赖
const chalk = require('chalk')
const semver = require('semver') //对版本进行检查
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
const shell = require('shelljs')
function exec (cmd) {
//返回通过child_process模块的新建子进程,执行 Unix 系统命令后转成没有空格的字符串
return require('child_process').execSync(cmd).toString().trim()
}
const versionRequirements = [
{
name: 'node',
currentVersion: semver.clean(process.version), //使用semver格式化版本
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.node //获取package.json中设置的node版本
}
]
if (shell.which('npm')) {
versionRequirements.push({
name: 'npm',
currentVersion: exec('npm --version'), // 自动调用npm --version命令,并且把参数返回给exec函数,从而获取纯净的版本号
versionRequirement: packageConfig.engines.npm
})
}
module.exports = function () {
const warnings = []
for (let i = 0; i < versionRequirements.length; i++) {
const mod = versionRequirements[i]
if (!semver.satisfies(mod.currentVersion, mod.versionRequirement)) {
//上面这个判断就是如果版本号不符合package.json文件中指定的版本号,就执行下面错误提示的代码
warnings.push(mod.name + ': ' +
chalk.red(mod.currentVersion) + ' should be ' +
chalk.green(mod.versionRequirement)
)
}
}
if (warnings.length) {
console.log('')
console.log(chalk.yellow('To use this template, you must update following to modules:'))
console.log()
for (let i = 0; i < warnings.length; i++) {
const warning = warnings[i]
console.log(' ' + warning)
}
console.log()
process.exit(1)
}
}
utils.js
utils是工具的意思,是一个用来处理css的文件。
const path = require('path')
const config = require('../config')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const packageConfig = require('../package.json')
exports.assetsPath = function (_path) {
const assetsSubDirectory = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsSubDirectory
: config.dev.assetsSubDirectory
return path.posix.join(assetsSubDirectory, _path)
}
exports.cssLoaders = function (options) {
options = options || {}
//使用了css-loader和postcssLoader,通过options.usePostCSS属性来判断是否使用postcssLoader中压缩等方法
const cssLoader = {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
const postcssLoader = {
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
}
}
// generate loader string to be used with extract text plugin
function generateLoaders (loader, loaderOptions) {
const loaders = options.usePostCSS ? [cssLoader, postcssLoader] : [cssLoader]
if (loader) {
loaders.push({
loader: loader + '-loader',
//Object.assign是es6语法的浅复制,后两者合并后复制完成赋值
options: Object.assign({}, loaderOptions, {
sourceMap: options.sourceMap
})
})
}
// Extract CSS when that option is specified
// (which is the case during production build)
if (options.extract) {
//ExtractTextPlugin可提取出文本,代表首先使用上面处理的loaders,当未能正确引入时使用vue-style-loader
return ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: loaders,
fallback: 'vue-style-loader',
publicPath: '../../'
})
} else {
//返回vue-style-loader连接loaders的最终值
return ['vue-style-loader'].concat(loaders)
}
}
// https://vue-loader.vuejs.org/en/configurations/extract-css.html
return {
css: generateLoaders(),//需要css-loader 和 vue-style-loader
postcss: generateLoaders(),//需要css-loader和postcssLoader 和 vue-style-loader
less: generateLoaders('less'), //需要less-loader 和 vue-style-loader
sass: generateLoaders('sass', { indentedSyntax: true }), //需要sass-loader 和 vue-style-loader
scss: generateLoaders('sass'), //需要sass-loader 和 vue-style-loader
stylus: generateLoaders('stylus'), //需要stylus-loader 和 vue-style-loader
styl: generateLoaders('stylus') //需要stylus-loader 和 vue-style-loader
}
}
// Generate loaders for standalone style files (outside of .vue)
exports.styleLoaders = function (options) {
const output = []
const loaders = exports.cssLoaders(options)
//将各种css,less,sass等综合在一起得出结果输出output
for (const extension in loaders) {
const loader = loaders[extension]
output.push({
test: new RegExp('\\.' + extension + '$'),
use: loader
})
}
return output
}
exports.createNotifierCallback = () => {
//发送跨平台通知系统
const notifier = require('node-notifier')
return (severity, errors) => {
if (severity !== 'error') return
//当报错时输出错误信息的标题,错误信息详情,副标题以及图标
const error = errors[0]
const filename = error.file && error.file.split('!').pop()
notifier.notify({
title: packageConfig.name,
message: severity + ': ' + error.name,
subtitle: filename || '',
icon: path.join(__dirname, 'logo.png')
})
}
}
vue-loader.conf.js
该文件的主要作用就是处理.vue文件,解析这个文件中的每个语言块(template、script、style),转换成js可用的js模块。
const utils = require('./utils')
const config = require('../config')
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const sourceMapEnabled = isProduction
? config.build.productionSourceMap
: config.dev.cssSourceMap
//处理项目中的css文件,生产环境和测试环境默认是打开sourceMap,而extract中的提取样式到单独文件只有在生产环境中才需要
module.exports = {
loaders: utils.cssLoaders({
sourceMap: sourceMapEnabled,
extract: isProduction
}),
cssSourceMap: sourceMapEnabled,
cacheBusting: config.dev.cacheBusting,
// 在模版编译过程中,编译器可以将某些属性,如 src 路径,转换为require调用,以便目标资源可以由 webpack 处理
transformToRequire: {
video: ['src', 'poster'],
source: 'src',
img: 'src',
image: 'xlink:href'
}
}
webpack.base.conf.js
webpack.base.conf.js是开发和生产共同使用提出来的基础配置文件,主要实现配制入口,配置输出环境,配置模块resolve和插件等
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
/**
* [引入index.js文件路径]
*/
const config = require('../config')
const vueLoaderConfig = require('./vue-loader.conf')
/**
* [获取文件路径]
* @param dir [文件名称]
*_dirname为当前模块文件所在目录的绝对路径*
*@return 文件绝对路径
*/
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', dir)
}
const createLintingRule = () => ({
test: /\.(js|vue)$/,
loader: 'eslint-loader',
enforce: 'pre',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test')],
options: {
formatter: require('eslint-friendly-formatter'),
emitWarning: !config.dev.showEslintErrorsInOverlay
}
})
module.exports = {
context: path.resolve(__dirname, '../'),
/**
* [入口文件配置]
*/
entry: {
/**
* [入口文件路径, babel-polyfill是对es6语法的支持]
*/
app: ['babel-polyfill', './src/main.js'],
login: ['babel-polyfill', './src/loginMain.js'],
license: ['babel-polyfill', './src/licenseMain.js']
},
/**
* [文件导出配置]
*/
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: '[name].js',
publicPath: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? config.build.assetsPublicPath
: config.dev.assetsPublicPath //公共存放路径
},
resolve: {
/**
* [extensions: 配置文件的扩展名,当在important文件时,不用需要添加扩展名]
*/
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
/**
* [alias 给路径定义别名]
*/
alias: {
'vue$': 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': resolve('src')
}
},
/**
*使用插件配置相应文件的处理方法
*/
module: {
rules: [
...(config.dev.useEslint ? [createLintingRule()] : []),
/**
* [使用vue-loader将vue文件转化成js的模块]
*/
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: vueLoaderConfig
},
/**
* [通过babel-loader将js进行编译成es5/es6 文件]
*/
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
include: [resolve('src'), resolve('test')]
},
/**
* [图片、音像、字体都使用url-loader进行处理,超过10000会编译成base64]
*/
{
test: /\.(png|jpe?g|gif|svg)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('img/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(mp4|webm|ogg|mp3|wav|flac|aac)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('media/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
{
test: /\.(woff2?|eot|ttf|otf)(\?.*)?$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: utils.assetsPath('fonts/[name].[hash:7].[ext]')
}
},
/**
* [canvas 解析]
*/
{
test: path.resolve(`${resolve('src')}/lib/jtopo.js`),
loader: ['exports-loader?window.JTopo', 'script-loader']
}
]
},
//以下选项是Node.js全局变量或模块,这里主要是防止webpack注入一些Node.js的东西到vue中
node: {
setImmediate: false,
dgram: 'empty',
fs: 'empty',
net: 'empty',
tls: 'empty',
child_process: 'empty'
}
}
webpack.dev.conf.js
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
//通过webpack-merge实现webpack.dev.conf.js对wepack.base.config.js的继承
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
//美化webpack的错误信息和日志的插件
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
// 查看空闲端口位置,默认情况下搜索8000这个端口
const portfinder = require('portfinder')
// processs为node的一个全局对象获取当前程序的环境变量,即host
const HOST = process.env.HOST
const PORT = process.env.PORT && Number(process.env.PORT)
function resolveApp(relativePath) {
return path.resolve(relativePath);
}
const devWebpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
//规则是工具utils中处理出来的styleLoaders,生成了css,less,postcss等规则
rules: utils.styleLoaders({ sourceMap: config.dev.cssSourceMap, usePostCSS: true })
},
// 增强调试
devtool: config.dev.devtool,
// 此处的配置都是在config的index.js中设定好了
devServer: {
//控制台显示的选项有none, error, warning 或者 info
clientLogLevel: 'warning',
//使用 HTML5 History API
historyApiFallback: true,
hot: true, //热加载
compress: true, //压缩
host: HOST || config.dev.host,
port: PORT || config.dev.port,
open: config.dev.autoOpenBrowser, //调试时自动打开浏览器
overlay: config.dev.errorOverlay
? { warnings: false, errors: true }
: false,
publicPath: config.dev.assetsPublicPath,
proxy: config.dev.proxyTable,//接口代理
quiet: true, //控制台是否禁止打印警告和错误,若用FriendlyErrorsPlugin 此处为 true watchOptions: {
poll: config.dev.poll, // 文件系统检测改动
}
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': require('../config/dev.env')
}),
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),//模块热替换插件,修改模块时不需要刷新页面
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(), // 显示文件的正确名字
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(), //当webpack编译错误的时候,来中端打包进程,防止错误代码打包到文件中
// https://github.com/ampedandwired/html-webpack-plugin
// 该插件可自动生成一个 html5 文件或使用模板文件将编译好的代码注入进去
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true,
chunks: ['app']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'login.html',
template: 'login.html',
inject: true,
chunks: ['login']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'license.html',
template: 'license.html',
inject: true,
chunks: ['license']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'licenses.html',
template: 'licenses.html',
inject: true,
chunks: []
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: '404.html',
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/404.html'),
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
inject: true,
chunks: []
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: '403.html',
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/403.html'),
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
inject: true,
chunks: []
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: '500.html',
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/500.html'),
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
inject: true,
chunks: []
})
]
})
module.exports = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
portfinder.basePort = process.env.PORT || config.dev.port
//查找端口号
portfinder.getPort((err, port) => {
if (err) {
reject(err)
} else {
//端口被占用时就重新设置evn和devServer的端口
process.env.PORT = port
// add port to devServer config
devWebpackConfig.devServer.port = port
//友好地输出信息
devWebpackConfig.plugins.push(new FriendlyErrorsPlugin({
compilationSuccessInfo: {
messages: [`Your application is running here: http://${devWebpackConfig.devServer.host}:${port}`],
},
onErrors: config.dev.notifyOnErrors
? utils.createNotifierCallback()
: undefined
}))
resolve(devWebpackConfig)
}
})
})
webpack.prod.conf.js
const path = require('path')
const utils = require('./utils')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const config = require('../config')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseWebpackConfig = require('./webpack.base.conf')
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const OptimizeCSSPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin')
const UglifyJsPlugin = require('uglifyjs-webpack-plugin')
const env = require('../config/prod.env')
function resolveApp(relativePath) {
return path.resolve(relativePath);
}
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {
rules: utils.styleLoaders({
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,//开启调试的模式。默认为true
extract: true,
usePostCSS: true
})
},
devtool: config.build.productionSourceMap ? config.build.devtool : false,
output: {
path: config.build.assetsRoot,
filename: utils.assetsPath('js/[name].[chunkhash].js'),
chunkFilename: utils.assetsPath('js/[id].[chunkhash].js')
},
plugins: [
// http://vuejs.github.io/vue-loader/en/workflow/production.html
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': env
}),
new UglifyJsPlugin({
uglifyOptions: {
compress: {
warnings: false //警告:true保留警告,false不保留
}
},
sourceMap: config.build.productionSourceMap,
parallel: true
}),
// extract css into its own file
//抽取文本。比如打包之后的index页面有style插入,就是这个插件抽取出来的,减少请求
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: utils.assetsPath('css/[name].[contenthash].css'),
allChunks: true,
}),
//优化css的插件
new OptimizeCSSPlugin({
cssProcessorOptions: config.build.productionSourceMap
? { safe: true, map: { inline: false } }
: { safe: true }
}),
//html打包
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.index,
template: 'index.html',
inject: true,
//压缩
minify: {
removeComments: true, //删除注释
collapseWhitespace: true, //删除空格
removeAttributeQuotes: true //删除属性的引号
},
chunks: ['vendor', 'manifest', 'app'],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.login,
template: 'login.html',
inject: true,
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: ['vendor', 'manifest', 'login'],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.license,
template: 'license.html',
inject: true,
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: ['vendor', 'manifest', 'license'],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.notfound,
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/404.html'),
inject: true,
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: [],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.forbidden,
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/403.html'),
inject: true,
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: [],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.internal,
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../errors/500.html'),
inject: true,
favicon: resolveApp('favicon.ico'),
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: [],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: config.build.licenses,
template: 'licenses.html',
inject: true,
minify: {
removeComments: true,
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true
},
chunks: [],
// necessary to consistently work with multiple chunks via CommonsChunkPlugin
chunksSortMode: 'dependency'
}),
// keep module.id stable when vender modules does not change
new webpack.HashedModuleIdsPlugin(),
// enable scope hoisting
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
//抽取公共的模块, 提升你的代码在浏览器中的执行速度。
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'vendor',
minChunks (module) {
// any required modules inside node_modules are extracted to vendor
return (
module.resource &&
/\.js$/.test(module.resource) &&
module.resource.indexOf(
path.join(__dirname, '../node_modules')
) === 0
)
}
}),
// extract webpack runtime and module manifest to its own file in order to
// prevent vendor hash from being updated whenever app bundle is updated
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'manifest',
minChunks: Infinity
}),
// 预编译所有模块到一个闭包中,
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: 'app',
async: 'vendor-async',
children: true,
minChunks: 3
}),
//复制,比如打包完之后需要把打包的文件复制到dist里面
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../static'),
to: config.build.assetsSubDirectory,
ignore: ['.*']
}
])
]
})
if (config.build.productionGzip) {
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin')
webpackConfig.plugins.push(
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
asset: '[path].gz[query]',
algorithm: 'gzip',
test: new RegExp(
'\\.(' +
config.build.productionGzipExtensions.join('|') +
')$'
),
threshold: 10240,
minRatio: 0.8
})
)
}
// 提供带 Content-Encoding 编码的压缩版的资源
if (config.build.bundleAnalyzerReport) {
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin
webpackConfig.plugins.push(new BundleAnalyzerPlugin())
}
module.exports = webpackConfig
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

