python微元法计算函数曲线长度的方法
计算曲线长度,根据线积分公式:
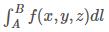 ,令积分函数 f(x,y,z) 为1,即计算曲线的长度,将其微元化:
,令积分函数 f(x,y,z) 为1,即计算曲线的长度,将其微元化:
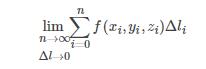
其中

根据此时便可在python编程实现,给出4个例子,代码中已有详细注释,不再赘述
'''
计算曲线长度,根据线积分公式:
\int_A^Bf(x,y,z)dl,令积分函数为1,即计算曲线的长度
'''
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## 求二维圆周长,半径为1,采用参数形式
def circle_2d(dt=0.001,plot=True):
dt = dt # 变化率
t = np.arange(0,2*np.pi, dt)
x = np.cos(t)
y = np.sin(t)
# print(len(t))
area_list = [] # 存储每一微小步长的曲线长度
for i in range(1,len(t)):
# 计算每一微小步长的曲线长度,dx = x_{i}-x{i-1},索引从1开始
dl_i = np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 )
# 将计算结果存储起来
area_list.append(dl_i)
area = sum(area_list)# 求和计算曲线在t:[0,2*pi]的长度
print("二维圆周长:{:.4f}".format(area))
if plot:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.title("circle")
plt.show()
## 二维空间曲线,采用参数形式
def curve_param_2d(dt=0.0001,plot=True):
dt = dt # 变化率
t = np.arange(0,2*np.pi, dt)
x = t*np.cos(t)
y = t*np.sin(t)
# print(len(t))
area_list = [] # 存储每一微小步长的曲线长度
# 下面的方式是循环实现
# for i in range(1,len(t)):
# # 计算每一微小步长的曲线长度,dx = x_{i}-x{i-1},索引从1开始
# dl_i = np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 )
# # 将计算结果存储起来
# area_list.append(dl_i)
# 更加pythonic的写法
area_list = [np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 ) for i in range(1,len(t))]
area = sum(area_list)# 求和计算曲线在t:[0,2*pi]的长度
print("二维参数曲线长度:{:.4f}".format(area))
if plot:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.title("2-D Parameter Curve")
plt.show()
## 二维空间曲线
def curve_2d(dt=0.0001,plot=True):
dt = dt # 变化率
t = np.arange(-6,10, dt)
x = t
y = x**3/8 - 4*x + np.sin(3*x)
# print(len(t))
area_list = [] # 存储每一微小步长的曲线长度
# for i in range(1,len(t)):
# # 计算每一微小步长的曲线长度,dx = x_{i}-x{i-1},索引从1开始
# dl_i = np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 )
# # 将计算结果存储起来
# area_list.append(dl_i)
area_list = [np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 ) for i in range(1,len(t))]
area = sum(area_list)# 求和计算曲线在t:[0,2*pi]的长度
print("二维曲线长度:{:.4f}".format(area))
if plot:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.title("2-D Curve")
plt.show()
## 三维空间曲线,采用参数形式
def curve_3d(dt=0.001,plot=True):
dt = dt # 变化率
t = np.arange(0,2*np.pi, dt)
x = t*np.cos(t)
y = t*np.sin(t)
z = 2*t
# print(len(t))
area_list = [] # 存储每一微小步长的曲线长度
for i in range(1,len(t)):
# 计算每一微小步长的曲线长度,dx = x_{i}-x{i-1},索引从1开始
dl_i = np.sqrt( (x[i]-x[i-1])**2 + (y[i]-y[i-1])**2 + (z[i]-z[i-1])**2 )
# 将计算结果存储起来
area_list.append(dl_i)
area = sum(area_list)# 求和计算曲线在t:[0,2*pi]的长度
print("三维空间曲线长度:{:.4f}".format(area))
if plot:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
ax.plot(x,y,z)
plt.title("3-D Curve")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
circle_2d(plot=True)
curve_param_2d(plot=True)
curve_2d(plot=True)
curve_3d(plot=True)
得到结果:
二维圆周长:6.2830 二维参数曲线长度:21.2558 二维曲线长度:128.2037 三维空间曲线长度:25.3421




以上这篇python微元法计算函数曲线长度的方法就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持我们。
赞 (0)

