Python 调用GPT-3 API实现过程详解
目录
- 用 Python 调用 GPT-3 API
- 安装 GPT-3
- 特征工程
- 模型选择
- 生成合成数据
- 公共数据集的询问提示
- 机器学习问题整理
- 询问研究项目
用 Python 调用 GPT-3 API
GPT-3 是去年由 Open AI 推出的语言机器学习模型。它因其能够写作、写歌、写诗,甚至写代码而获得了广泛的媒体关注!该工具免费使用,只需要注册一个电子邮件即可。
GPT-3 是一种叫 transformer 的机器学习模型。具体来说,它就是 Generative Pre-training Transformer,因此叫做“GPT”。Transformer 架构使用自我注意和强化学习来模拟会话文本。通常,它一次处理一个单词,并使用前面的单词预测序列中的下一个单词。
GPT-3 具有广泛的应用场景,涵盖科学、艺术和技术等所有领域。它可以用来回答有关科学和数学的基本问题。甚至可以准确回答研究生级别的数学和科学概念相关的问题。更令人惊讶的是,我询问了一些与我的物理化学博士研究有关的问题,它能够提供较好的解释。不过,它也有其局限性。当我询问 GPT-3 有关物理化学中更新奇的研究方法时,它无法提供明确的答案。因此,在作为教育和研究的搜索引擎使用时,应该谨慎使用 GPT-3。GPT-3 没有事实核查功能。随着事实核查功能的提高,我可以想象 GPT-3 在研究生阶段甚至在研究领域将非常有用。
此外,除了我个人的经验外,我还看到了其他很多很酷的工具应用。例如,一个开发人员使用 GPT-3 来编排完成复杂任务的云服务。其他用户使用 GPT-3 生成了工作的 python 和 SQL 脚本,以及其他语言的程序。在艺术领域,用户请 GPT-3 写一篇比较现代和当代艺术的文章。GPT-3 的潜在应用几乎在任何领域都是丰富的。
GPT-3 在回答有准确内容的基本问题方面表现得很好。例如,它可以对光合作用做出相当不错的解释。它不能很好地回答关于光合作用的前沿研究问题,例如,它不能描述光合作用的机理和涉及的量子概念。它可以给出体面的回应,但不太可能提供大多数研究问题的技术细节。同样,GPT-3 可以编写一些简单的工作代码,但是随着任务的复杂度增加,生成的代码就越容易出错。它也不能生成政 治观点、伦理价值观、投资建议、准确的新闻报道等通常是由人类生成的内容。
尽管 GPT-3 有其局限性,但其广泛适用性令人印象深刻。我认为提出一些有趣的数据科学和机器学习提示,以看看它们是否可以补充数据科学工作流程的部分是有趣的。
首先,我们将根据一些简单的提示生成一些与数据科学有关的文本。一旦我们对该工具有了一些了解,就可以询问一些可以帮助解决数据科学任务的问题。有几个有趣的数据科学和机器学习问题,我们可以向 GPT-3 询问。例如,是否可以使用 GPT-3 源自公开可用的数据集?GPT-3 的训练数据有多少等。另一个有趣的应用是问题框架。 GPT-3 可以帮助用户构建良好的机器学习研究问题吗?虽然它难以给出具体的技术答案,但也许它可以很好地构建出未解决的研究问题。
另一个很酷的应用是使用 GPT-3 来决定用于特定应用程序的 ML 模型。这很好,因为对于在线文献丰富的经过验证的技术,它应该能够很好地帮助用户选择模型,并解释为什么选定的模型最适合。最后,我们可以尝试使用GPT-3 编写一些数据科学任务的 Python 代码。例如,我们将看看是否可以使用它来编写生成特定用例的合成数据的代码。
注意:GPT-3 API 的结果是不确定的。因此,您获得的结果可能与此处显示的输出略有不同。此外,由于 GPT-3 没有事实核查机制,建议您对计划用于工作,学校或个人项目的任何事实结果进行双重核查。
在这项工作中,我将在 Deepnote 中编写代码,它是一个协作数据科学笔记本,使得运行可再现实验非常简单。
安装 GPT-3
首先,让我们到 Deepnote 并创建一个新项目(如果您还没有账户,可以免费注册)。
创建一个名为“GPT3”的项目以及该项目中的一个名为“GPT3_ds”的 notebook。
接下来,我们在第一个单元中使用 pip 安装 OpenAI:
%pip install openai %pip install catboost
将密钥保存在 openAI 对象的 api_key 属性:
import openai openai.api_key = "your-key"
接下来就可以提问了,比如问“什么是 Pandas 库”,GP3 会给反馈:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What is the pandas library?", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output Pandas is an open source software library written in Python for data manipulation and analysis. Pandas is widely used in data science, machine learning and many other fields. It provides high-level data structures and tools for handling and manipulating data, including data frames, series, plotting tools and more.
我们甚至可以询问更具体的问题,例如“Pandas 的一些常见用途是什么?”。它给出了合理的答案,列出了数据整理、数据可视化、数据聚合和时间序列分析:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="what are some common Pandas use cases?", max_tokens=240) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. Data Cleaning and Transformation 2. Data Analysis and Exploration 3. Time Series Analysis 4. Data Visualization 5. Statistical Modeling 6. Predictive Modeling 7. Machine Learning 8. Web Scraping
询问“最常见的深度学习库是什么?”:
#what are the most common deep learning libraries? completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="what are the most common deep learning libraries?", max_tokens=240) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output . TensorFlow 2. PyTorch 3. Keras 4. Caffe 5. CNTK 6. MXNet 7. Theano 8. Deeplearning4j 9. Gensim 10. LUNA
甚至可以询问“什么是深度神经网络?”:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What is a deep neural network?", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output A deep neural network (DNN) is a type of artificial neural network (ANN) with multiple layers of neurons between the input and output layers. DNNs are designed to learn complex non-linear relationships from data, and have been successfully applied in a wide range of areas such as image recognition, natural language processing, and financial forecasting.
使用 GPT-3 进行事实搜索应该谨慎进行,因为没有任何事实核查机制。在大多数情况下,如果您想获得关于数据科学和机器学习的众多在线博客和论坛中已知概念的表面理解,GPT-3 应该能够很好地工作。
特征工程
GPT-3 的另一个有趣的应用案例是用作指导数据科学工作的辅助工具。例如,GPT-3 能否给出一些改进模型性能的特征变换的想法?让我们询问 GPT-3:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="give some ideas on feature transformations that can improve model performance", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. Standardization/Normalization: A common feature transform used to ensure features are on the same scale, standardizing or normalizing variables can help limit the severity of outliers and improve the overall model performance. 2. Feature Binning: Binning is a process of transforming numerical variables into categorical ones. This can be useful when working with variables that have too many levels and can have a significant effect on the model performance. 3. Polynomial Expansion: When a nonlinear relationship is expected between features and the output variable, a polynomial expansion feature transformation can help improve model performance. 4. Feature Selection: Removing redundant or irrelevant features from the dataset can help improve the model performance as these features may lead to overfitting. 5. Ensemble: Combining different types of models (or different versions of the same model) can often improve performance due to their combined capabilities.
我们看到它给出了一些很好的特征变换建议以及每个变换的解释。
让我们看看是否可以更进一步。让它写一些 Python 代码:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that performs data standardization", max_tokens=1000)
print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
#output
# Import the necessary libraries
import numpy as np
# Define the data
data = np.array([[-3, 9, 0, 8],
[ 4, 6, 5, 12],
[20, 2, 3, 15]])
# Calculate mean and standard deviation
mean = np.mean(data, axis=0)
std = np.std(data, axis=0)
# Perform data standardization
standardized_data = (data - mean) / std
# Print the results
print(standardized_data)
复制并粘贴到一个新单元格中并运行它:
# Import the necessary libraries
import numpy as np
# Define the data
data = np.array([[-3, 9, 0, 8],
[ 4, 6, 5, 12],
[20, 2, 3, 15]])
# Calculate mean and standard deviation
mean = np.mean(data, axis=0)
std = np.std(data, axis=0)
# Perform data standardization
standardized_data = (data - mean) / std
# Print the results
print(standardized_data)
# output
[[-1.03881504 1.16247639 -1.29777137 -1.27872403]
[-0.31164451 0.11624764 1.13554995 0.11624764]
[ 1.35045955 -1.27872403 0.16222142 1.16247639]]
接下来,让我们对特征标准化变换做同样的操作:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that performs data normalization on fake data", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output # Normalizing data will rescale features in the range [0,1] data = [3, 7, 10, 13] # Sample data # Calculate the maximum and minimum of the data max_data = max(data) min_data = min(data) # Normalize the data normalized_data = [(x-min_data)/(max_data-min_data) for x in data] # Print first value to check print(normalized_data[0]) # Prints 0.2
执行返回的代码:
# Normalizing data will rescale features in the range [0,1] data = [3, 7, 10, 13] # Sample data # Calculate the maximum and minimum of the data max_data = max(data) min_data = min(data) # Normalize the data normalized_data = [(x-min_data)/(max_data-min_data) for x in data] # Print first value to check print(normalized_data)
模型选择
另一个酷的应用是模型选择。让我们看看 GPT-3 是否可以指导我们选择机器学习模型。询问“如何选择时间序列模型?”
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="How do i select a time series model?", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output The selection of a time series model depends on the type of data that is being analyzed. If there are long-term trends or cycles in the data, then an autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model or a exponential smoothing (ETS) model may be the best option. If the data are seasonal or there are outliers present, then a Holt-Winters model may be a better choice. If the data do not contain any long-term trends or seasonality, a Box-Jenkins model may be suitable. Regardless of the model selected, it is important to consider the type of data that is being modeled when selecting a time series model.
答案是合理的,列出了平稳性、季节性、趋势以及模型性能评估的检查。让我们询问更具体的问题,例如“何时使用 ARIMA vs Prophet?”:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="When to use ARIMA vs FB prophet?", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output ARIMA and FB Prophet are both used for time series forecasting. ARIMA is a linear model and is better for predicting long-term trends with stationary data. FB Prophet is a non-linear model and is better for predicting short-term trends with non-stationary data. So, you would use ARIMA when you are mainly concerned with predicting long-term trends, and you would use FB Prophet when you are mainly concerned with predicting short-term trends.
生成合成数据
能用 GPT-3 生成合成数据吗?让我们看一看!我们将生成一个众所周知的数据:医院再入院和交易数据。
- 医院再入院数据
询问 GPT-3:“编写 python 代码,生成合成医院再入院数据”。
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that generates synthetic healthcare readmission data stored in a dataframe", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output import pandas as pd import numpy as np # Create Dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Patient_ID', 'Age', 'Admission_Type', 'Readmitted']) # Generate Data np.random.seed(0) for i in range(10): admission_type = np.random.choice(['Urgent', 'Scheduled', 'Emergency']) patient_age = np.random.randint(18, 80) readmission = np.random.choice([0, 1]) df.loc[i] = [i+1, patient_age, admission_type, readmission] # Print Dataframe to Console print(df)
执行此代码:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np # Create Dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Patient_ID', 'Age', 'Admission_Type', 'Readmitted']) # Generate Data np.random.seed(0) for i in range(10): admission_type = np.random.choice(['Urgent', 'Scheduled', 'Emergency']) patient_age = np.random.randint(18, 80) readmission = np.random.choice([0, 1]) df.loc[i] = [i+1, patient_age, admission_type, readmission] # Print Dataframe to Console df
输出结果:
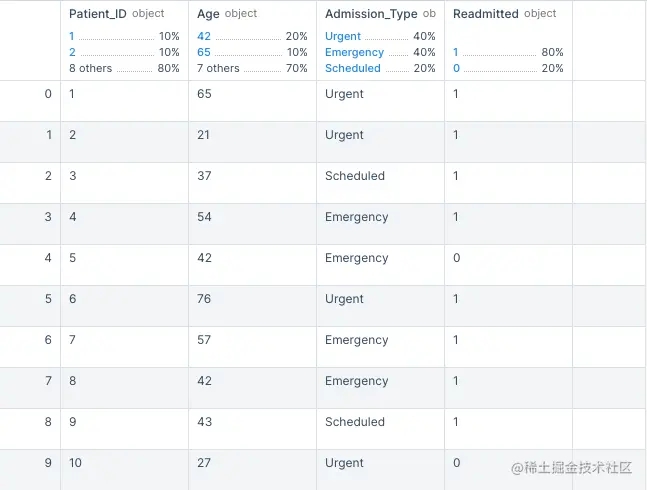
让我们看看是否可以用这个合成数据构建一个分类模型,预测重新入院的人,并评估性能。
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that generates synthetic healthcare readmission data stored in a dataframe. From this write code that builds a catboost model that predicts readmission outcomes. Also write code to calculate and print performance", max_tokens=3000)
print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
# output
metrics
## Generate Synthetic Healthcare Readmission Data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# set the seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(1)
# create dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(100, 10)), columns=['age','gender','length_of_stay','diagnosis','NIV','laboratory','past_hospitalizations','medications','bmi','readmission'])
# add labels to data frame
df['age'] = np.random.randint(20, 80, size=(100))
df['gender'] = np.random.randint(1, 2, size=(100))
df['length_of_stay'] = np.random.randint(2, 14, size=(100))
df['diagnosis'] = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=(100))
df['NIV'] = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100))
df['laboratory'] = np.random.randint(1, 6, size=(100))
df['past_hospitalizations'] = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(100))
df['medications'] = np.random.randint(1, 6, size=(100))
df['bmi'] = np.random.randint(18, 35, size=(100))
df['readmission'] = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100))
# print the dataframe
print(df)
## Build a CatBoost Model
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
# separate X and y
X = df.iloc[:, 0:9]
y = df.iloc[:, 9]
# initialize catboost classifier
cat_clf = CatBoostClassifier(iterations=50,
learning_rate=0.3,
depth=8,
eval_metric='Accuracy',
random_seed=42)
# fit the model
cat_clf.fit(X, y)
# predict values
y_pred = cat_clf.predict(X)
# print confusion matrix
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
print(conf_mat)
## Calculate and Print Performance Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
# calculate performance metrics
acc = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
precision = precision_score(y, y_pred)
recall = recall_score(y, y_pred)
# print performance metrics
print("Accuracy: {}".format(acc))
print("Precision: {}".format(precision))
print("Recall: {}".format(recall))
复制上面的代码,并执行:
## Generate Synthetic Healthcare Readmission Data
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# set the seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(1)
# create dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, size=(100, 10)), columns=['age','gender','length_of_stay','diagnosis','NIV','laboratory','past_hospitalizations','medications','bmi','readmission'])
# add labels to data frame
df['age'] = np.random.randint(20, 80, size=(100))
df['gender'] = np.random.randint(1, 2, size=(100))
df['length_of_stay'] = np.random.randint(2, 14, size=(100))
df['diagnosis'] = np.random.randint(1, 5, size=(100))
df['NIV'] = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100))
df['laboratory'] = np.random.randint(1, 6, size=(100))
df['past_hospitalizations'] = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(100))
df['medications'] = np.random.randint(1, 6, size=(100))
df['bmi'] = np.random.randint(18, 35, size=(100))
df['readmission'] = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(100))
# print the dataframe
print(df)
## Build a CatBoost Model
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
# separate X and y
X = df.iloc[:, 0:9]
y = df.iloc[:, 9]
# initialize catboost classifier
cat_clf = CatBoostClassifier(iterations=50,
learning_rate=0.3,
depth=8,
eval_metric='Accuracy',
random_seed=42)
# fit the model
cat_clf.fit(X, y)
# predict values
y_pred = cat_clf.predict(X)
# print confusion matrix
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y, y_pred)
print(conf_mat)
## Calculate and Print Performance Metrics
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
# calculate performance metrics
acc = accuracy_score(y, y_pred)
precision = precision_score(y, y_pred)
recall = recall_score(y, y_pred)
# print performance metrics
print("Accuracy: {}".format(acc))
print("Precision: {}".format(precision))
print("Recall: {}".format(recall))
# output
略
- 交易数据
询问 GPT-3:“编写 Python 代码,生成交易数据”。
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that generates synthetic transaction data stored in a dataframe", max_tokens=1000)
print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
# output
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#create randomly generated customer data
customer_id = np.arange(1,101)
customer_names = [f'John Doe {x}' for x in range(1,101)]
#create randomly generated transaction data
transaction_id = np.arange(1,101)
dates = [f'2020-07-{x}' for x in range(1,101)]
amounts = np.random.randint(low=1, high=1000, size=(100,))
#create dataframe with randomly generated data
transaction_data = pd.DataFrame({'Customer ID': customer_id,
'Customer Name': customer_names,
'Transaction ID': transaction_id,
'Date': dates,
'Amount': amounts})
print(transaction_data)
拷贝代码,并执行:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#create randomly generated customer data
customer_id = np.arange(1,101)
customer_names = [f'John Doe {x}' for x in range(1,101)]
#create randomly generated transaction data
transaction_id = np.arange(1,101)
dates = [f'2020-07-{x}' for x in range(1,101)]
amounts = np.random.randint(low=1, high=1000, size=(100,))
#create dataframe with randomly generated data
transaction_data = pd.DataFrame({'Customer ID': customer_id,
'Customer Name': customer_names,
'Transaction ID': transaction_id,
'Date': dates,
'Amount': amounts})
transaction_data
(部分输出结果)
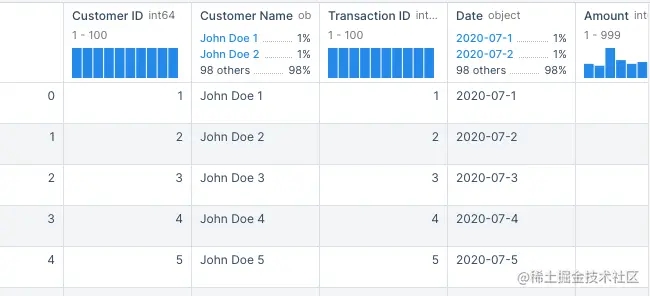
现在有物品 ID、客户和购买金额。让我们看看是否可以更具体一点。再增加年龄、性别和邮政编码。
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="Write example python code that generates synthetic transaction data stored in a dataframe. Include customer ID, transaction amount, item ID, item name, age, gender, and zipcode", max_tokens=2000)
print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
# output
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
rows = ['customer_ID', 'transaction_amnt', 'item_ID', 'item_name', 'age', 'gender', 'zipcode']
data = pd.DataFrame(columns=rows)
for i in range(1,100):
customer_ID = int( np.random.uniform(100,600-100))
transaction_amnt = np.random.uniform(1.25, 10.00)
item_ID = int( np.random.uniform(1,35))
item_name = np.random.choice(["phone", "tablet", "laptop", "smartwatch"])
age = int( np.random.uniform(17,75))
gender = np.random.choice(["male", "female"])
zipcode = np.random.choice(["98101", "98200", "98469", "98801"])
data.loc[i] = [customer_ID, transaction_amnt, item_ID, item_name, age, gender, zipcode]
print (data)
执行代码:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
rows = ['customer_ID', 'transaction_amnt', 'item_ID', 'item_name', 'age', 'gender', 'zipcode']
data = pd.DataFrame(columns=rows)
for i in range(1,100):
customer_ID = int( np.random.uniform(100,600-100))
transaction_amnt = np.random.uniform(1.25, 10.00)
item_ID = int( np.random.uniform(1,35))
item_name = np.random.choice(["phone", "tablet", "laptop", "smartwatch"])
age = int( np.random.uniform(17,75))
gender = np.random.choice(["male", "female"])
zipcode = np.random.choice(["98101", "98200", "98469", "98801"])
data.loc[i] = [customer_ID, transaction_amnt, item_ID, item_name, age, gender, zipcode]
data
(部分输出结果)
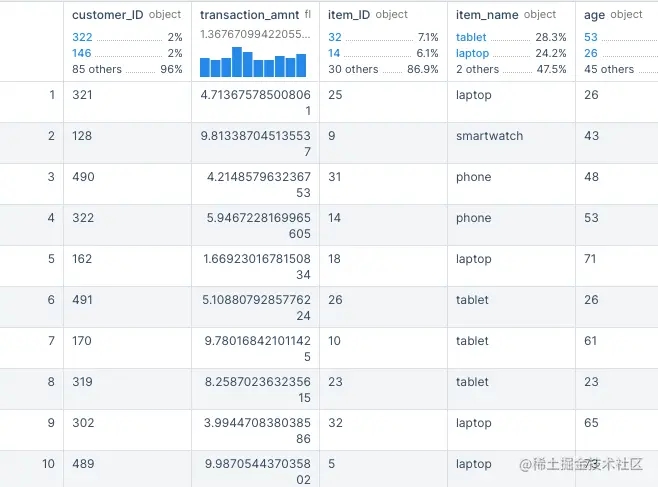
公共数据集的询问提示
另一种应用是询问 GPT-3 关于公共数据集。让我们询问 GPT-3 列出一些公共数据集:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt=" list some good public datasets", max_tokens=1000) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. US Census Data 2. Enron Email Dataset 3. Global Open Data Index 4. Air Quality Monitoring Data 5. New York City Taxi Trip Data 6. IMF Data 7. World Bank Open Data 8. Google Books Ngrams Dataset 9. Amazon Reviews Dataset 10. UCI Machine Learning Repository
让我们看看是否可以找到根据 Apache 2.0 许可的公共数据。还询问源链接:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt=" list some good public datasets under apache 2.0 license. provide links to their source", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. OpenStreetMap: https://www.openstreetmap.org/ 2. US Census Data: https://www.census.gov/data.html 3. Google Books Ngrams: https://aws.amazon.com/datasets/google-books-ngrams/ 4. Wikipedia: https://dumps.wikimedia.org/enwiki/ 5. US Government Spending Data: https://www.usaspending.gov/ 6. World Bank Open Data: https://data.worldbank.org/ 7. Common Crawl: http://commoncrawl.org/ 8. Open Images: https://storage.googleapis.com/openimages/web/index.html 9. OpenFlights: https://openflights.org/data.html 10. GDELT: http://data.gdeltproject.org/
虽然并不是所有这些链接都是正确的,但它在寻找源链接方面做得相当不错。Google Ngrams、Common Crawl和 NASA 数据都相当出色。如果不提供数据的确切位置,在大多数情况下,它提供了一个可以找到数据的网页链接。
再请求对数据进行描述。请注意,虽然结果可能重叠,但它们在每次运行时略有不同。据我所知,结果并不总是可以相同的:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt=" list some good public datasets under apache 2.0 license. provide links to their source and descriptions", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. OpenStreetMap: OpenStreetMap is a free, editable map of the world, created and maintained by volunteers and available for use under an open license. It contains millions of data points, including roads, buildings, and points of interest. Source: https://www.openstreetmap.org/ 2. Google Books Ngrams: Google Books Ngrams is a dataset of over 5 million books from Google Books, spanning from 1500 to 2008. It contains word counts for each year, allowing researchers to track the usage of words over time. Source: https://aws.amazon.com/datasets/google-books-ngrams/ 3. Wikipedia: Wikipedia is a free, open-source encyclopedia with millions of articles in hundreds of languages. It is available for use under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license. Source: https://www.wikipedia.org/ 4. Common Crawl: Common Crawl is a large-scale web crawl that collects data from over 5 billion webpages. It is available for use under the Apache 2.0 license. Source: https://commoncrawl.org/ 5. Open Images Dataset: The Open Images Dataset is a collection of 9 million images annotated with labels spanning over 6000 categories. It is available for use under the Apache 2.0 license. Source: https://storage.googleapis.com/openimages/web/index.html
机器学习问题整理
最后一个示例,将看看 GPT-3 是否可以帮助我们整理机器学习问题。
- 询问用例
虽然 GPT-3 中的数据仅截至2021年,但它仍然可以帮助我们构建与今天仍然相关的 ML 用例。让我们询问“社交媒体中有哪些新兴的机器学习用例?”:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What are some emerging machine learning use-cases in social media?", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. Automated Content Curation: Automatically curating content from social media platforms to create personalized content feeds for users. 2. Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing user sentiment from social media posts to gain insights into customer opinions and preferences. 3. Social Media Monitoring: Using machine learning algorithms to monitor social media conversations and detect potential issues or trends. 4. Social Media Advertising: Leveraging machine learning to optimize social media advertising campaigns and target the right audience. 5. Social Media Recommendations: Using machine learning to recommend content to users based on their interests and preferences.
我们也可以看到在医疗领域的回复:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What are some emerging machine learning use-cases in healthcare?", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. Automated Diagnosis: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze patient data and medical images to detect and diagnose diseases. 2. Personalized Medicine: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze patient data and medical images to create personalized treatment plans for each patient. 3. Drug Discovery: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze large datasets of chemical compounds to identify potential new drugs. 4. Clinical Decision Support: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze patient data and medical images to provide clinicians with real-time decision support. 5. Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze patient data and medical images to predict future health outcomes.
询问研究项目
现在让我们看看它是否可以提出一些研究问题。让我们询问:“使用深度学习进行图像检测有哪些好的研究项目?”
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What are some good research questions on using deep learning for image detection?", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. What are the most effective deep learning architectures for image detection? 2. How can deep learning be used to improve the accuracy of image detection? 3. What are the most effective methods for training deep learning models for image detection? 4. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of complexity? 5. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of illumination? 6. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of noise? 7. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of resolution? 8. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of occlusion? 9. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of background clutter? 10. How can deep learning be used to detect objects in images with varying levels of rotation?
再问一下 NLP 方向:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="text-davinci-003", prompt="What are some good research questions related to NLP transformer models?", max_tokens=1000, temperature=0) print(completion.choices[0]['text']) # output 1. How can transformer models be used to improve the accuracy of natural language processing tasks? 2. What are the most effective methods for training transformer models for natural language processing tasks? 3. How can transformer models be used to improve the efficiency of natural language processing tasks? 4. What are the most effective methods for optimizing transformer models for natural language processing tasks? 5. How can transformer models be used to improve the interpretability of natural language processing tasks? 6. What are the most effective methods for deploying transformer models for natural language processing tasks? 7. How can transformer models be used to improve the scalability of natural language processing tasks? 8. What are the most effective methods for combining transformer models with other natural language processing techniques? 9. How can transformer models be used to improve the robustness of natural language processing tasks? 10. What are the most effective methods for evaluating transformer models for natural language processing tasks?
本文所有代码都发布在 GitHub 上。
以上就是Python 调用GPT-3 API实现过程详解的详细内容,更多关于Python调用GPT-3 API的资料请关注我们其它相关文章!

