完整B树算法Java实现代码
定义
在计算机科学中,B树(英语:B-tree)是一种自平衡的树,能够保持数据有序。这种数据结构能够让查找数据、顺序访问、插入数据及删除的动作,都在对数时间内完成。
为什么要引入B树?
首先,包括前面我们介绍的红黑树是将输入存入内存的一种内部查找树。
而B树是前面平衡树算法的扩展,它支持保存在磁盘或者网络上的符号表进行外部查找,这些文件可能比我们以前考虑的输入要大的多(难以存入内存)。
既然内容保存在磁盘中,那么自然会因为树的深度过大而造成磁盘I/O读写过于频繁(磁盘读写速率是有限制的),进而导致查询效率低下。
那么降低树的深度自然很重要了。因此,我们引入了B树,多路查找树。
特点
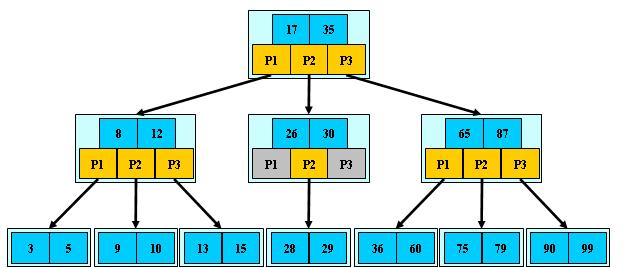
树中每个结点最多含有m个孩子(m>=2);
除根结点和叶子结点外,其它每个结点至少有[ceil(m / 2)]个孩子(其中ceil(x)是一个取上限的函数);
若根结点不是叶子结点,则至少有2个孩子(特殊情况:没有孩子的根结点,即根结点为叶子结点,整棵树只有一个根节点);
所有叶子结点都出现在同一层(最底层),叶子结点为外部结点,保存内容,即key和value。
其他结点为内部结点,保存索引,即key和next。
内部结点的关键字key:K[1], K[2], …, K[M-1];且K[i] < K[i+1];
内容结点的指针next:P[1], P[2], …, P[M];其中P[1]指向关键字小于K[1]的子树,P[M]指向关键字大于K[M-1]的子树,其它P[i]指向关键字属于(K[i-1], K[i])的子树;
例如:(M=3)
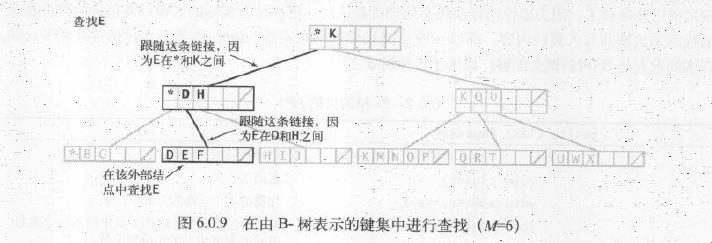
查找和插入
为了方便这里用了一个特殊的哨兵键,它小于其他所有键,用*表示。
一开始B树只含有一个根结点,而根结点在初始化时仅含有该哨兵键。
内部结点中的每个键都与一个结点相关联,以此结点为根的子树种,所有的键都大于等于与此结点关联的键,但小于其他所有键。
这些约定在很大程度上能够简化代码。
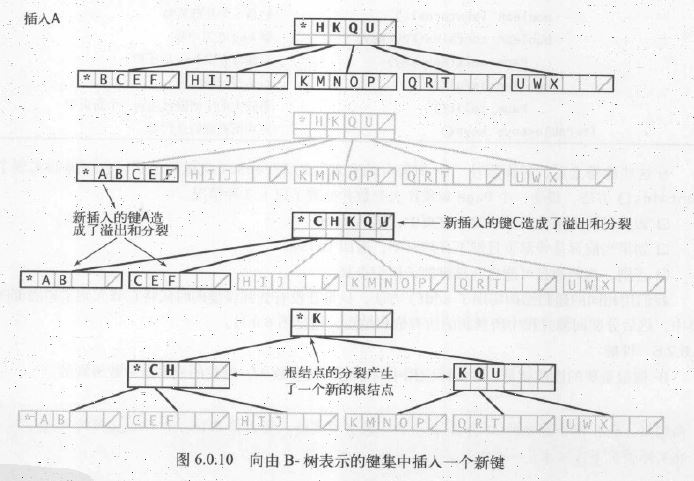
代码
点击下载。
该代码实现引入了哨兵键,代码输出则剔除了它。
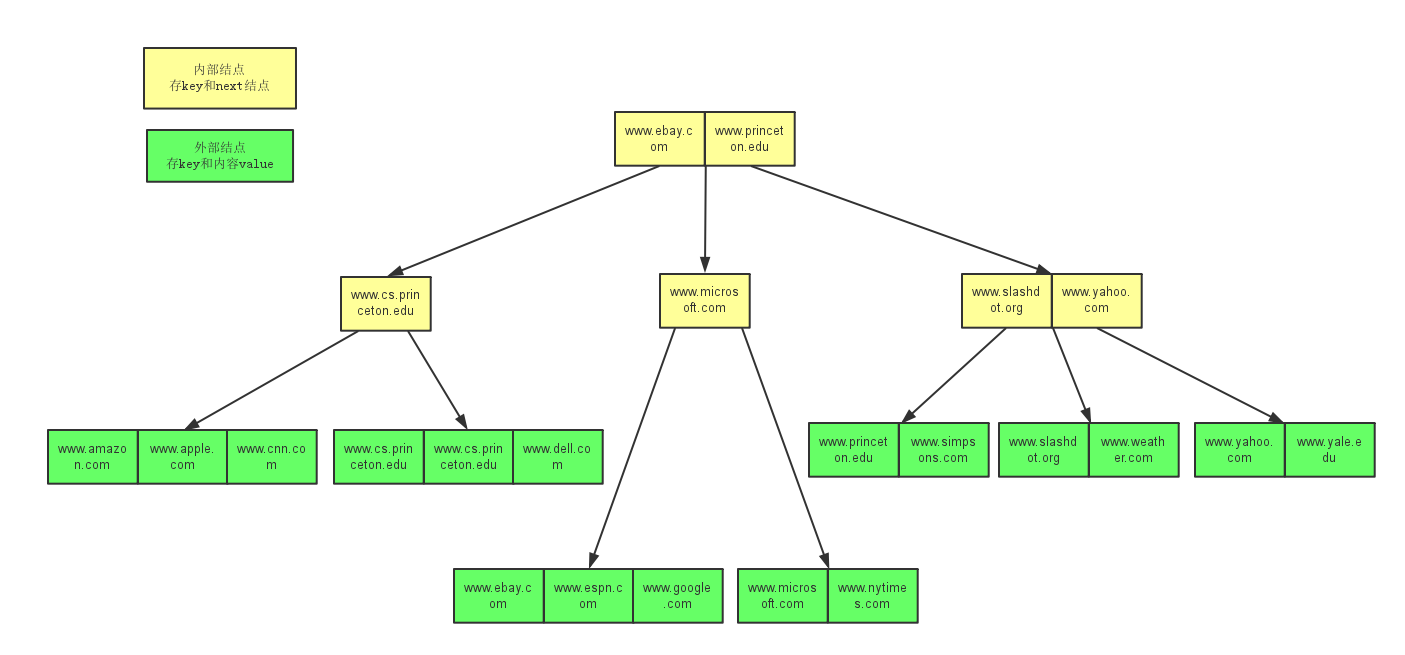
代码里含有哨兵键的B树(将图片保存到本地查看,字会清晰些):

代码输出的B树(将图片保存到本地查看,字会清晰些):
public class BTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value>
{
// max children per B-tree node = M-1
// (must be even and greater than 2)
private static final int M = 4;
private Node root; // root of the B-tree
private int height; // height of the B-tree
private int n; // number of key-value pairs in the B-tree
// helper B-tree node data type
private static final class Node
{
private int m; // number of children
private Entry[] children = new Entry[M]; // the array of children
// create a node with k children
private Node(int k)
{
m = k;
}
}
// internal nodes: only use key and next
// external nodes: only use key and value
private static class Entry
{
private Comparable key;
private Object val;
private Node next; // helper field to iterate over array entries
public Entry(Comparable key, Object val, Node next)
{
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* Initializes an empty B-tree.
*/
public BTree()
{
root = new Node(0);
}
/**
* Returns true if this symbol table is empty.
* @return {@code true} if this symbol table is empty; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.
* @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table
*/
public int size()
{
return n;
}
/**
* Returns the height of this B-tree (for debugging).
*
* @return the height of this B-tree
*/
public int height()
{
return height;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the given key.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table
* and {@code null} if the key is not in the symbol table
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Value get(Key key)
{
if (key == null)
{
throw new NullPointerException("key must not be null");
}
return search(root, key, height);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private Value search(Node x, Key key, int ht)
{
Entry[] children = x.children;
// external node到最底层叶子结点,遍历
if (ht == 0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < x.m; j++)
{
if (eq(key, children[j].key))
{
return (Value) children[j].val;
}
}
}
// internal node递归查找next地址
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < x.m; j++)
{
if (j+1 == x.m || less(key, children[j+1].key))
{
return search(children[j].next, key, ht-1);
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Inserts the key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old value
* with the new value if the key is already in the symbol table.
* If the value is {@code null}, this effectively deletes the key from the symbol table.
*
* @param key the key
* @param val the value
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void put(Key key, Value val)
{
if (key == null)
{
throw new NullPointerException("key must not be null");
}
Node u = insert(root, key, val, height); //分裂后生成的右结点
n++;
if (u == null)
{
return;
}
// need to split root重组root
Node t = new Node(2);
t.children[0] = new Entry(root.children[0].key, null, root);
t.children[1] = new Entry(u.children[0].key, null, u);
root = t;
height++;
}
private Node insert(Node h, Key key, Value val, int ht)
{
int j;
Entry t = new Entry(key, val, null);
// external node外部结点,也是叶子结点,在树的最底层,存的是内容value
if (ht == 0)
{
for (j = 0; j < h.m; j++)
{
if (less(key, h.children[j].key))
{
break;
}
}
}
// internal node内部结点,存的是next地址
else
{
for (j = 0; j < h.m; j++)
{
if ((j+1 == h.m) || less(key, h.children[j+1].key))
{
Node u = insert(h.children[j++].next, key, val, ht-1);
if (u == null)
{
return null;
}
t.key = u.children[0].key;
t.next = u;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = h.m; i > j; i--)
{
h.children[i] = h.children[i-1];
}
h.children[j] = t;
h.m++;
if (h.m < M)
{
return null;
}
else
{ //分裂结点
return split(h);
}
}
// split node in half
private Node split(Node h)
{
Node t = new Node(M/2);
h.m = M/2;
for (int j = 0; j < M/2; j++)
{
t.children[j] = h.children[M/2+j];
}
return t;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this B-tree (for debugging).
*
* @return a string representation of this B-tree.
*/
public String toString()
{
return toString(root, height, "") + "\n";
}
private String toString(Node h, int ht, String indent)
{
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
Entry[] children = h.children;
if (ht == 0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < h.m; j++)
{
s.append(indent + children[j].key + " " + children[j].val + "\n");
}
}
else
{
for (int j = 0; j < h.m; j++)
{
if (j > 0)
{
s.append(indent + "(" + children[j].key + ")\n");
}
s.append(toString(children[j].next, ht-1, indent + " "));
}
}
return s.toString();
}
// comparison functions - make Comparable instead of Key to avoid casts
private boolean less(Comparable k1, Comparable k2)
{
return k1.compareTo(k2) < 0;
}
private boolean eq(Comparable k1, Comparable k2)
{
return k1.compareTo(k2) == 0;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code BTree} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BTree<String, String> st = new BTree<String, String>();
st.put("www.cs.princeton.edu", "128.112.136.12");
st.put("www.cs.princeton.edu", "128.112.136.11");
st.put("www.princeton.edu", "128.112.128.15");
st.put("www.yale.edu", "130.132.143.21");
st.put("www.simpsons.com", "209.052.165.60");
st.put("www.apple.com", "17.112.152.32");
st.put("www.amazon.com", "207.171.182.16");
st.put("www.ebay.com", "66.135.192.87");
st.put("www.cnn.com", "64.236.16.20");
st.put("www.google.com", "216.239.41.99");
st.put("www.nytimes.com", "199.239.136.200");
st.put("www.microsoft.com", "207.126.99.140");
st.put("www.dell.com", "143.166.224.230");
st.put("www.slashdot.org", "66.35.250.151");
st.put("www.espn.com", "199.181.135.201");
st.put("www.weather.com", "63.111.66.11");
st.put("www.yahoo.com", "216.109.118.65");
System.out.println("cs.princeton.edu: " + st.get("www.cs.princeton.edu"));
System.out.println("hardvardsucks.com: " + st.get("www.harvardsucks.com"));
System.out.println("simpsons.com: " + st.get("www.simpsons.com"));
System.out.println("apple.com: " + st.get("www.apple.com"));
System.out.println("ebay.com: " + st.get("www.ebay.com"));
System.out.println("dell.com: " + st.get("www.dell.com"));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("size: " + st.size());
System.out.println("height: " + st.height());
System.out.println(st);
System.out.println();
}
}
输出:
cs.princeton.edu: 128.112.136.12
hardvardsucks.com: null
simpsons.com: 209.052.165.60
apple.com: 17.112.152.32
ebay.com: 66.135.192.87
dell.com: 143.166.224.230
size: 17
height: 2
www.amazon.com 207.171.182.16
www.apple.com 17.112.152.32
www.cnn.com 64.236.16.20
(www.cs.princeton.edu)
www.cs.princeton.edu 128.112.136.12
www.cs.princeton.edu 128.112.136.11
www.dell.com 143.166.224.230
(www.ebay.com)
www.ebay.com 66.135.192.87
www.espn.com 199.181.135.201
www.google.com 216.239.41.99
(www.microsoft.com)
www.microsoft.com 207.126.99.140
www.nytimes.com 199.239.136.200
(www.princeton.edu)
www.princeton.edu 128.112.128.15
www.simpsons.com 209.052.165.60
(www.slashdot.org)
www.slashdot.org 66.35.250.151
www.weather.com 63.111.66.11
(www.yahoo.com)
www.yahoo.com 216.109.118.65
www.yale.edu 130.132.143.21
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持我们。

